Natural 5-Minute Approach to Lowering Blood Pressure

Reviewed and approved by the pedagogue in physical education and nutritionist Elisa Morales Lupayante
Lowering high blood pressure is important as this is a serious health problem that can significantly impact your quality of life. Thus, you must seek immediate medical treatment.
Known as hypertension and also as “the silent killer,” cardiovascular disorder is currently affecting more and more people around the world.
Many people have high blood pressure bu, a large proportion of them remain undiagnosed. It makes harder to treat and increases the risk of a heart attack, stroke, and other serious diseases. This is why it’s so important to learn about high blood pressure and find out what you can do to reduce it.
What’s blood pressure?

Blood pressure is the force the heart exerts when pumping blood through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries to reach your organs. There are two completely different figures to measure it. The first one corresponds to the diastolic or high pressure. In turn, the second one is the systolic or low pressure. Both measurements are in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
In an adult, normal systolic blood pressure in an adult is around 120 mm Hg during physical activity and 80 mm Hg while resting. However, blood pressure levels may be higher during physical activity or in certain stressful situations.
You can say you have hypertension when the first measurement exceeds 140 mm Hg and the second is over 90 mm Hg. This can occur when the arteries known as “arterioles” become narrow, as their function is to regulate blood flow throughout the body.
When the arteries contract, the heart must work harder to supply blood to the rest of the body. It results in increased blood pressure. The worrisome aspect is it’s sort of asymptomatic, which increases your chance of developing a more serious problem.
Only occasionally does it cause palpitations in the head or chest, dizziness, fatigue, and other mild symptoms that might alert you to the problem.
See also 8 Tips to Correctly Take Your Blood Pressure at Home
What are the causes of high blood pressure?
So far, the causes of high blood pressure remain unknown, but some factors can influence its appearance. These include:
- Being a smoker
- Being over 60 years old
- Chronic stress
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle
- Having diabetes and being overweight
- Being a heavy alcohol drinker
- Having a family history of hypertension
- Having a poor diet, high in saturated fats, sodium, sugar, ultra-processed products, and such
What can you do to lower your blood pressure?
To prevent and control high blood pressure, you need to have regular medical checkups to test your levels. If they’re indeed high, you may need to completely change your lifestyle to stabilize them.
It’s important to improve your eating habits and exercise regularly, as these significantly contribute to your overall health and also regulate blood pressure.

In general, the guidelines to improve diet are:
- Limit your salt intake
- Increase your consumption of fruits and vegetables
- Add foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids to your balanced diet
- Avoid processed and fatty foods
Other recommendations are to:
- Lose weight
- Practice relaxation techniques
- Get at least 30 minutes of exercise every day
- Skip the alcohol and tobacco
In addition to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following your doctor’s guidelines, you can also use an ancient Chinese method for lowering your blood pressure in just five minutes.
See also: Five Positive Changes You’ll Notice after You Quit Smoking
What’s this traditional Chinese method to lower high blood pressure?
Traditional Chinese medicinal techniques are based on the energetic connections between various pressure points on your body and your organs.
This natural practice involves putting pressure on three specific points to lower your blood pressure within minutes.
The physiological explanation for the efficacy of this method is it stimulates specific receptors in the carotid artery. These receptors will detect the increase in blood pressure, thereby activating the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The PNS will trigger various processes to lower blood pressure.
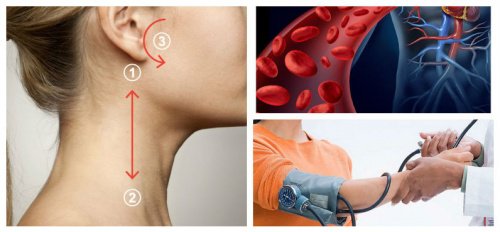
The line from point one to point two
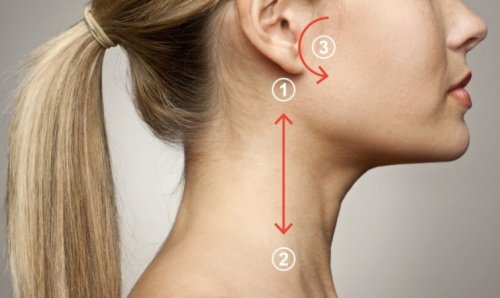
- There’s a line from points one to two which goes from the back of your earlobe to the collarbone
- Then, apply gentle pressure as you run your fingertips along this line
- Then, repeat the same movement about 10 times on each side of your neck or for about three minutes
Point 3
- After you apply pressure on the line, press your fingertips against the point that’s located half an inch from your earlobe in the direction of your nose
- Then, perform a gentle massage using careful pressure for one minute on each side.
This method isn’t a treatment, just a complement to treatment
While, according to popular belief, this technique can be very effective when your condition is due to stress, anxiety or other emotional factors. Finally, it’s important to remember that under no circumstances should it ever be used as a substitute for the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
In fact, it’s best to use these techniques as a complement to a healthy lifestyle, as long as your doctors okays it.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Acosta, C., Sposito, P., Torres Esteche, V., Sacchi, F., Pomies, L., Pereda, M., Viñas, S., & Soto, E. (2021). Variablilidad de la presión arterial, hipertensión arterial nocturna y su asociación con tabaquismo. Revista Uruguaya de Medicina Interna , 6(1), 54-65. http://www.scielo.edu.uy/scielo.php?pid=S2393-67972021000100054&script=sci_arttext
- Álvarez-Ochoa, R., Miguel Torres-Criollo, L., Garcés Ortega, J. P., Izquierdo Coronel, D. C., Magaly, D., Cayamcela, B., … & Saquicela Salinas, A. S. (2022). Factores de riesgo de hipertensión arterial en adultos. Una revisión crítica. Revista Latinoamericana de Hipertensión, 17(2). https://www.revhipertension.com/rlh_2_2022/7_factores_riesgo_hipertension_arterial.pdf
- American Heart Association. (25 de mayo de 2023). The Facts About High Blood Pressure.
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/the-facts-about-high-blood-pressure - De Souza Bastos, T. V. (2022). Utilização do Hibisco (Hibiscus sabdariffa) no controle da pressão arterial: uma revisão da literatura [Tesis de licenciatura, Universidade Federal de Campina Grande]. http://dspace.sti.ufcg.edu.br:8080/xmlui/handle/riufcg/23956
- He, X., Luan, F., Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Zhao, Z., Fang, J., Wang, M., Zuo, M., & Li, Y. (2020). Passiflora edulis: An Insight Into Current Researches on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Frontiers in pharmacology, 11, 617. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.00617/full
- Derya Ister, E., & Altinbas, Y. (2022). Effect of Acupressure on the Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, and Pain Severity of Patients who Underwent Coronary Angiography: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Alternative therapies in health and medicine, 964. https://europepmc.org/article/med/36112790
- Lattanzio, M., & Weir, M. R. (2020). An evidence-based appraisal of complementary and alternative medicine strategies for the management of hypertension. Journal of Hypertension, 38(8), 1412-1419. https://journals.lww.com/jhypertension/Fulltext/2020/08000/An_evidence_based_appraisal_of_complementary_and.4.aspx
- Mehta, P., Dhapte, V., Kadam, S., & Dhapte, V. (2016). Contemporary acupressure therapy: Adroit cure for painless recovery of therapeutic ailments. Journal of traditional and complementary medicine, 7(2), 251–263. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5388088/
- National Health Service. (20 de abril de 2023). Treatment. High blood pressure (hypertension). https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/treatment/
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (24 de marzo de 2022). High blood pressure. Treatment. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/high-blood-pressure/treatment
- Pescatello, L. S., Buchner, D. M., Jakicic, J. M., Powell, K. E., Kraus, W. E., Bloodgood, B., … & Piercy, K. L. (2019). Physical Activity to Prevent and Treat Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 51(6), 1314-1323. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31095088/
- Restawan, I. G., Sjattar, E. L., & Irwan, A. M. (2023). Effectiveness of acupressure therapy in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension: A systematic review. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 21, 101292. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213398423000799
- Romero, M., Toral, M., Gómez-Guzmán, M., Jiménez, R., Galindo, P., Sánchez, M., Olivares, M., Gálvez, J., & Duarte, J. (2016). Antihypertensive effects of oleuropein-enriched olive leaf extract in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food & Function, 7(1), 584–593. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2016/fo/c5fo01101a
- World Health Organization. (13 de marzo de 2023). Hypertension.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension - Xiong, X. J., Wang, P. Q., Li, S. J., Li, X. K., Zhang, Y. Q., & Wang, J. (2015). Garlic for hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytomedicine, 22(3), 352-361. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711315000264
- Zhang, W. B., Wang, G. J., & Fuxe, K. (2015). Classic and Modern Meridian Studies: A Review of Low Hydraulic Resistance Channels along Meridians and Their Relevance for Therapeutic Effects in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine, 2015, 410979. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2015/410979/
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








