Warts on the Head: Causes, Risks and How to Remove Them
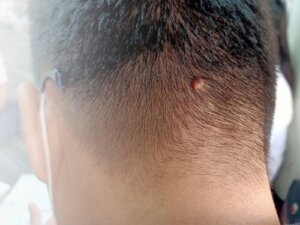
Warts on the head are usually benign bumps, but it’s always best to be cautious. Sometimes, they could be the symptom of an important underlying disease. That is why it’s not advisable to ignore them.
The truth is that in most cases, warts on the head disappear on their own and don’t cause any serious problems. What they do cause is discomfort, since their appearance is often unpleasant and sometimes very noticeable.
If they don’t disappear after a while, the best thing to do is to visit a dermatologist. There are several treatments to eliminate them.
What are warts on the head?
Warts on the head are a relatively common problem, although its more common for these lesions to appear on the fingers and hands. They have a rounded appearance and are almost always brown, but can also be beige or pink.
Sometimes, these warts have black dots. They feel rough or scaly to the touch but are painless.
They measure from 1 millimeter to a few centimeters. In addition to common warts, other types can occur:
- Flat warts: These are less rough and smaller. Sometimes they are yellowish in color and sometimes brown. They usually appear several at a time.
- Filiform warts: These look like threads or brushes and grow very quickly.
Warts on the head are mistaken for other types of conditions, such as the following:
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Actinic keratosis
- Sebaceous nevus
- Moles
We think you may also enjoy reading this article: Get Rid of Warts with This Garlic-Lemon Treatment
Why do they occur?
Head warts are a skin condition caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). There are more than 100 types of this viral agent, but if they appear on the head, they’re usually of the subtypes 1, 2, 4 or 7. These are different from the ones that cause genital warts.
HPV is very contagious. Therefore, warts on the head appear by direct or indirect contact. The former is skin-to-skin contact with another person. Indirect contact is through personal items, such as hairbrushes or hats.
Also, the affected person can be self-contagious. This occurs when there’s a wart on another area of the body and it’s touched or scratched. If that person then touches his or her scalp, he or she can carry the virus there.

The possible risks of head warts
People who have warts on their heads often wonder if they pose any danger. Usually , these lesions do not pose any risk and don’t cause any significant consequences.
They usually disappear once the HPV virus completes its cycle. This takes anywhere from a few months to a little over a year. In the meantime, the only discomfort is aesthetic.
In any case, it’s important to be vigilant. In some cases, they can be mistaken for another type of bump that is indeed dangerous.
The best thing to do is to consult a dermatologist if any of these changes occur:
- Intense itching
- Pus discharge
- Bleeding in the lesion
- The affected person suffers from diabetes
- An increase in the size of the warts
- Changes in the texture or color of the wart
- Discomfort or pain when combing or washing the head
Like this article? You may also like to read: Five Solutions to Remove Warts on Your Fingers
How to treat warts on the head?
Warts on the head can take quite a while to disappear. Therefore, if they don’t cause any discomfort, there are no changes, and they’re well-tolerated by the person, the appropriate measure is to wait until they disappear.
If you don’t want to wait or you are uncomfortable with such growths, there are several treatments that allow you to remove this type of warts. The main ones are the following.
Anti-wart products
There are some creams that stimulate the immune system and provoke an irritating reaction. After this, the same system eliminates the cells containing the human papillomavirus.
Salicylic acid
This is an over-the-counter medication found in liquid, gel, or pad form. It should be applied daily directly to the wart. The drug gradually dissolves the layers of the growth, but it may take a few weeks.
Cryotherapy
In this case, warts on the head are frozen by using liquid nitrogen. Once this has been achieved, they can be removed. This is a treatment that must be performed by a physician and is usually very effective.
Electrocautery
Electrocautery consists of applying an electric current to the wart in order to burn it. Afterward, a scraping is performed. It’s also very effective for immediate removal.
Laser treatment
This type of procedure is often used when warts on the head are stubborn or difficult to treat. It uses CO2 or pulsed dye. This is a safe method that usually produces very good results.
Surgical excision
With this surgery, the wart is cut out using a scalpel. The wound recovery time is usually up to three weeks. There may be a scar, but it’s very practical for solving the problem.
Home remedies
There are several home remedies that may be effective in removing warts on the head. Likewise, some of them help fight the virus and, if they don’t completely eliminate the lesions, they may help cause them to shrink. They are the following:
- Apple cider vinegar: Apply it to the wart and leave it overnight. This is a natural anti-inflammatory and antiseptic liquid.
- Aloe vera: Apply the plant gel in the same way as sd explained with apple cider vinegar. Aloe regenerates and renews skin cells. It also repairs damaged tissues.
- Tea tree oil: Dilute the oil in a little water and apply a small amount to the growth.
Do not try to remove them at home
It’s not advisable to try to get rid of warts on the head by yourself by cutting or pulling them off. Not only can this lead to infection, but it also encourages self-contagion. It’s also important to be careful when brushing or washing your hair.
It’s advisable to keep the head dry, as warts proliferate more in damp areas. After touching these growths, it’s necessary to wash your hands. It’s not a good idea to share personal items such as combs, towels, or caps.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Mendez Mathey, V. E. (2017). Queratosis seborreica. Revista Médica Herediana, 28(4), 266-266.
- González Martínez, G., & Núñez Troconis, J. (2015). Tratamiento de las verrugas genitales: una actualización. Revista chilena de obstetricia y ginecología, 80(1), 76-83.
- Espino Otero, S., Romero Rodrígez, J., Boza Mejías, Y., Acevedo Sierra, O., Quintana Hijano, I., & Selme, P. (2009). Concordancia clínico-histopatológica en lesiones de cabeza y cuello. Medisur, 7(1), 25-29.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








