The hCG Diet: Characteristics and Possible Risks


Written and verified by the nutritionist Maria Patricia Pinero Corredor
The hCG diet is a rather controversial method of weight loss. It has proponents who claim it’s effective, but the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it dangerous, illegal, and fraudulent.
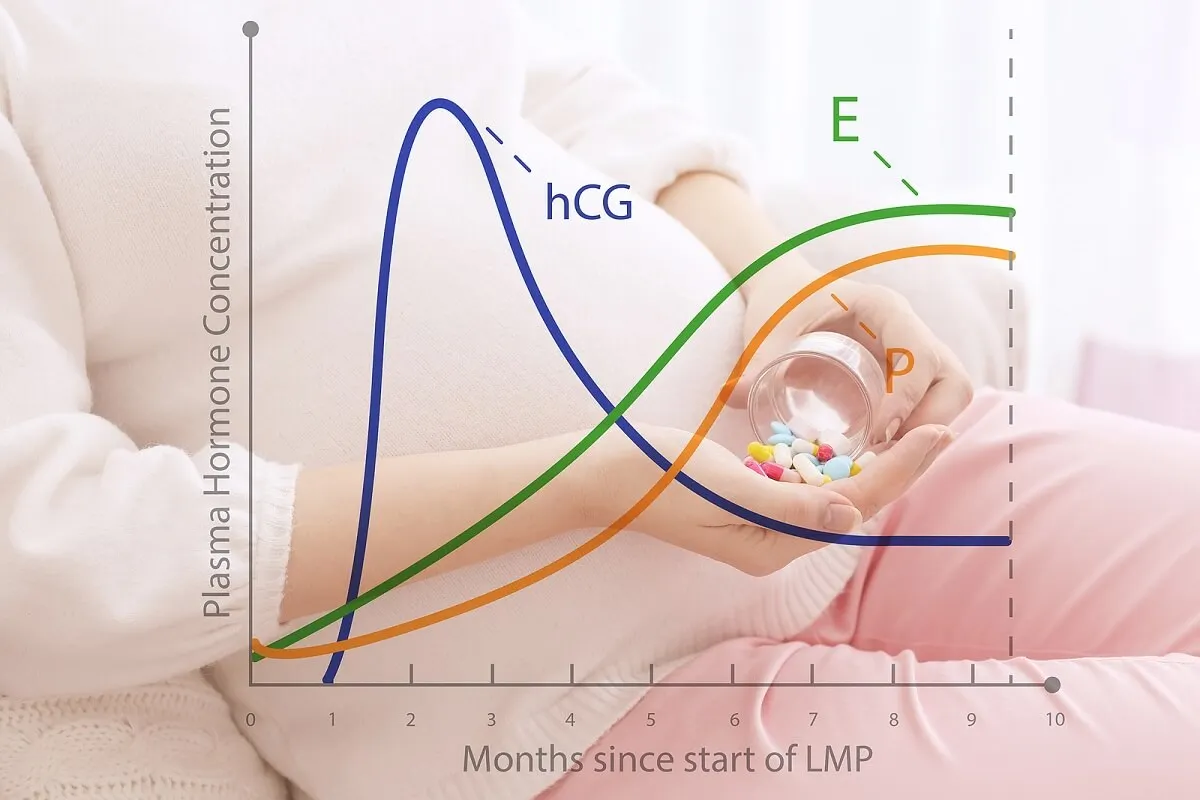
But what really is the hCG diet? Why is it said to aid in weight loss? Well, hCG refers to the hormone “human gonadotropin,” whose levels are elevated in early pregnancy. It’s also used in fertility treatments.
However, a few years ago, Dr. Albert Simeons proposed its use as a weight loss modality. Specifically, the plan suggests consuming only 500 calories a day plus an injection of the hormone. Of course, doing such a thing involves several serious risks. Here are all the details.
What is the hCG diet based on?
The hCG diet consists of an extreme caloric restriction – only 500 calories a day – and the injection of the hCG hormone (human choriogonadotropin). This hormone is released by pregnant women to support the healthy growth of the uterus and the development of the fetus.
As a weight loss method, its use became popular in the 1950s. According to its proponents, the hCG injection could decrease the feeling of hunger and support weight loss. It was even claimed to contribute to fat redistribution in the thighs, hips, and stomach.
Despite this, there are no studies to support its safety and efficacy. On the contrary, most research claims that the effectiveness of this diet lies in the low-calorie intake and has nothing to do with the use of the hormone.
In most evaluations, a placebo was given to one group of dieters and the hormone to another group. They found that weight reduction was similar between the two groups. In addition, they showed that hCG does not take away hunger.
We think you may be interested in reading this, too: The Vertical Diet: What Is It and What Are Its Disadvantages?
What does the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) say?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved hCG as a prescription drug to treat female infertility and hypogonadism in men. However, it disapproves of its use as a weight-loss product.
According to the FDA, manufacturers promote these products by claiming that they “change abnormal eating patterns” or “restore metabolism.” In fact, it’s claimed that it can aid in the loss of 10 to 15 kilos in 30 to 40 days.
Despite this, the FDA warns of its dangers, and they explain that “any weight loss is due to extreme caloric restriction, not hCG. In certain doses, it even puts a person’s health at risk.”
For this reason, in 2016 they sent seven warning letters to companies that marketed these products. They consider their commercialization as violating the law and only admit it when the doctor suggests them as part of a hormonal treatment.
How do people follow an hCG diet?
To distribute 500 calories a day is not an easy thing. Therefore, it must be a very low-fat diet. It’s usually divided into three phases:
- Loading phase: During the first 2 days, foods abundant in fat and calories are consumed. In addition, hCG use is started.
- Weight loss phase: From weeks 3 to 6, 500 calories are eaten along with the hCG. Only lunch and dinner are allowed.
- Maintenance phase: This is the time to exclude hCG; in addition, food intake is gradually increased, but without sugar and starch, for 3 weeks.
The promoters of this diet recommend only 3 weeks in the intermediate phase for those seeking minimal weight loss. However, if more significant weight loss is desired, it should be followed for six weeks. In fact, some people repeat all phases until they reach the expected weight.
Each meal should contain at least a serving of lean protein, a piece of bread, a vegetable, and a serving of fruit. Butter, sugar, and oils should be avoided. At the same time, the person should drink plenty of liquids, especially water.
Does the hCG diet really help people to lose weight?
In general, when a low-calorie diet is followed, the body uses its energy reserves to be able to fulfill its functions. In this way, it starts to decrease the accumulated fat.
To understand it better, it’s worth remembering how metabolism works. All food and beverages become energy through calories. When taken in excess, the body fails to use it and tends to accumulate.
Accordingly, it’s logical to think that the hCG diet does help to reduce weight significantly. For an average adult, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends an intake of 2000 to 2500 calories per day.
The risks of the hCG diet
Beware! Although this diet model may allow you to lose weight, the truth is that it poses several serious health risks. Today, it’s a type of diet discouraged by professionals. Let’s take a look at all of the possible health risks.
1. A deterioration of the nutritional status of minerals
In a study reported in the Latin American Archives of Nutrition, a group of obese women was divided into two. One followed a 1000-calorie diet, and the other, a 1300-calorie diet.
At 12 weeks, the nutritional value of iron, zinc, copper, and calcium was evaluated. Then, it was discovered that hypocaloric diets deteriorate the nutritional value of micronutrients.
As a consequence, disorders such as anemia, hair loss, altered bone calcification, and dental changes may appear.
Like this article? You may also like to read: Ferrán Torres: The Rigorous Training and Diet of the FC Barcelona Player
2. Electrolyte imbalance
Electrolytes are found in the blood. They’re positively and negatively charged ions. They have important functions in the body, such as nerve reactions and muscle functions. An inadequate diet and a lack of vitamins can lead to their imbalance. Its symptoms include the following:
- Irregular heartbeat
- Changes in blood pressure
- Confusion.
- Nervous system disorders
- Bone problems
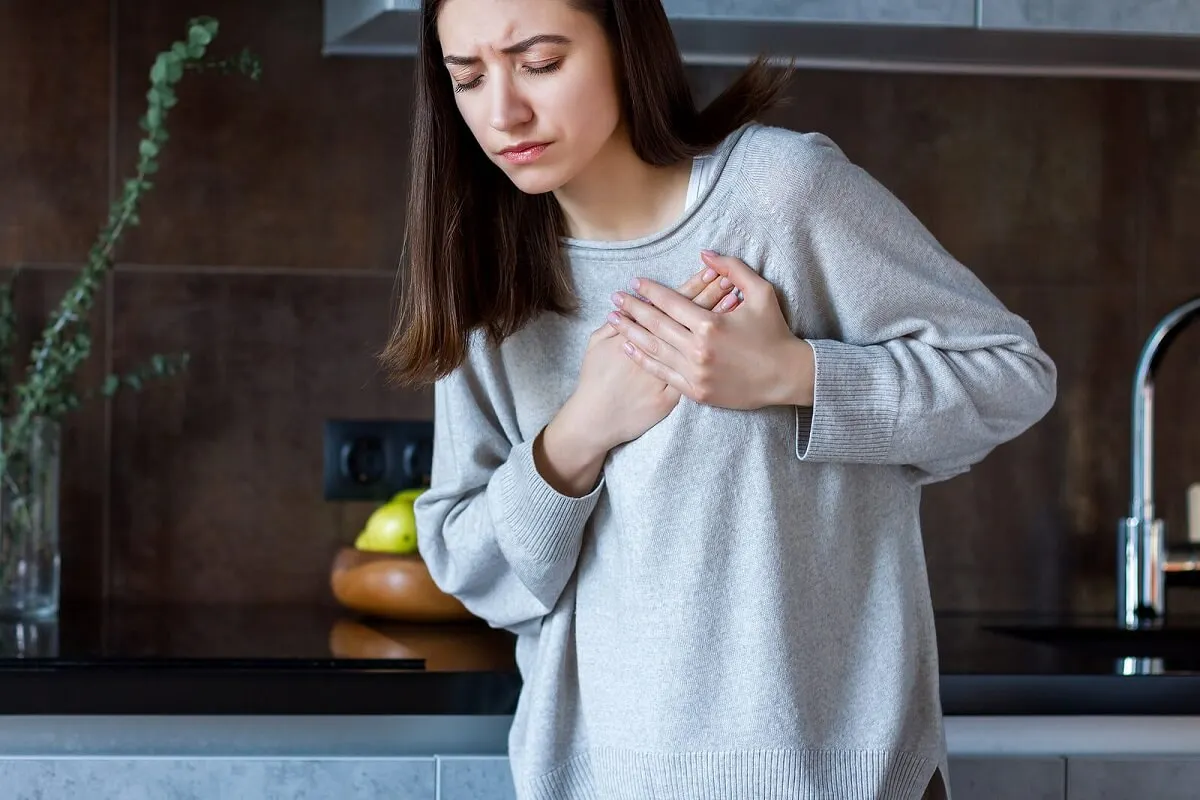
3. An irregular heartbeat
A heartbeat that’s too slow or too fast can be caused by dietary problems. This is because the heart is always working and needs energy continuously.
In fact, it’s known that a deficient supply of energy produces structural and functional alterations in the heart in the long term. It usually appears in patients with anorexia nervosa, who also have a caloric insufficiency in their diet.

4. Various other side effects
Science has shown that hCG can cause side effects such as the following:
- Tiredness
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Depression
- Edema or fluid accumulation
- The formation of blood clots
- Enlarged breasts in men
Calorie restriction can also lead to loss of muscle mass, adverse effects on mental and physical health, malnutrition, increased risk of kidney stones, and complications in diabetics and people with kidney disorders.
The hCG diet isn’t safe
Overall, it’s important to remember that the FDA has not approved hCG as a weight loss adjuvant. Moreover, there is no evidence to support the alleged benefits of this diet.
On the contrary, there are warnings of possible side effects due to the use of the hormone and the caloric restriction proposed by this regimen. Thus, if it’s a question of losing weight, it’s best to seek professional guidance from a doctor and a nutritionist.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Aguirre M. Efecto de dietas con restricción moderada de energía sobre el estado nutricional de algunos minerales en mujeres obesas. 2007. Archivos latinoamericanos de nutrición. http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0004-06222007000300006
- K Johansson. Risk of symptomatic gallstones and cholecystectomy after a very-low-calorie diet or low-calorie diet in a commercial
weight loss program: 1-year matched cohort study. International Journal of Obesity (2014) 38, 279–284. 2014 - Parikh H. Trombosis venosa profunda múltiple (TVP) aguda como probable evento adverso del uso de gonadotropina coriónica humana (HCG) para la pérdida de peso. Ash Publication. Volumen 126, Número 23. 3 de diciembre de 2015
- Cuesta F. Desnutrición y corazón. Fbbva. https://www.fbbva.es/microsites/salud_cardio/mult/fbbva_libroCorazon_cap63.pdf
- FDA. Preguntas y respuestas sobre los productos HCG para bajar de peso. 2016.
- Butler S. Evidence for, and Associated Risks with, the Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Supplemented Diet. 2016 Nov;13(6):694-9. doi: 10.3109/19390211.2016.1156208. Epub 2016 Mar 24.
- FDA. Evite los productos peligrosos de la dieta HCG. 2020.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








