What’s the Difference Between a Cyst and a Tumor?

Most people can’t tell the difference between a cyst and a tumor. Both are lumps that appear in certain parts of the body and are usually of concern to the sufferer. This is because most people immediately associate them with cancer.
In fact, many people believe that the difference between a cyst and a tumor is that the former is benign and harmless, while the latter is malignant and fatal. That isn’t true. Some cysts can be dangerous, while some tumors can be benign.
An important difference between a cyst and a tumor is their cause. Also, of course, their composition and symptoms they cause. Although both tend to be very similar in appearance, the truth is that they have a different nature and consequences.
Cysts
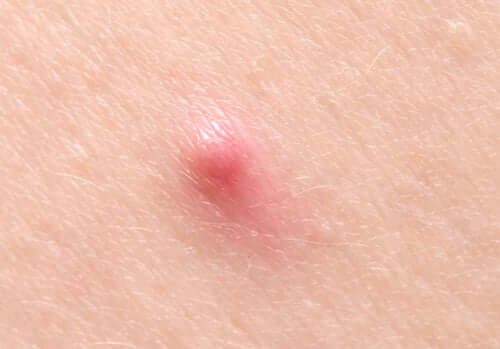
There are different types of cysts. The most common are the following:
- Breast cysts. These are fluid-filled sacs that appear on the breasts and are easily movable under the skin. A woman suffers from fibrocystic breast disease if she has many cysts in the same breast.
- Follicular cysts. Fluid-filled pockets of tissue that form in hair follicles and generally contain keratin. They usually form on the scalp.
- Epidermoid cysts. They form in the epidermis, basically in the chest, back, neck, and scrotum.
- Ovarian cysts. They form in the ovaries, usually during ovulation. They can sometimes cause pain and discomfort.
- Liver cysts. As their name states, they’re fluid-filled sacs that form in the liver.
- Kidney cysts. Fluid-filled sacs that form in the kidneys.
Cysts vary in size. Sometimes, they’re no bigger than a pin, while other cysts can be as big as a basketball. The bigger they are, the more dangerous, due to the potential damage they can cause to nearby organs.
Tumors
Tumors can result from disease, immune system problems, smoking or drinking, prolonged sun exposure, contact with certain toxins or chemicals, radiation, obesity, and viruses, among other factors.
This article may interest you: The Pan-Cancer Genomic Study: Spotting Tumors Before They Appear
Tumors can be benign, premalignant, or malignant. In other words, cancerous, precancerous or cancerous, respectively. The main types of tumors are:
- Lipomas. Tumors that are made up of fat cells. They’re located under the skin and are soft. They’re usually benign and generally appear in people 40 and older.
- Fibroids. They form in fibrous or connective tissues, most often on or around the uterus. They’re benign tumors.
- Adenomas. They form in the layer that lines the organs and glands. They’re made of glandular epithelial tissue. Most of them are benign.
- Malignant. These tumors can form in any part of the body. They’re cancerous tumors.
Read on to learn more: Scientific Advances Develop Vaccine Against Cancerous Tumors
The difference between a cyst and a tumor
As you can see, several factors determine the difference between a cyst and a tumor. The first one is the cause. Although cysts generally form due to a gland obstruction or infection, tumors are the result of excessive cell growth.
Likewise, while cysts generally contain air, fluid, or a semi-solid substance, tumors are solid tissue masses. Although almost all cysts are benign, cancer also causes a significant number of cysts. Cysts that contain solid material can be cancerous.
Another important difference between a cyst and a tumor is that the former tend to be moveable. In other words, you can move them from one place to another just by touching them. On the other hand, tumors are rigid masses that can’t move. In fact, they seem to be attached to the body.
Both cysts and tumors can appear anywhere in the body and require medical assessment. The danger of one or the other depends on several factors. Therefore, if you have a cyst or a tumor, you need to get the appropriate tests to get diagnosed.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Cotte, B., Haag, T., Vaudoyer, F., Canis, M., & Mage, G. (2011). Ecografía de los quistes y tumores de ovario. EMC-Ginecología-Obstetricia, 47(4), 1-24.
- Giwerc, A., Masson-Lecomte, A., Desgrandchamps, F., & Méria, P. (2019). Quistes y tumores del epidídimo. EMC – Urología. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1761-3310(19)42719-9
- Avenue, B. M. (2012). Tumores Cerebrales Tumores Cerebrales. American Brain Tumor Association. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICADIWT.2009.5273951
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








