Characteristics of Campylobacter Infections

Written and verified by the biologist Samuel Antonio Sánchez Amador
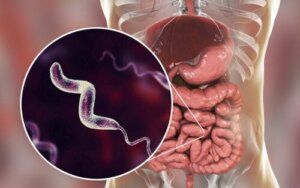
Campylobacter infections, also known as campylobacteriosis, are the most common cause of diarrhea worldwide and responsible for up to 14% of these cases, according to studies.
Beyond this, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that foodborne diseases – including campylobacteriosis – affect one in 10 people worldwide at any given time.
Of course, keeping the bacteria that cause these diseases at bay is not only a matter of hygiene. It can save many lives in the long term, especially in countries with poor health infrastructures. Stick around – today’s article will discuss campylobacter infections in more detail.
What are campylobacter infections?
First of all, let’s emphasize that the name campylobacter doesn’t refer to a single bacterial species, but to a genus in the form of a bacillus that contains at least 12 human disease-causing species. The most common of all is C. jejuni and it causes up to 90% of infections.
This pathogen is one of the most common causes of diarrhea in the USA. According to estimates, it affects about 2.4 million people in the country every year. There were more than 29 epidemiological outbreaks between 2013 and 2017. Of course, the data confirms that campylobacteriosis is the order of the day.
Do you know What Are Stool Cultures?
Causes of campylobacter infections
In general, this infection is caused by the ingestion of unpasteurized milk or by raw or uncooked meat and poultry. According to the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), an inoculation as small as 500 oral pathogenic cells can lead to infection in a person.
Campylobacter bacteria invade cells in the small intestine using a mechanism similar to non-typhoid salmonella, they cause injury, and alter fluid absorption. This generates the characteristic medical situation that we’ll talk about below.
The main sources of infection are:
- Firstly, through the consumption of undercooked meat products, mainly of avian origin
- Through the consumption of unpasteurized milk
- Due to the presence of the bacteria in untreated water
- Finally, due to contact with infected pets or farm animals
Main symptoms
The most common symptom of a campylobacter infection is diarrhea — sometimes bloody. It usually appears between 2 and 5 days after contact with the bacteria, and usually stops on its own after 6 days. There are other symptoms such as:
- Cramps and abdominal pain
- Fever and fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
However, some infected patients never develop clear symptoms according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine. In addition, death from campylobacteriosis is quite rare. It’s mainly deadly in young infants, senior citizens, and people with immune deficiency, such as those with HIV.
Diagnosis
It’s easy to make a diagnosis once the symptoms are present. The professional must obtain a sample of the fecal matter and identify and isolate the bacteria causing the gastrointestinal maladjustment by conducting a tool test. There are also other faster kinds of tests that can identify the genome of the microorganism.
Treatment options for campylobacter infections
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), campylobacter infections usually clear up on their own within 3 to 6 days after the appearance of the first symptoms. Still, heavy fluid intake is recommended to replace electrolytes lost in diarrhea.
Drugs aren’t necessary in most cases because their excessive intake can lead to the appearance of resistant strains. Thus, self-medication isn’t advised and antibiotics are only prescribed for the most serious cases.

How to prevent these infections?
As with most Foodborne Diseases (FBDs), the proper handling of food is the best form of prevention. CDC also shares some measures to consider:
- Wash your hands before handling any food or after touching any possible source of infection, be it an infected person or an animal
- Cut raw fruit and vegetables and meat on different boards
- Cook any food of animal origin, whether or not it’s been previously frozen
- Always drink pasteurized milk and juice
- Under no circumstances should you drink untreated water
Learn more about Chronic and Acute Diarrhea: Causes and Treatment
Final considerations
As you can see, campylobacter infections are the leading cause of diarrhea worldwide and C. jejuni species are the most widespread at a global level. Most of the epidemiological outbreaks happen due to the consumption of raw meat, unpasteurized milk, and untreated water.
Thus, the best measure to combat campylobacteriosis is to eat well sanitized and properly cooked food. This implies not mixing ingredients of animal and vegetable origin, always subjecting meats to high temperatures before consumption, and, of course, washing your hands before and during cooking.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Campilobacteriosis, protocolo para la vigilancia en la comunitat valenciana. Recogido a 13 de noviembre en http://chguv.san.gva.es/documents/10184/189524/Campilobacteriosis.pdf/7821b3c4-5321-44d4-85dd-e627a0a8de0c#:~:text=La%20campilobacteriosis%20es%20una%20zoonosis,diarrea%20en%20todo%20el%20mundo.
- Campylobacter, OMS. Recogido a 13 de noviembre en https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter
- Epidemiología, Transmisión y Control de Campylobacter spp, grupomontevideo.org. Recogido a 13 de noviembre en http://grupomontevideo.org/ndca/casaludanimal/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Epidemiolog%C3%ADa-Transmisi%C3%B3n-y-Control-de-Campylobacter-spp.pdf
- Campilobacteriosis, biblioteca nacional de medicina de EE. UU. Recogido a 13 de noviembre en https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/campylobacterinfections.html
- Campylobacter, CDC. Recogido a 13 de noviembre en https://www.cdc.gov/campylobacter/diagnosis.html
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








