What Is an Emotional Allergy and How Is it Treated?


Reviewed and approved by the nurse Leidy Mora Molina
In certain occasions, an anxiety crisis or a situation of great stress could provoke an emotional allergy . Respiratory or cutaneous symptoms, such as redness, are manifested.
These signs, as well as the treatment to be applied, can be similar to those proposed for a normal allergic reaction. However, other interventions may be required, such as psychological therapy. Read on to learn more about emotional allergy.
Allergies and allergic reactions
Allergy is a state of hypersensitivity in which various reactions are generated due to contact with certain elements, called allergens. There are several types of allergies:
- Respiratory reactions, caused by inhalation of chemicals, as well as allergy to dust mites, animals, pollen or fungal spores.
- Food allergies are triggered in sensitive people by the ingestion of certain ingredients (dairy, shellfish, soy, peanuts, etc.).
- Reactions due to contact with objects or substances, causing dermatitis. This can occur with rust, cement, and gasoline, among others.
- Skin reactions and others caused by insect and arachnid bites.
- Allergy to medicines or compounds present in them.
Now, when the sensitive person comes into contact with the substance or element (allergen), a complex sequence of events takes place, which begins with the activation of lymphocytes and culminates with the release of histamine. Although it should be noted that histamine is not the only substance that is secreted.
Causes of allergies
Allergic reactions occur due to the confluence of allergen exposure plus allergen sensitivity. However, the question is why some people are sensitive and others are not.
There are several explanations for this. For example, it’s believed that there’s a genetic factor involved, since allergies are more common in those who have a family member with sensitivity to a certain allergen.
It’s also stated that the person is not born with an allergy, but develops it at some point. In this order of ideas, there are environmental factors that, together with genetic predisposition, increase the risk. Among them, the following:
- Environmental contamination
- Exposure to tobacco smoke
- Socioeconomic factors (greater overcrowding)
- Presence of dust in suspension in the environment
- Climatic factors (higher humidity, for example)
- Diet: consumption of processed foods, artificial colorings, etc
Like this article? We think you may also like to read: Allergy to Pollen? Try These Hypoallergenic Flowers
The symptoms of an emotional allergy
To these aforementioned factors, we must add the emotional aspect, referring to the way in which the person faces his circumstances and problems. Thus, anxiety, stress, and other emotional disturbances can influence the appearance and development of allergies, according to research (in Spanish).
An emotional allergy can be defined as a condition in which, in the face of certain negative emotions, the immune system generates a reaction in the body similar to that which would occur due to the presence of an allergen.
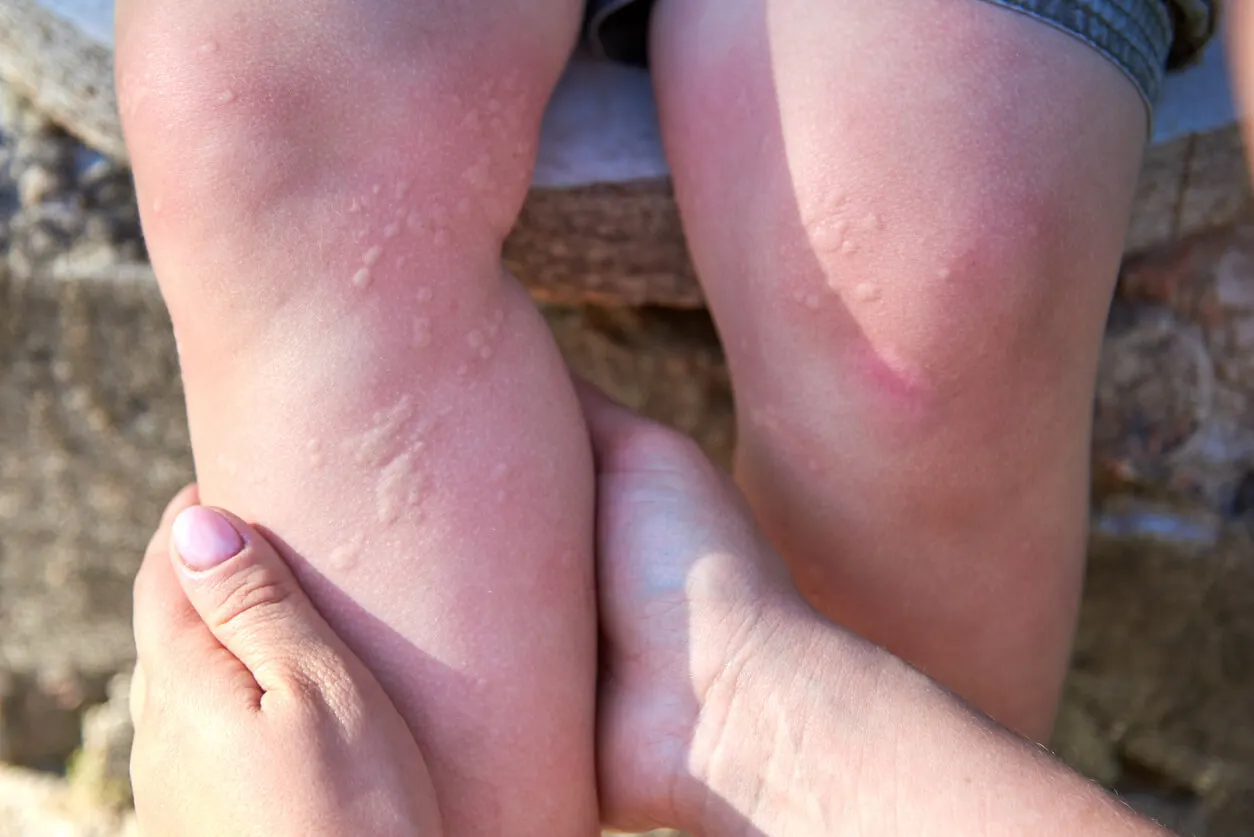
The symptoms of emotional allergy manifest themselves mainly in the skin, although not exclusively. They are similar to hives:
- Itching
- Rashes
- Red spots
These symptoms may vary from patient to patient. In turn, they will depend on other factors, such as age and intensity of emotions.
Why does an emotional allergy occur?
Emotional stress can affect the nervous and immune systems. It’s believed that, in these circumstances, the release of cortisol increases, as well as the production of catecholamines, which cause the inflammatory reaction.
Several explanations are proposed for this. For example, from the point of view of bio-neuroemotion, it’s believed that the disease is an adaptive mechanism that affects the person and that appears from programs. An allergy is then understood to be a resistance of the body against an aspect of the past life that we don’t like or that we don’t want to face. In fact, each allergen is even believed to have an associated symbology:
- Milk: Mother
- Grains: Family
- Pollen: Emotions
Similarly, it’s claimed that at a certain moment in the past, an emotional shock likely occurred, during which the unconscious would have detected something or someone as a potential aggressor, relating it to a present element. This element then becomes an allergen.
For its part, naturopathy explains that allergens are not such, but that allergies are due to an imbalance of our immune system caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. This ranges from the consumption of transgenic products to the excess of hygiene and exposure to chemicals in cleaning products, as well as our way of being and acting.
Treatment for emotional allergies
The treatment of emotional allergy can be similar to that of other types of reactions. In this sense, the use of anti-allergic (antihistamines) and topical products, including corticosteroids for skin symptoms, is prescribed.
If symptoms persist, in addition to seeing a dermatologist, it’s recommended to attend therapy with a psychologist or other mental health professional. Medications for stress and anxiety may also be prescribed.
On the other hand, some alternative treatments are mentioned that may be effective in reducing allergy-related symptoms. In one study, the natural products Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Malpighia glabra, and Bidens pilosa were found to have anti-allergic properties and may be as effective as loratadine.
Acupuncture has also been considered to be an option. Research on the subject indicates that this technique is effective in the symptomatic treatment of persistent allergic rhinitis.
Both these and other natural treatments could be used in the case of emotional allergy, as long as they’re not a substitute for a medical approach.

You may also be interested in reading this article: Citrus Allergy: Symptoms, Treatment, and Recommendations
Define the allergy before starting treatment
The treatment of any condition requires an adequate diagnosis. In the case of emotional allergies, one must be sure that the root of the problem is a stress or anxiety condition and not an allergen.
Hence, testing is considered necessary to determine to which substances the person may be sensitive – or if, in fact, the emotional factor is the prevailing one.
In any case, it should be a health professional who makes the diagnosis and prescribes the treatment. Finally, it’s worth remembering that, in this and in all cases in which we experience any symptoms, we should never self-medicate.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Corren J, Lemay M, Lin Y et al. Clinical and biochemical effects of a combination botanical product (ClearGuard™) for allergy: a pilot randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J. 2008; 20 (7). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-7-20
- García I, Ponce M, Lozano S. Tipos de alergias y afectación en la población. Revista Sanitaria de Investigación. 2021; 8 (2). Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=8074710
- Milián G, Velázquez J, Colomer M, et al. Bioneuroemoción y trastorno afectivo bipolar. Geroinfo. 2013;8(1): 1-9.
- Romero-Tapia S. Prevención de alergia y asma. Salud en Tabasco. 2002; 8(2): 83-86.
- Rossel M, Araya M. Alergia alimentaria en la infancia. Revista Médica Clínica Las Condes. 2011; 22(2): 184 – 189,
- Valenzuela Solano F, Mendoza Castillo J. La depresión y la ansiedad en las enfermedades alérgicas: el papel de las emociones en la patogénesis de la alergia. Alergia (Méx.). 1989; 36(1): 11-14.
- Xue C, An X, Cheung T, et al. Acupuncture for persistent allergic rhinitis: a randomised, sham-controlled trial. Medical Journal of Australia. 2007; 187: 337-341. https://doi.org/10.5694/j.1326-5377.2007.tb01275.x
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








