Try This Japanese Relaxation Technique
There are many different ways to combat stress and prevent it from becoming a problem in your life. To keep your stress levels in check, we’d like to share a simple Japanese relaxation technique that can reestablish the energetic balance in the body. It can also help alleviate physical and emotional pain.
This issue is a problem for people all over the world who have heavy workloads, obligations at home, personal problems, and illnesses, among other issues. People suffering from the effects of stress experience difficulty performing their daily activities; this often leads to other health problems, both physical and emotional.
It’s important to learn how to control your stress levels when they first start to rise; stress can become a chronic disorder if you’re not careful, requiring treatment with drugs and therapy.
Don’t forget to check out:
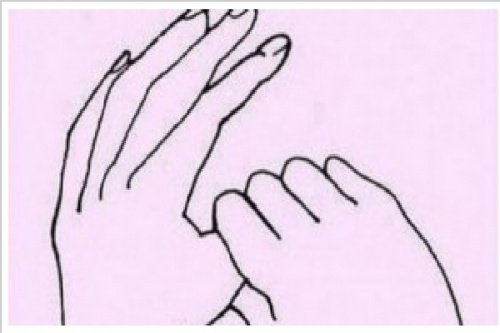
What is the Japanese relaxation technique?
Before you begin, you should know that each of the fingers are associated with different feelings or attitudes. Using the opposite hand, pressure is applied to each finger to work on the desired emotion.
You’ll be able to feel it working with each pulse of pressure. Take a look at the emotions associated with each finger:
- Thumb: Helps combat emotions like worry and anxiety.
- Index: Can help combat fear.
- Middle: Helps control anger and indignation.
- Ring: This finger is associated with sadness and depression; helps you to be more decisive.
- Pinky: Helps to calm anxiety, increases optimism.
This simple relaxation technique uses concepts from traditional medicine, but integrates them into a simple exercise that anyone can do at home.
This Japanese relaxation technique is truly extraordinary; it provides a simple way to achieve balance on a mental, physical and even spiritual level. This practice is a form of self-awareness, relaxation, and harmonization of the body and mind.
Read also:
Aromatherapy: What Does It Consist of?
Other natural relaxation techniques

In addition to the Japanese technique mentioned above, here are a few natural alternatives that can be very useful when dealing with negative emotions:
- Breathe: Many studies show that breathing deeply lowers the levels of a hormone called cortisol. Therefore, this results in the release of tension and anxiety.
- Aromatherapy: Aromatherapy is another excellent alternative for relaxing and eliminating negative emotions like stress. Scents like lavender, marjoram, lemon verbena, orange, or chamomile possess properties which are highly effective against stress and anxiety.
- Drink tea: Drinking tea is a great way to take advantage of the healing power of plants to combat stress, depression and anxiety. Infusions of lavender, lemon balm, lemon verbena, linden, Valerian root, chamomile or passionflower are all excellent for treating stress. They can also help with depression, anger, anxiety, insomnia and other negative emotions.
- Laugh: One of the best ways to fight back against stress is simply laughing. Many studies have found that laughing decreases the level of hormones and other compounds that cause stress, anxiety, and other complaints. In fact, a recent study suggests that laughing has a pain-relieving effect, similar to aspirin, making it an ideal way to relieve pain and reduce stress.
- Gymnastics for the eyes: Stress can affect your vision and cause tension and painful headaches. To avoid eye strain it’s important to exercise and relax your vision. Look up from the computer and focus your eyes on the same object, like a tree or picture, for 30 seconds, then blink a few times. Repeat this exercise several times a day.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
Gullickson, B. R. (2011). Taking Laughter Seriously. Strategic Finance. https://doi.org/10.2307/2107432
Moran, C. C., & Hughes, L. P. (2006). Coping with Stress: Social Work Students and Humour. Social Work Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/02615470600738890
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








