Trichomoniasis in Women: Can It Be Treated with Natural Remedies?


Reviewed and approved by the doctor Leonardo Biolatto
Some people have wondered if trichomoniasis in women can be addressed with natural remedies. Given the complexity of this sexually transmitted infection, many people seek solutions to stop its symptoms and prevent more serious problems.
However, it should be noted that a medical approach is essential. Although some homemade remedies can bring certain relief, it’s often necessary to administer prescription drugs to deal with the parasite that causes this pathology. We’ll tell you more about it.
Treatment of female trichomoniasis
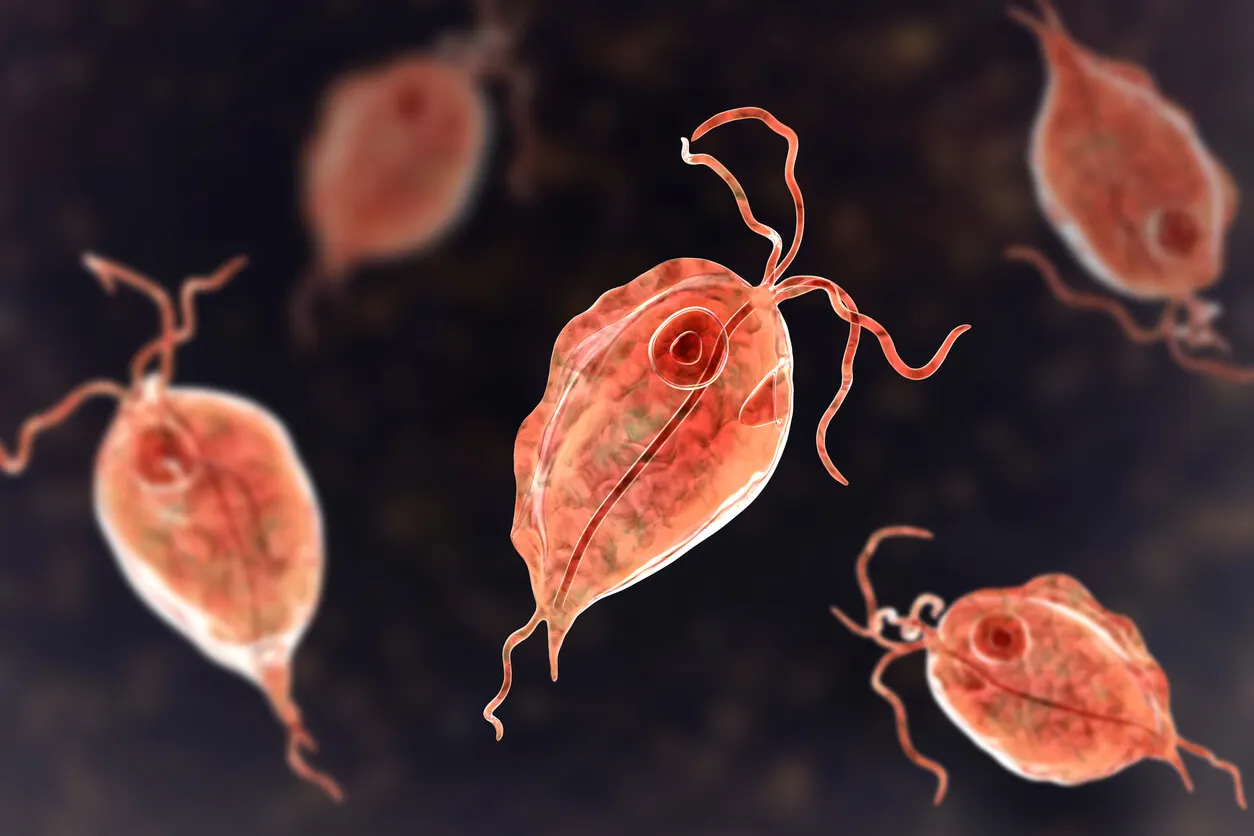
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. It can affect both men and women, although it’s more common in women. Transmission occurs through genital contact, either during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that only 30% of cases have any symptoms. In women, in particular, symptoms usually include vaginal odor, irritation, itching, and burning during urination. In addition, vaginal discharge tends to turn white, yellowish, or greenish.
Without prompt treatment, the infection causes genital inflammation and increases the risk of contracting other STIs. In addition, in the case of pregnant women, it can lead to complications such as low birth weight or premature birth.
Because of this, once the condition is suspected, you need to consult a physician to confirm the diagnosis. This is usually corroborated by a physical examination and laboratory tests.
Oral administration of drugs is then suggested. The options are as follows:
- Metronidazole
- Tinidazole
- Secnidazole
The drugs can be taken in a single dose (megadoses), or in small doses divided over several days. It’s necessary to complete the entire treatment to completely eliminate the parasite. In addition, the sexual partner should also receive the medication to prevent reinfection.
Is it possible to treat trichomoniasis in women with natural remedies?
A number of home remedies have long been circulated that promise to bring relief from trichomoniasis in women. However, to date, there’s no scientific evidence to support their safety and efficacy. The only effective treatment is the administration of drugs prescribed by the doctor.
However, there are some natural remedies that can serve as a complement to minimize the symptoms of the infection. They don’t replace the medical approach, but anecdotal evidence suggests that they can help with temporary relief of itching, burning, and inflammation. Let’s take a closer look.
Pomegranate juice or extract
In traditional medicine, pomegranate juice or extract has been one of the most widely used supplements to combat various types of infections, most notably trichomoniasis in women. Antibiotic, antiparasitic, and anti-inflammatory properties are attributed to it.
An in vitro and in vivo study shared in the Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology reported that purified pomegranate extract has the potential to inhibit the growth of the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. These effects were linked to its abundant content of polyphenols, fatty acids, sterols, terpenoids and amino acids.
However, larger and more comprehensive studies are needed to verify this. However, it’s a safe and nutritious remedy for most people.
The recommendation is to drink 2 to 3 glasses of pomegranate juice a day, for 1 week.
Black tea
Black tea is one of the popular remedies in the treatment of trichomoniasis in women. It’s valued for its high content of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that help to control the infection. And, while it’s not a cure, it does have potential as an adjunct to stop parasite growth.
In research shared via BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, the extract of this ingredient helped fight metronidazole-resistant strains of Trichomonas vaginalis. The best part? It didn’t affect the balance of vaginal flora.
Its effect was largely explained by its aflavin content, an antioxidant polyphenol. However, more research is needed.
Garlic
Since ancient times, garlic has been used as an adjuvant to combat various types of infections. In particular, antibacterial, antifungal, and antiprotozoal properties are attributed to garlic. Regarding the latter, a comparative study determined that it can help to inhibit the growth of Trichomonas vaginalis.
In particular, the researchers established that a commercial garlic-based product stops the motility of this microorganism. Because of this, it has therapeutic potential against trichomoniasis. However, despite these findings, further studies are required.
In general, garlic-based products come in tablets or pills. They’re usually consumed 2 or 3 times daily, 40 minutes before each main meal.
Trichomoniasis in women: remedies not recommended
While the above remedies are generally safe and well tolerated, there are other options that aren’t recommended because of the risks they carry. It’s important to mention them, as their use tends to lead to complications or unwanted effects.
Douching
This remedy usually combines water with other liquids and substances, such as vinegar, zinc sulfate, and some essential oils. While it sometimes momentarily soothes itching and burning, its application has significant side effects.
As detailed in a study shared through Epidemiologic Reviews, douching is associated with an increased risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, bacterial vaginosis, sexually transmitted diseases, candidiasis, and uterine problems. Hence, they are discouraged by gynecologists.

Live culture yogurt
While consumption of plain yogurt with live cultures may benefit health by promoting the balance of bacterial flora, its application in the vagina can lead to problems. Some claim that its probiotics help balance the vaginal flora. However, there’s no evidence to prove this.
Contrary to this, it has been determined that introducing yogurt into the vagina can be counterproductive. This isn’t only because it can alter the balance of bacteria already present, but also because it promotes problems of infection and bad odor.
Discover more: How Can Women Protect Themselves from STDs?
What should we remember about remedies for trichomoniasis in women?
Currently, there isn’t enough scientific evidence to claim that natural remedies can effectively combat trichomoniasis in women. While options such as pomegranate extract, black tea, and garlic have shown promising effects, more evidence is needed. For now, they can be used in a complementary form.
The essential thing to keep in mind is that no natural preparation is a substitute for medical treatment. With this infection, it’s essential to receive the appropriate dose of drugs to effectively treat it and prevent complications. If you suspect you may have it, consult your gynecologist as soon as possible.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bouchemal K, Bories C, Loiseau PM. Strategies for Prevention and Treatment of Trichomonas vaginalis Infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017 Jul;30(3):811-825. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00109-16. PMID: 28539504; PMCID: PMC5475227.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. STD facts – trichomoniasis.
- Schumann JA, Plasner S. Trichomoniasis. [Updated 2022 Jun 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534826/
- El-Sherbini, Gehad & Ibrahim, Khadra & Sherbiny, Eman & abdel hady, Nevein & Morsy, Tosson. (2010). Efficacy of Punica granatum extract on in vitro and in vivo control of Trichomonas vaginalis. Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology. 40. 229-44.
- Noritake SM, Liu J, Kanetake S, Levin CE, Tam C, Cheng LW, Land KM, Friedman M. Phytochemical-rich foods inhibit the growth of pathogenic trichomonads. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Sep 13;17(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1967-x. PMID: 28903731; PMCID: PMC5598040.
- Ibrahim AN. Comparison of in vitro activity of metronidazole and garlic-based product (Tomex®) on Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasitol Res. 2013 May;112(5):2063-7. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3367-6. Epub 2013 Mar 2. PMID: 23455944.
- Martino JL, Vermund SH. Vaginal douching: evidence for risks or benefits to women’s health. Epidemiol Rev. 2002;24(2):109-24. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxf004. PMID: 12762087; PMCID: PMC2567125.
- Mei Z, Li D. The role of probiotics in vaginal health. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 28;12:963868. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.963868. PMID: 35967876; PMCID: PMC9366906.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








