What to Do for a Bee Sting

Have you ever wondered how to deal with a bee sting? Although in most cases they’re mild, they can sometimes cause complications. Therefore, it’s important to learn a little first aid to deal with these kinds of problems. We’ll give you some useful tips below.
A bee sting can cause pain, swelling, redness, and heat in the affected area. However, sometimes it can cause more severe symptoms if the affected person has an allergic reaction. What’s more, many cases are life-threatening, especially when multiple bees attack. What should you do for a bee sting?
5 tips for a bee sting
When bees sting, they release a poisonous toxin that can cause inflammation, pain, and other symptoms. In fact, many people are allergic to this toxin and can experience severe symptoms. If you experience severe symptoms, you have to see a professional, as they can cause serious health complications.
However, even mild stings cause severe redness and increased swelling in the affected area. They also cause itching, burning and other discomforts. In these cases, some home care may be enough to relieve your symptoms. Take note!
Don’t hesitate to read: 3 Natural and Homemade Mosquito Repellents
1. Remove the stinger
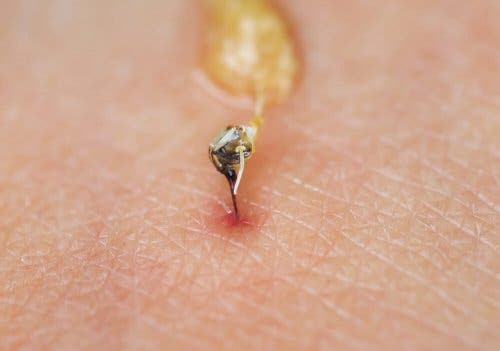
When a bee stings, its stinger usually gets stuck in your skin. After this, the bee dies. In fact, it’s the only insect that dies after it stings. Other species, including wasps, keep their stinger and may keep stinging you. How can you remove the stinger?
It’s important to remove the stinger as soon as possible. However, you should avoid abrupt methods like using tweezers or similar tactics. The correct way to do it is to gently scrape a flat-edged object across the skin (you can use a document or credit card).
2. Wash with soap and water
One of the first risks of bee stings is infection. For this reason, after suffering a sting, you should wash the affected with water and antibacterial soap. You should even wash it daily until it’s completely healed, since it can get infected later.
3. Use cold compresses

The symptoms you get after being stung can be uncomfortable or painful. The severity depends on your immune system’s reaction to the toxin released by the insect.
In any case, applying a cold pack or ice pack to the area can reduce discomfort. Ideally, you should do it for about 8 or 10 minutes until you feel relief.
Read also: Fenistil: A Great Remedy for Stings, Burns, and Hives
4. Don’t scratch the affected area
Many people scratch their skin when they feel itchy after being stung by insects. However, this is a mistake. Although it initially causes some relief, scratching your skin increases swelling, prolongs itching, and increases the risk of infection. Therefore, you should avoid it entirely.
5. Apply a soothing product
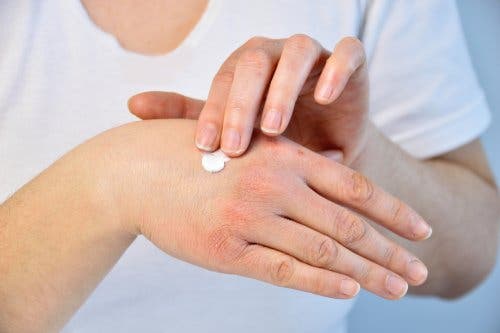
Calamine lotion or a baking soda paste can help with a bee sting. In fact, you should use them several times a day to keep burning and itching under control. Calamine lotion is an antihistamine product available in pharmacies.
When should you see a doctor?
Most of the time you can take care of a bee sting without going to the doctor. However, there are some complications that must be checked by a professional. If the discomfort continues or worsens, it’s best to go to the emergency room. Some serious reactions include:
- Urticaria (hives)
- Pale skin
- Severe itching
- Swelling of the tongue and throat
- Labored breathing
- Fast pulse
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Moderate or high fever
- Loss of consciousness
If you experience these symptoms, it may be a sign of anaphylactic shock, a life-threatening allergic reaction. You have to act quickly to avoid complications. Therefore, it’s essential you go to the hospital as soon as possible.
You should also see a doctor when you’ve had several stings at the same time. Although the symptoms might seem mild, it’s important to get treatment so as not to have severe reactions later. The doctor might prescribe some pain relievers and antibiotics in case of infection.
In summary…
Although most cases of bee stings are mild, it’s important to know how to act in order to prevent complications. Using these recommendations for proper treatment will accelerate your recovery and reduce the risk of infection.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Hoo, F. K., Hasan, S., Wan Sulaiman, W. A., & Basri, H. (2014). A Case Report of an Unusual Complication from Bee Sting: Acute Brachial Plexopathy. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.302.4891
-
Informed Health Online [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Insect venom allergies: Short-term and long-term treatment. 2017 Jul 13. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK447119/
-
Visscher, P. K., Vetter, R. S., & Camazine, S. (1996). Removing bee stings. Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(96)01367-0
- Przybilla, B., & Ruëff, F. (2012). Insect stings: clinical features and management. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2012.0238
- de Roodt, A. R., Salomon, O. D., Orduna, T. A., Robles Ortiz, L. E., Paniagua Solis, J. F., & Alagon Cano, A. (2005). [Poisoning by bee sting]. Gac Med Mex.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








