What is the GGT Test and What Do the Results Mean?

Reviewed and approved by the doctor Diego Pereira
The purpose of the GGT test or ‘gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase test’ is to diagnose liver problems. It consists of measuring the concentration of the enzyme gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in the blood. It tends to alter when the liver or bile ducts are in bad shape.
However, it is a non-specific parameter, as it also elevates in certain bone diseases or in alcoholics. Despite its nonspecificity, it allows early detection of many pathologies. Moreover, it is a simple and cost-effective test. What exactly is it? Here are all the details.
What does the GGT test consist of?
The GGT test consists of measuring the levels of the enzyme gamma glutamyl transpeptidase in the blood. According to a Kids Health publication, this enzyme is produced in different parts of the body. However, the greatest synthesis occurs in the liver and gallbladder.
In the blood and other organs the levels are usually minimal. Therefore, when a high concentration is observed, it is possible to suspect damage or disease. In particular, the altered GGT test indicates that the enzyme may be escaping from the liver into the blood.
In turn, this alerts that the liver or bile ducts are being damaged. However, its levels are variable. For example, in infants they are usually highest just after birth. In addition, the higher the concentration in the blood, the more liver damage the person has.
When is the GGT test necessary?
The GGT test helps to detect liver diseases. It also serves to diagnose those pathologies that affect the gallbladder and bile ducts. In fact, it is specifically used if damage is suspected as a result of the consumption of substances or drugs, such as alcohol or certain drugs.
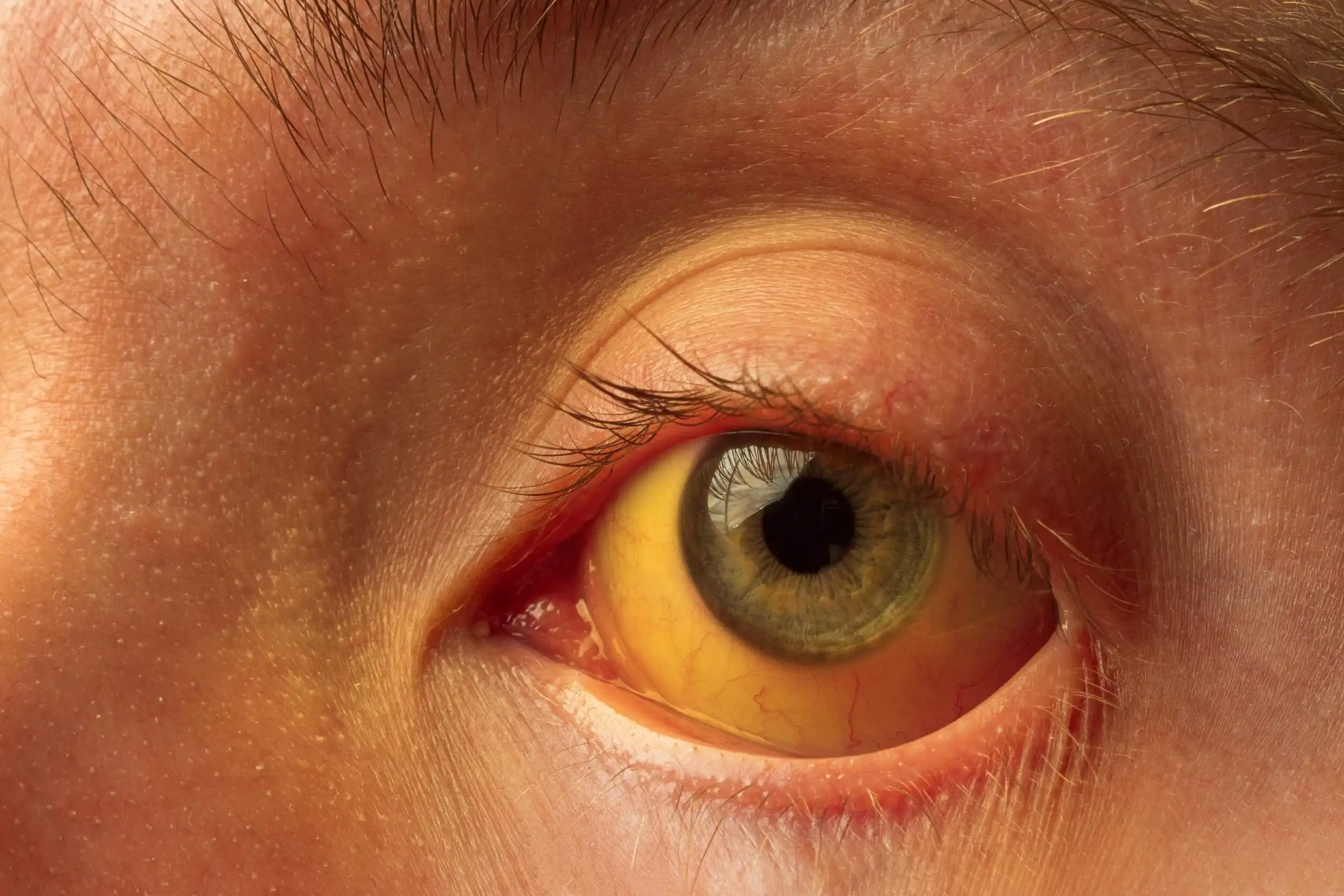
The test itself is indicated when symptoms characteristic of these pathologies appear. To cite an example, jaundice, which is the yellowish pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes. It is produced by the accumulation of bilirubin, which cannot be eliminated by the liver.
Other symptoms that may lead to the performance of this test are the following:
- Dark urine.
- Very light-colored stools (acholia).
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal pain.
Liver or bile duct damage
The GGT test can detect liver or bile duct damage. The reason is that gamma glutamyl transpeptidase levels are the first to increase if a person has an obstruction in this area.
For this reason, it is considered one of the most sensitive tests in relation to bile duct pathologies. It is part of the so-called ‘liver panel‘, which groups together several tests that measure the most important liver enzymes (transaminases).
The most relevant transaminases, in addition to GGT, are alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Also included in this set of tests are alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin. Each of these tends to be more elevated in certain diseases.
However, as with the GGT test, they are all non-specific parameters. Most relevant is that if AST is high, it may be due to a bone or biliary problem. In this case, if the GGT test is normal, the damage to the bone system is localized.
GGT test and chronic alcohol abuse
People who drink alcohol regularly tend to have an altered GGT test. The enzyme increases their blood levels. In fact, they are higher compared to people who drink sporadically but in larger quantities.
Therefore, it is a test that helps to distinguish between chronic and acute alcohol abusers. It is useful if you want to know whether a patient is still drinking or has really stopped.
What does the test consists of?
The GGT test is very simple to perform. According to a publication by San Diego Hospital, no prior preparation is necessary. However, it is advisable to fast for at least 8 hours beforehand.
The physician can give specific instructions for each patient. For example, you may be asked to avoid certain drugs or alcohol before the test. Technicians do the test by obtaining a venous blood sample. Therefore, wearing a short-sleeved shirt makes it easier to draw blood.
The first thing to do is to clean the skin surface with an antiseptic. To make it easier to find the vein, an elastic band is placed as a tourniquet around the arm. This allows the veins to engorge with blood.
They then insert a needle and take a sample from the inside of the elbow. They may also take it from the back of the hand or even the foot and collect the blood in a vial for transport to the lab.
Once they collect the required amount, they remove the elastic band from the arm. Then, they press the puncture site with absorbent cotton and withdraw the needle. They perform the GGT test in the laboratory from the blood they previously obtained.
Obtaining the results and risks
After obtaining the blood, the technician takes it to the laboratory and processes it in a machine. The results are quick, within a few hours. But, if there are alterations, further tests will be necessary.
In general, it is a simple, safe and practical procedure. As with any blood test, some problems may arise. For example, a small hematoma may appear at the puncture site.
It is also possible that patients may become dizzy and faint when drawing the blood. Similarly, there may be pain in the area where doctors inserted the needle. However, these are self-limiting and minor side effects.
What do the results mean?

The enzyme gamma glutamyl transpeptidase usually has very low concentrations in the blood. It is usually between 0 and 30 international units per liter (IU/L). As we have seen, you can get within a few hours.
The test is alterable, as per a Lab Test Online publication -if GGT levels are high- or normal. When the concentration elevates, it points to a liver or bile duct condition.
Moreover, the higher the concentration, the greater the damage. For example, it occurs in diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis. However, this elevation can also be present in other pathologies. Some of them are the following:
- Metabolic syndrome.
- Pancreatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Heart failure.
- Toxic or drug abuse.
On the other hand, a normal GGT test usually almost certainly rules out liver disease. It also helps to know whether someone drank alcohol. The main problem is that you might require more tests because it is non-specific.
You may even choose to repeat the test at another time if the parameters are borderline. The reason is that the elevation of this enzyme may be transient. For example, when drinking alcohol.
What you should remember about the GGT test
The GGT test is a blood test to measure the levels of the enzyme gamma glutamyl transpeptidase in the liver and gallbladder. In blood, physiologically, its levels are usually almost undetectable.
Therefore, when its concentration increases, it indicates that there is damage to these organs. However, it is a very non-specific test. It usually requires other additional tests to find the cause and a diagnosis of certainty.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Análisis de sangre: gamma glutamil transpeptidasa (GGTP) (para Padres) – Nemours KidsHealth. (n.d.). Retrieved June 8, 2021, from https://kidshealth.org/es/parents/test-ggt-esp.html.
- Gamma-glutamil transferasa (GGT): comprenda la prueba y sus resultados. (n.d.). Retrieved June 8, 2021, from https://labtestsonline.org/tests/gamma-glutamyl-transferase-ggt.
-
Hanigan MH. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: redox regulation and drug resistance. Adv Cancer Res. 2014;122:103-41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420117-0.00003-7. PMID: 24974180; PMCID: PMC4388159.
-
Lala V, Zubair M, Minter DA. Liver Function Tests. [Updated 2022 Oct 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482489/
- The GGT test: Normal ranges, uses, results, and what to expect. (n.d.). Retrieved June 8, 2021, from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325199#high-levels.
- Análisis de sangre: gamma glutamil transpeptidasa (GGT). (n.d.). Retrieved June 8, 2021, from https://www.rchsd.org/health-articles/anlisis-de-sangre-gamma-glutamil-transpeptidasa-ggt/.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








