How to Prevent Bacterial Resistance

Bacterial resistance is one of the most disturbing problems in the world today. This is because infections are increasingly becoming resistant to antibiotic treatment at a rather fast pace.
Estimates indicate that this kind of resistance is growing exponentially. This is largely due to the misuse of antibiotics, which people often overuse. We’ve reached a point in which many treatments against bacteria are no longer effective.
This situation is dangerous as we’re increasingly becoming defenseless against various infectious diseases. Furthermore, we require individual, collective, and governmental actions to keep the problem from getting worse.
What’s bacterial resistance?
It’s the mechanism by which bacteria reduce the action of attacking agents. It’s a process of natural selection and genetic adaptation by which these microorganisms overcome certain drugs.
In addition, bacterial resistance occurs when the concentration of an antibacterial is four times lower than the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC). In other words, when the bacterium has a fourfold increase in its ability to overpower its attacker.
Currently, the speed with which new resistant organisms emerge is greater than the speed with which new ones are available. We have, therefore, a deficit that continues to grow and leaves us in a compromising situation in the face of infectious diseases.
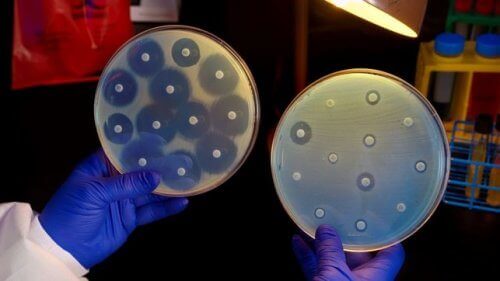
Types and mechanisms of bacterial resistance
There are two types of bacterial resistance. One is natural. Therefore, it’s part of the very nature of bacteria. The other one happens when genetic mutations that repel antibiotic substances take place. Such mutations are passed down to other bacteria, including those of other species.
There are several mechanisms of bacterial resistance:
- The first is the active expulsion of the bacteria, which functions as a kind of ejector pump.
- The second mechanism is the reduction of the permeability of the bacterial wall (the increase of access barriers for the bacterial, for example).
- The third mechanism is the production of enzymes that render the antibiotic inactive. This means they inhibit the normal action of the drug and make it ineffective.
Read more about Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics
Strategies to prevent bacteria resistance
The first strategy to prevent bacteria resistance is to prevent infections. One can achieve this through simple actions such as frequent hand washing, cooking food properly, avoiding contact with infected people, having safe sex, and staying up-to-date on vaccinations.
At this point, it’s important to note the importance of proper hygiene when cooking. The World Health Organization (WHO) points out five keys to do so:
- Keep kitchen spaces and elements clean.
- Separate raw food from cooked food.
- Exercise food safety when cooking.
- Preserve food at the right temperature.
- Use clean water and uncontaminated raw materials.
Likewise, it’s important for people to only take antibiotics when prescribed by a doctor and not to self-medicate. They must also follow professional’s instructions regarding schedules and doses.
It isn’t advisable to interrupt the treatment even if you feel better. There’s a risk that more resistant bacteria may develop if you don’t take the prescribed amount of drugs.

Learn how to identify a Weakened Immune System and the Signs to Look For
Other control measures
Agricultural workers should use antibiotics on animals only under the strict supervision of a veterinarian. This is because the inappropriate use of these drugs in agriculture or animal husbandry is one of the main causes of bacterial resistance. It spreads to the environment and to humans through the food chain.
Health personnel should also take extreme control measures in this regard. Researchers detected that doctors prescribe 50% of antibiotics for viral diseases, despite the fact that they shouldn’t. In fact, they should only prescribe antibiotics if there’s a certainty that these are absolutely necessary.
Government authorities and independent institutions should remain vigilant to an outbreak of infection and determine whether it’s resistant to antibiotics ASAP. It’s also essential for them to inform and educate their citizens on the best way to prevent infectious diseases.
It’s necessary for researchers and the pharmaceutical industry to join forces in order to intensify studies on this subject. The whole world should support research on this since much of our well-being and future depend on it.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Alós JI. Resistencia bacteriana a los antibióticos: una crisis global [Antibiotic resistance: A global crisis]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2015 Dec;33(10):692-9.
- Wencewicz TA. Crossroads of Antibiotic Resistance and Biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 2019 Aug 23;431(18):3370-3399.
- Davies J, Davies D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010 Sep;74(3):417-33.
- Huemer M, Mairpady Shambat S, Brugger SD, Zinkernagel AS. Antibiotic resistance and persistence-Implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO Rep. 2020 Dec 3;21(12):e51034.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








