Dark or Cloudy Urine: 11 Possible Causes and Their Treatment

Urine is a liquid produced by the filtration of blood at the level of the kidneys. Variations in its characteristics, such as color, odor, or quantity, may indicate the presence of a disease. In this sense, it’s important to be attentive to such changes, especially if the urine becomes dark or cloudy.
The normal color of urine can vary between a light yellow and a transparent tone like water. This shade is due to the presence of a pigment called urochrome and its concentration.
Urine can become dark due to multiple factors, with dehydration and food consumed being the most frequent causes. However, certain more delicate conditions can also generate such changes.
1. Dark urine due to dehydration
Dehydration is one of the main causes of dark or cloudy urine. This is an organic alteration that appears when the body loses more water than it takes in.
If there’s a state of dehydration, the kidneys will absorb a greater amount of water to ensure that the body functions properly. This will cause the urine produced to be more concentrated and therefore a bit more cloudy.
Children and older adults are more likely to suffer from dehydration due to the distribution of water in their bodies. In addition to dark urine, severe dehydration causes other symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Dry eyes
- Dry mouth
- Confusion and dizziness
- A feeling of intense thirst
- Poor urine output
Treatment
Fortunately, treatment for dehydration is very simple and consists of increasing your water intake. The consumption of fruits such as watermelon can also help to recover the levels of the vital liquid.
There are severe cases of dehydration in which people are not able to tolerate oral fluid intake. In these cases, hospitalization is necessary and intravenous hydration should be started until the general condition improves.
We think you may also enjoy reading this article: 7 Ways to Reduce Protein in Urine Naturally
2. Diet
Another common cause of dark or cloudy urine is the intake of certain foods. Beets, carrots, berries, and beans contain pigments that alter the color of urine without any underlying condition.
High intakes of vitamin D and phosphorus also alter the color of urine, causing it to become slightly more cloudy. This is because the kidneys filter the excess of these micronutrients.
Treatment
In these cases, the alteration in the color of the urine is transitory, so it’s only necessary to wait a couple of hours for it to recover its usual tone. The best way to avoid the darkening of the urine in these cases is not to ingest the foods mentioned and to reduce your consumption of meats and dairy products due to their high phosphorus content.

3. Holding the urge to urinate
Holding the urge to urinate can be another cause of dark urine. This is because the substances eliminated through urine accumulate in the bladder, altering the color of the liquid.
As if that were not enough, this is one of the predisposing factors for urinary tract disorders such as infections, incontinence, and kidney stones. In this sense, it’s a bad habit that should be eliminated.
Treatment
As with diet, there’s no specific treatment. It’s best to urinate whenever you feel like it, even if your bladder is not completely full.
4. Urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections occur when pathogenic microorganisms inhabit and proliferate in the urinary tract. In fact, a study published in The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. states that they are the most frequent ambulatory infections, although their diagnosis is complicated.
One of the main clinical manifestations of urinary tract infections is the presence of dark, fetid urine. This may be due to blood, pus, or white blood cells that become present.
Other common symptoms of this condition include the following:
- Frothy urine
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain or burning with urination
- A fever in severe cases
- Frequent need to go to the bathroom
- Pain in the pelvis, lower abdomen, or lower back
Treatment
Individuals with symptoms of a urinary tract infection should see a specialist as soon as possible for diagnosis. Multiple tests and even a urine culture may be ordered to determine the causative agent.
Most urinary tract infections respond well to oral antibiotic treatment. However, there are severe cases in which intravenous medications will be necessary prior to initiating oral therapy.
5. Blood in the urine
The presence of blood in the urine may cause a reddish or brownish hue in the urine. The intensity of the coloration will depend on the amount of blood present in the fluid.
The causes of blood in the urine can be very varied, from urinary tract infections or kidney stones to some types of cancer and the use of medications such as warfarin. It can also be present during menstruation, due to the mixing of vaginal blood with urine.
Treatment
This is a rather delicate condition that warrants immediate consultation with a physician. The treatment will depend on the cause that is originating the alteration. Therefore, the professional will perform multiple tests and look for other additional symptoms.
Infections are usually treated with antibiotics, depending on the causative agent. On the other hand, kidney stones and cancer will require a more complex treatment.
6. Kidney stones: another cause of dark urine
Kidney stones, also known as bladder stones, are a common condition that affects 8 out of every 1,000 adults, according to some statistics. The stones develop from the accumulation of multiple minerals in the kidneys.
Urine can become dark or cloudy because the stones move, generating internal bleeding lesions. In addition, they predispose a person to other infections, so it’s possible to find pus in the urine.
Clinical manifestations can be very evident in severe cases and are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the lower back radiating to the groin, abdomen, or genitals
- Fever and chills
- Pain when urinating
- Foul-smelling urine
- Nausea
Treatment
Small stones usually pass on their own without any major inconvenience. The use of analgesics will decrease pain and reduce discomfort. On the other hand, your doctor can use other techniques when the stones are a considerable size.
One of the most used treatments is shock wave therapy in order to reduce the size of the stone and promote its exit. In case this doesn’t work, surgical extraction will be necessary.
Like this article? You may also like to read: 8 Types of Urine That May Say Something Important About Your Health
7. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Some sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can also cause dark or cloudy urine as part of their symptoms. The color change is due to the increased production of white blood cells, which can be found in the fluid and alter its composition.
One of the main symptoms of sexually transmitted infections is an unusual discharge from the penis or vagina. The discharge may be white or clear, depending on the case.
Other clinical manifestations of these infections are as follows:
- A burning sensation with urination
- Unexplained pain in the genitals
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Skin rashes in the intimate area
- Itching and stinging in the genitals and pelvis
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the pelvis
Treatment
Both chlamydia and gonorrhea respond very well to antibiotic treatment. However, the drugs used will depend on the underlying disease.
8. Kidney diseases
Many of the conditions that affect the kidneys are capable of generating dark urine. This is because, as they are responsible for producing this waste liquid, an alteration in their functioning will have repercussions on excretion.
Glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, and diabetic nephropathy are some of the kidney diseases that can generate this symptom. The clinical manifestations that accompany these pathologies can be very varied, however, within the common symptoms the following stand out:
- Intense thirst
- Weight loss
- Discomfort when urinating
- Frequent infections
- Foul-smelling or foamy urine
- Lower back pain
- Decreased urine production
Treatment
If you suspect a kidney condition, it’s essential to go to a doctor immediately.
Only a specialist will be able to diagnose the condition that causes the alteration and initiate the appropriate treatment. Otherwise, it’s possible that renal function may worsen until irreversible damage.
The drugs used will depend on the condition. However, the main pharmaceutical options include antibiotics, diuretics, and cortiocoids. It will also be necessary to control a systemic disease such as diabetes or lupus, if present.
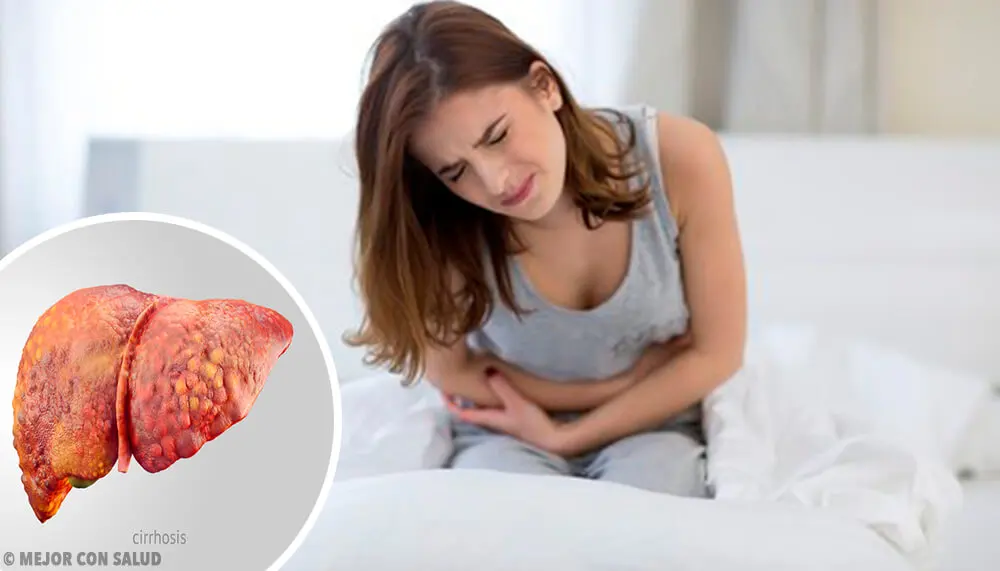
9. Liver problems
Another possible cause of dark or cloudy urine is liver and biliary problems. Some diseases, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis, can compromise the function of the organ, causing it to not properly metabolize bilirubin.
In this sense, bilirubin will leak through the kidneys, giving a dark or black color to the urine. The symptoms of liver disease are very varied, however, some of them are the following:
- White stool
- Fever in acute infections
- The presence of fat in the stool
- Abdominal distention and discomfort
- Jaundice or yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes
- Pain in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Weight loss if it’s a chronic disease
Treatment
As with kidney problems, the treatment will depend on the condition suffered. In this sense, it’s essential to consult with a medical specialist in case you have any of the symptoms we just described.
10. Vulvovaginitis
Vulvovaginitis is one of the most common gynecological problems, according to some research, and may be the cause of dark urine. It’s inflammation of the vulva or vagina due to a bacterial infection, although viruses and fungi are also sometimes causative agents.
As with many other infections, dark urine may be due to the presence of white blood cells to fight infection. Some of the symptoms are as follows:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Itching around the vulva
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Pain when urinating
Treatment
Treatment of vulvovaginitis will depend on whether it is a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection. In this sense, it’s possible to use antibiotics, antifungal, or antiviral drugs in each case.
The condition may also be due to exposure to irritating substances, such as soaps or softeners. Given the latter, it’s best to avoid contact with the triggering agents.
11. Prostatitis
Prostatitis is nothing more than inflammation of the prostate and the last of our causes of dark urine. It’s usually due to an infection, which can lead to bleeding that darkens the color of the urine.
Clinical manifestations include the following:
- Burning during urination
- Abdominal pain
- Pain when ejaculating
- A frequent need to urinate
- Discomfort in the lower pelvis
Treatment for dark urine
Most cases of prostatitis tend to improve without treatment. However, the use of antibiotics may be necessary for infections, as well as the intake of anti-inflammatory drugs in chronic forms.
Like this article? You may also like to read: Urine Culture: What Is it and What’s it Used For?
Dark urine: A symptom that should not go unnoticed
There are multiple causes that generate the appearance of dark urine. The most common ones are benign and disappear on their own. However, there are serious conditions behind the symptom, so it’s always recommended to consult a specialist.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bolenz, C., Schröppel, B., Eisenhardt, A., Schmitz-Dräger, B. J., & Grimm, M. O. (2018). The investigation of hematuria. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 115(48), 801. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6365675/
- Chu, C. M., & Lowder, J. L. (2018). Diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections across age groups. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 219(1), 40-51. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002937817328053
- Fontenelle, L. F., & Sarti, T. D. (2019). Kidney stones: treatment and prevention. American Family Physician, 99(8), 490-496. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0415/p490.html
- Khan, F. U., Ihsan, A. U., Khan, H. U., Jana, R., Wazir, J., Khongorzul, P., … & Zhou, X. (2017). Comprehensive overview of prostatitis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 94, 1064-1076. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332217319418
- Kitching, A. R., & Hutton, H. L. (2016). The players: cells involved in glomerular disease. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 11(9), 1664-1674. https://journals.lww.com/CJASN/fulltext/2016/09000/The_Players__Cells_Involved_in_Glomerular_Disease.20.aspx
- Miller, H. J. (2015). Dehydration in the older adult. Journal of Gerontological Nursing, 41(9), 8-13. https://journals.healio.com/doi/abs/10.3928/00989134-20150814-02
- Powell, A. M., & Nyirjesy, P. (2014). Recurrent vulvovaginitis. Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 28(7), 967-976. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1521693414001308
- Steinberg, P. L., & Chang, S. L. (2016). Pain relief for acute urolithiasis: The case for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs, 76, 993-997. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40265-016-0595-y
- Tobón, A. (2009). Signos de peligro en el paciente con malaria. Biomédica, 29(2), 320-329. http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0120-41572009000200016
- Wijma, R. A., Huttner, A., Koch, B. C., Mouton, J. W., & Muller, A. E. (2018). Review of the pharmacokinetic properties of nitrofurantoin and nitroxoline. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 73(11), 2916-2926. https://academic.oup.com/jac/article-abstract/73/11/2916/5058069
- Workowski, K. A. (2015). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 61(8), 759-762. https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/61/suppl_8/S759/345211
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








