Body Pump: The Benefits and What the Classes Are Like


Reviewed and approved by the doctor Leonardo Biolatto
Body pump is a training modality created in 1991 by Les Mills International. It consists of physical exercise programs that are performed in a group and with one-hour sessions. Its main distinctive feature is that it combines the style of aerobics with traditional weight lifting.
Despite its age, the body pump has become popular during the last decade among fitness fanatics because of its health benefits, the dynamic classes, the possibility of training in the company, and the grouping of two practices much admired by all lovers of comprehensive exercises.
In fact, unlike most programs, body pump combines aerobic and anaerobic styles in a single session. Today, we’re going to show you how a typical class is carried out and what benefits it brings if you implement it in programs of several weeks.
What is a body pump class like?
As happens in the case of pilates, yoga, spinning, and other classes that take place in the gym, body pump programs are developed with the help of a qualified trainer. It’s the trainer who decides, in principle, the nature of the session, what type of exercises are included, and their degree of difficulty.
However, a classic body pump session lasts 60 minutes and starts with 10 strategically chosen songs. These are the ones that set the rhythm of the movements and are based on motivational tracks.
These can be rock or mixed with electronic music and their duration is usually between 5 and 6 minutes. An aerobic bench is used along with bars, discs, and dumbbells to execute the movements, with a weight decided by each participant according to their level.
The development of the class consists of the following:
- Warm-up: The first track is used to warm up and stretch all the muscle groups involved. It’s performed with the lightest load of the entire session and with a medium-high intensity.
- Muscle work: After stretching, the actual class begins, in which one muscle group is worked for each of the 8 music tracks. The order of classic style consists of exercises for the quadriceps, chest, back, triceps, biceps, lunges, shoulders, and abdominals. This order may vary depending on the trainer.
- Closing with stretching: The last musical track is intended to close the session by stretching the muscles again.
The weight used is graduated in each exercise according to the strength of that muscle group. It’s very common that when working the last exercise, the abdominals, no weight is used and instead classic planks or crunches are done.
Although the 60-minute version is the most widespread, there are also 30 and 45-minute classes. The change from one exercise to another is done with an interval of a few seconds, in order to maximize aerobic power.
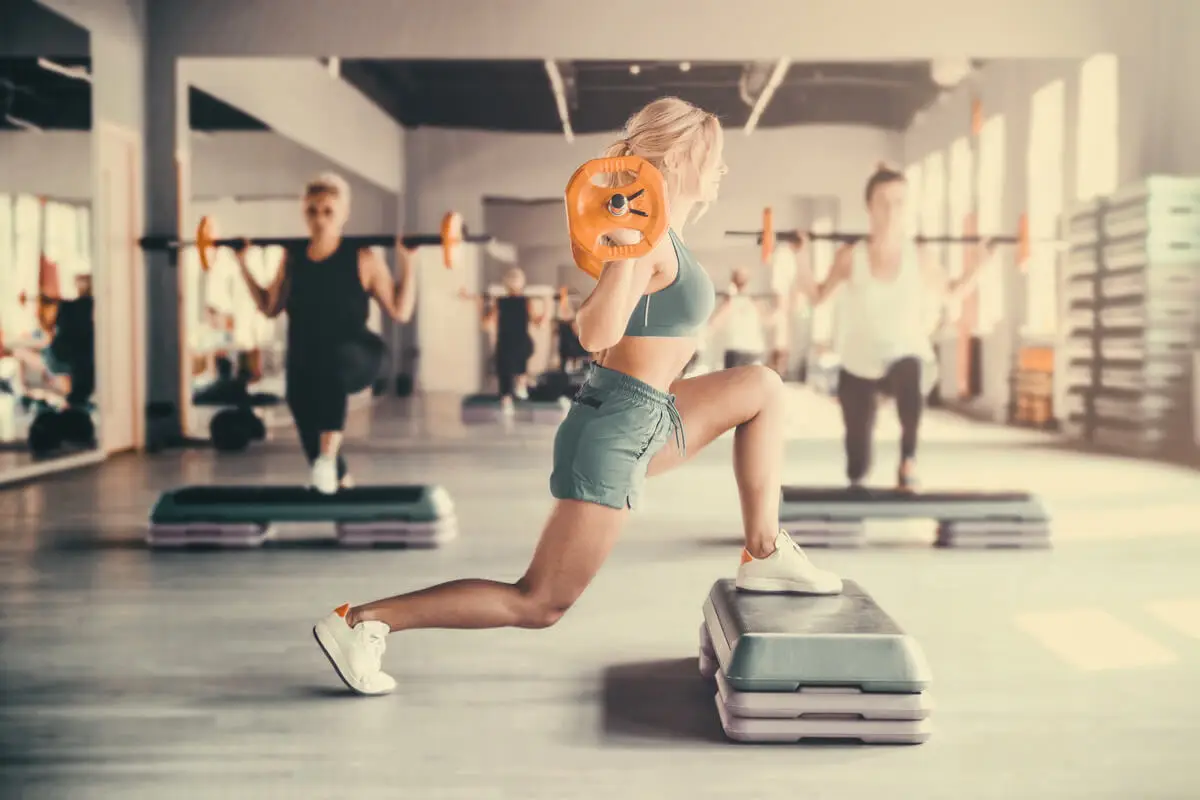
We think you may also enjoy reading this article: Don’t Have Time to Go to the Gym? You Can Exercise at Home
Who can practice body pump?
You may wonder if you qualify for a body pump class, especially if you’re not a fan of lifting weights. Although you’ll be carrying barbells and dumbbells throughout the session, you don’t actually need to be a weightlifting expert to participate.
There’s no minimum weight for body pump, so you can adjust it according to your strength. In this sense, it’s a program that anyone can do, from those who are always dabbling in new fitness methodologies to those who are just joining the gym.
Of course, there are certain conditions when practicing the discipline. The first is pregnant women. Although its use is indeed still recommended by Les Mills International during the first months of pregnancy, you should consult a specialist if sessions will be performed after five months of gestation.
In case you suffer from a heart condition, you should also have the endorsement of a doctor for safety. If you’re not a person who’s used to practicing physical activity, it’s advisable to have a general examination of your state of health. A stress test, for example, is very useful to know your limits.
Apart from this, and considering that for 60 minutes you will experience an intensive routine, it’s ideal that you are familiar with the basic exercises that are developed for the muscle groups outlined. This way, you can avoid injuries and execute the movements more efficiently.
What are the health benefits of body pump?
The benefits of body pump vary according to the frequency with which you practice it. Most gyms run their classes 2 or 3 times a week and spread out over 12 weeks. After this time, they usually take a short break before starting up again.
If you decide to sign up for a full program, and not just an occasional routine, you receive the following benefits.
1. It improves your endurance
A study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research in 2011 assessed muscular and metabolic fitness after a 12-week body pump program. The results showed an improvement in the endurance of the participants, who consisted of a group of 19 women with no previous training.
By incorporating total-body exercises, the benefits are felt in the upper and lower body. The intensive workout that is based on choreographed movements and a short rest between each execution is of great help to improve your muscular endurance no matter what fitness level you are at.
2. It’s useful to burn calories and lose weight
Although research published in The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness in 2015 stipulates that the average calories burned per session when practicing body pump are 250 at a moderate intensity, but if you develop a personalized routine and raise the intensity, you can burn up to 600 calories.
It all depends, in this sense, on the intensity with which it’s performed, as is the case of other types of exercises aimed at losing weight. In any case, it’s also useful for weight maintenance, an objective that can be achieved by incorporating a healthy, balanced diet at the same time.
3. You gain muscle strength
Although this type of activity is not the best to obtain the levels of hypertrophy that are achieved through conventional weight lifting, we know from several studies that it’s of great help to improve the strength of the muscle groups involved.
As the days progress, participants can perform the exercises with more weight, so that at the end of 12 weeks, their strength will present a significant increase.
Like this article? You may also like to read: Discover the Importance of Keeping a Day Off Your Exercise Routine
4. It can help reduce your stress and anxiety levels
Any physical activity that is developed with some continuity is beneficial for mental health. It’s widely documented that the relationship between exercise with decreased levels of depression and anxiety, regardless of whether these are aerobic or anaerobic in nature.
The best thing is that the results are manifested in all age groups and gender and doesn’t take long before perceiving its first effects. In part, this is achieved thanks to the segregation of hormones.
It’s not the best aerobic exercise that exists
At this point we must warn you something: despite the integrated choreography during the sessions and the intensity of most classes, body pump is not the best aerobic exercise out there. This has been demonstrated by various studies and research that have measured aerobic power during the development of a session.
This is important to keep in mind in case you’re looking for a 100% aerobic activity or want to replace one that you already do for this. Ideally, if this is your situation, it’s best that you complement it with others, such as cycling or running.
Tips to practice body pump
Finally, we can’t end this article without first pointing out some tips to do body pump. While if you sign up for a class you will always have a teacher as a guide, it’s advisable that you keep in mind the following principles.
1. Take care of your posture
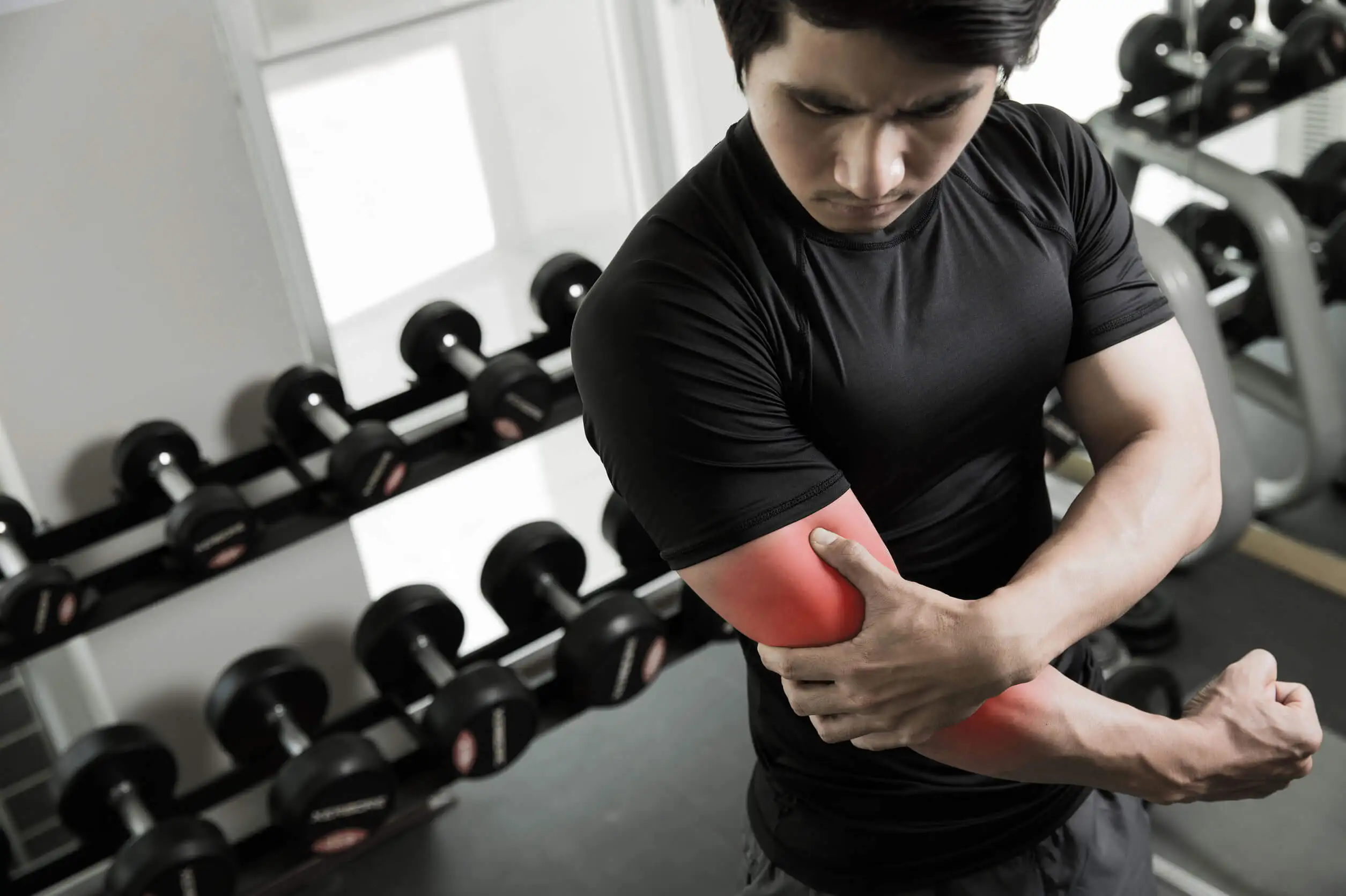
A tip that applies to all types of physical activity. Considering that for 60 minutes you will be continuously handling extra weight, you should take care of your posture to avoid muscle injuries. Those that focus on the back area are the most common, although you can also injure your knees and other joints.
If you’re a beginner, the chances of injury are greater, so let your trainer know so that he or she can guide you with the proper posture for each exercise. Don’t overlap your fingertips with your knees when doing a squat, for example; this is a basic consideration to always keep in mind.
2. Don’t lift more weight than you can handle
Naturally, your class won’t just include beginners. There are bound to be several classmates with a higher level of strength, endurance, and muscular power.
At no time should you try to imitate the weight load that they control, as the outcome will be harmful.
Remember that at least 9 of the 10 exercises in the class are done with weights, so you must manage your strength to be able to complete it to the end. For this reason, only lift what you are comfortable with, even if it’s below average.

3. Wear appropriate sports clothing
So that you can perform your movements freely, you should go to class with the right clothes; the key is to wear clothing that doesn’t fit too loosely or too tight to the body. This is the escape case with t-shirts and shorts, as it’s recommended that your underwear fits a little tight.
Also, make sure to wear appropriate shoes for the occasion; those that provide you with enough friction with the ground are best. They should be sporty, light, and comfortable. You can also wear sweatbands for your head and wrists so you prevent perspiration from reaching the bar and prevent proper support.
Enjoy the session
Many times we sign up for a sport or exercise forgetting to enjoy the process. You should never see physical activity as an obligation or as something you have to do. On the contrary, the key is that you enjoy it so that you include it in your routine as one of the things you look forward to doing with pleasure.
Only then will you face each class with the motivation and attitude that these classes demand. Body pump is not for everyone, nor are all the disciplines and sports that exist. Sign up for a class and, if you enjoy it, don’t hesitate to complete the program!
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Greco, C. C., Oliveira, A. S., Pereira, M. P., Figueira, T. R., Ruas, V. D., Gonçalves, M., & Denadai, B. S. Improvements in metabolic and neuromuscular fitness after 12-week Bodypump® training. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research. 2011; 25(12): 3422-3431.
- Oliveira, A. S., Greco, C. C., Pereira, M. P., Figueira, T. R., de Araújo Ruas, V. D., Gonçalves, M., & Se, B. Physiological and neuromuscular profile during a Bodypump session: Acute responses during a high-resistance training session. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research. 2009; 23(2): 579-586.
- Olmedo, M. C., Franco-García, J. M., García-Paniagua, R., Calzada-Rodríguez, J. I., & Pérez-Gómez, J. Efectos agudos y crónicos de la práctica de Bodypump. Journal of Negative and No Positive Results. 2021; 6(2): 258-270.
- Rustaden, A. M., Haakstad, L. A., Paulsen, G., & Bø, K. (2017). Effects of BodyPump and resistance training with and without a personal trainer on muscle strength and body composition in overweight and obese women—A randomised controlled trial. Obesity research & clinical practice. 2017; 11(6): 728-739.
- Stanforth, D., Stanforth, P. R., & HOEMEKE, M. E. Physiologic and metabolic responses to a body pump workout. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research. 2000; 14(2): 144-150.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








