What Is an Intraoral Scanner and What Are its Benefits?

Written and verified by the dentist Vanesa Evangelina Buffa
Technological advances have reached dental offices to optimize patient care and provide more comfortable experiences. The intraoral scanner is an instrument that is part of the state-of-the-art equipment in modern clinics, and in this article, we’re going to tell you what it’s all about.
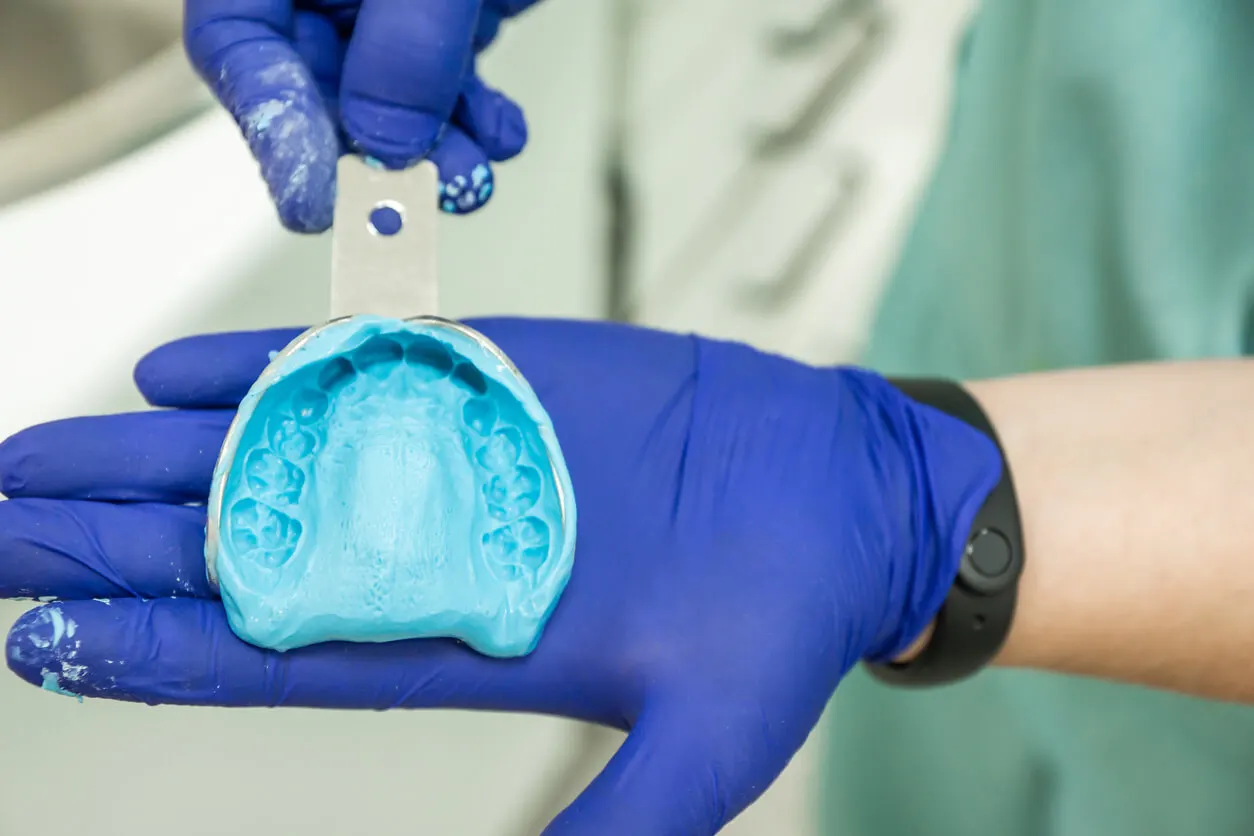
Until a few years ago, when it came to representing and studying the internal morphology of the mouth to make prostheses or appliances, it was necessary to take dental impressions. For this purpose, trays filled with alginate or silicone were used and taken into the patient’s mouth.
This technique required more time for the dentist and caused discomfort for the patient, such as nausea or a bad taste in the mouth. The results obtained could cause errors due to the instability of the material.
Today, thanks to the intraoral scanner, it’s possible to speed up the diagnosis and plan more precise treatments. This tool avoids traditional impressions, with pastes and trays in the mouth, obtaining 3D models and images.
Digitization in dentistry has many advantages, both for the patient and for the professional. In this article, we’re going to tell you everything you need to know about the intraoral scanner and its benefits.
What is an intraoral scanner?
A 3D intraoral scanner is a device used in dental offices to take digital impressions in three dimensions of people’s mouths. It is a computerized system that allows for recording the oral topography in detail.
The equipment consists, roughly speaking, of a pen with a built-in camera, connected to a monitor that recreates the patient’s mouth. The pen is introduced into the oral cavity to record the topography of its interior and pass this information to the screen through special software.
The intraoral scanner is capable of recording the size and detailed shape of each dental element, the interdental separation, the appearance of the surface of the palate, the gums, the implants, the prostheses, and the other elements that make up the interior of the oral cavity.
This information is processed through computer programs that perform the 3D reconstruction of the patient’s mouth.
As these are high-precision images, human error that can occur in traditional impression-taking is almost completely eliminated. Treatment planning is possible based on these detailed maps of the mouth.
In addition, the technology allows the dentist to share the information with the prosthetic laboratory in a matter of seconds. This speeds up waiting times for prosthetic or orthodontic rehabilitation treatments, since no model has to be sent physically.
Do you find this article interesting? Discover more: 7 Consequences of Poor Dental Hygiene for Your Health
Replacing traditional impressions
As mentioned above, the conventional technique for taking impressions of the mouth requires the use of a plastic or metal tray that is filled with a soft material, such as alginate or silicone. This is introduced inside the mouth and the contents are left to set or harden to obtain the negative model of the oral cavity.
Once the tray is removed from the patient’s mouth, the impression is filled with another material, such as plaster, to obtain a duplicate of the patient’s mouth. Dental laboratories use these rigid models to design and fabricate prostheses or orthodontic appliances.
This technique can be uncomfortable for the patient and requires several time-consuming steps. In addition, the models obtained are not as accurate and can lead to some errors in the design of the appliances or prostheses that are made on them.
For this reason, the use of intraoral scanners is currently gaining more and more popularity. These technological devices are more comfortable, easier to use, faster, and provide much more accurate and reliable results.
How is an intraoral scanner used?
An intraoral scanner has a pencil-shaped head with a built-in camera that’s responsible for taking images of the inside of the mouth. At the same time, this instrument is connected to a monitor that receives and processes all the information into 3D images.
To use the intraoral scanner, the dentist places the camera inside the patient’s oral cavity and moves it slowly over the teeth and gums. In this way, the necessary information is recorded so that the computer can reproduce in detail, simultaneously and in three dimensions, the characteristics of the inside of the mouth.
Once the dentist has finished passing the scanner over all the faces of the patient’s teeth, the software recreates the entire mouth with its artificial intelligence. The new information will provide accurate data on the oral condition that will allow a precise diagnosis to be made and treatment to be planned with greater certainty.
In addition, at the time of the intraoral scan, the data corresponding to the patient’s history is entered into the system. In this way, all the information on the current situation of the mouth is saved for future consultations or to compare with previous records and evaluate the evolution of the treatments.
When is a 3D intraoral scanner used?
There are several therapies that require the recording of the inside of the oral cavity. These are the most common ones:
- Guided surgeries
- Elaboration of retainers and splints
- Making customized prostheses and crowns
- In cosmetic dentistry for smile designing
- Customized orthodontic appliances
- In invisible orthodontics, to make aligners
- To study clinical cases, make diagnoses, and plan orthodontic, prosthetic, and implant treatments
The benefits of using an intraoral scanner in dental practices
We’ve already mentioned several of the advantages of the intraoral scanner in dental practices. The first and most obvious is the replacement of traditional impression methods, without the need to use trays, alginate, and plaster.
Thus, when it comes to recording the inside of the mouth, the process can be done cleanly, quickly, and comfortably. Nausea, a bad taste, and delays with the mouth open until the impression material hardens are also avoided.
Speed is another benefit of using the intraoral scanner. However, this is not only when it comes to recording the inside of the mouth and obtaining an instant image. It’s also possible to send the information to the dental laboratory immediately. Delivery times of prostheses and appliances are minimized.
Another advantage of this technology is that it allows the professionals and patients to visualize the evolution and changes that occur during the approaches. It’s also possible for people to observe their cavities, tartar, fractured teeth, or malpositions in their mouths.
Visualizing the shape of the mouth and its problems helps the patient to better understand the conditions they are suffering from and the treatments being performed. In this way, there is greater commitment and collaboration with the therapies and with the care of their oral health.
The accuracy and fidelity of the images obtained with intraoral scanning are another point in favor of this technology. This method reduces the errors that sometimes occur with conventional impressions.
If for some reason the result is distorted, the area can be rescanned in a matter of seconds and rectified immediately. By obtaining such accurate images, treatments are more successful.
The images are saved as files that can be consulted at any time. Having this type of valuable information in a format that does not take up physical space saves a lot of storage space in dental clinics.
We think you may also like to read this article: Dental Bridge: Types, Benefits, and Disadvantages
The expected results
In short, using an intraoral scanner makes it possible to obtain valuable and accurate information from inside the mouth, simply, comfortably, and quickly. The use of this technology favors diagnosis, allows for better treatment planning, and enhances the results.
If your dental clinic has this type of state-of-the-art equipment, you should know that you will benefit from it. If they have to take measurements of your mouth, they’ll do it in a comfortable and fast way for you.
The results of the treatment depend to a great extent on the previous meticulous study. Having accurate images of your oral cavity will allow the professionals to do a better job. It also helps you to get that beautiful and healthy smile you’re looking for.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bernal González, C. APLICACIONES DEL ESCÁNER INTRAORAL EN LAS DISTINTAS RAMAS DE LA ODONTOLOGÍA CONTEMPORÁNEA.
- Pradillo, R. V., González, I. C., Dávila, M. M., Pérez, J. A., Godín, B. A., Mansour, N. M., & Cascón, W. P. (2021). Factores que afectan a la precisión de los sistemas de escaneado intraoral: revisión sistemática. Maxillaris: Actualidad profesional e industrial del sector dental, 23(253), 12-26.
- Chávez, G. L., Medina, L. L. B., Martínez, P. O. C., Vásquez, B. E. M. G., & Ho, J. K. Uso del escáner intra-oral para la colocación de implantes dentales guiados por computadora. Craneoplastía con implante de titanio individualizado mediante tecnología CAD/CAM 4.
- Bascón Mallado, M. (2018). Precisión de los escáneres intraorales en las rehabilitaciones orales completas sobre implantes.
- Vélez Jaramillo, A. S., Martínez Saravia, J. A., & Villarraga Rodríguez, A. M. Exactitud de escáneres intraorales en prostodoncia. Una revisión de la literatura.
- Zuluaga Martinez, M. I., Osorio Correa, L. A., Duque Vélez, M., Naranjo Pizano, R. M., Muñoz Zapata, S., Uribe Trespalacios, P., & Manrique Hernandez, R. D. (2021). Precisión dimensional del escaner intraoral y extraoral con diferentes materiales de impresión: estudio in vitro.
- Rodríguez, C. M. (2021). Impacto de condiciones intra y extraorales en la eficacia y eficiencia de dos sistemas de escaneado intraoral (Doctoral dissertation, Universidad Complutense de Madrid).
- Morales-Núñez, M. D., Moreano-Moreano, R. O., & Salame-Ortiz, V. A. Escáneres intraorales vs impresiones convencionales para diagnóstico y tratamiento odontológico Intraoral scans vs. conventional impressions for dental diagnosis and treatment.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








