The Treatment for Systematic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
The treatment for Systematic Lupus Erythematosus is symptomatic. Because of this, there is no definitive etiological treatment that can cure this illness. However, there are numerous treatments that focus on relieving the symptoms.
No matter what, doctors must adapt treatment to each patient’s specific situation. In addition, the patient must consent to it while keeping in mind all of the benefits and risks.
Today, we’ll take a look at this process.
Read also: What is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus?
Treatment of Lupus
First of all, let’s take a look at the most common treatment for Systematic Lupus Erythematosus:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Glucocorticoids
- Antimalarials
- Immunosuppressants
- Biological therapies
NSAIDs
NSAIDs, like ibuprofen or paracetamol, are the drugs of choice for the symptomatic treatment of the musculoskeletal manifestations. They’re usually recommended for limited periods of time to lower the chances of risk when taking them.
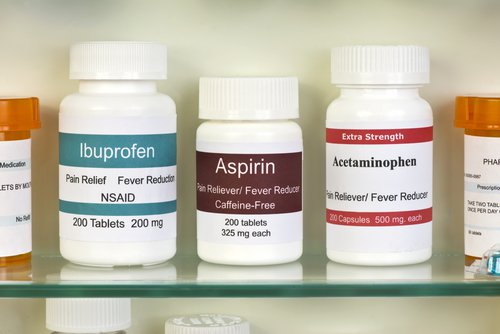
When these medications are prescribed, you must keep in mind the negative side effects they may have on your digestion, renal, and cardiovascular systems. You should avoid using them if you have or develop a renal affectation.
Glucocorticoids
This group of medications has been the basis of treatment for SLE due to its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant abilities. Thus, it continues to be the most important and most effective treatment when it comes to the acute phases of this illness.
Unfortunately, you cannot take these drugs for an extended period of time. This is because they can become toxic and can cause an adverse effect, including other conditions:
- Osteoporosis
- Cushing Syndrome
- Mellitus Diabetes
- An increase in the risk of infections
- Glaucoma
For these cases, doctors recommend taking a dosage of less than or equal to 5 mg/day of prednisone (or an equivalent) and to stop the treatment as soon as possible.
Despite its high level of toxicity, practically all of the complications that come by this illness can be treated successfully with corticoids.
Read also: 7 Remedies for Controlling Lupus
Antimalarials
Chloroquine stands out among this group, especially hydroxy-chloroquine. Overall, they’re the medications of choice for the majority of patients with SLE. In addition, they’re the only drugs specifically indicated for SLE (until the approval of belimumab, which we’ll talk about later).
These medications are mainly helpful to fight:
- Arthritis
- Fatigue
- Some skin injuries
- Pericarditis
- General symptoms
Patients often tolerate antimalarials well, and their main drawback is the possibility of toxicity in the retina. Because of this, doctors recommend that patients get periodic ophthalmologist exams.
In addition, doctors can even prescribe these drugs during the gestation period because they help to regulate cholesterol levels. Plus, they have a beneficial anti-aggregative action for these patients.
Immunosuppressants
Lupus treatment with immunosuppressants is reserved for patients who do not respond correctly to the antimalarial and glucocorticoid treatments.
Overall, the most commonly used immunosuppressants to fight this illness are:
- Cyclophosphamide
- Mycophenolate mofetil
- Azathioprine
- Methotrexate
Biological Therapy
This type of therapy is fairly new, so many clinical trials are still studying it. This therapy uses biological medication or monoclonal antibodies. The most common types are Belimumab and Rituximab.
If the symptoms have not improved after 6 months for patients using this therapy, they should think about discontinuing this treatment. Both of these medications are currently being tested.
To learn more about this illness, check out our article dedicated to it:
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Finzel, S., Schaffer, S., Rizzi, M., & Voll, R. E. (2018). Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Zeitschrift Fur Rheumatologie. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-018-0541-3
- Kuhn, A., Bonsmann, G., Anders, H. J., Herzer, P., Tenbrock, K., & Schneider, M. (2015). The Diagnosis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Deutsches Arzteblatt International. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2015.0423
- Castrejon, I., Nika, A., Sequeira, W., & Jolly, M. (2017). Systemic lupus erythematosus. In Comorbidity in Rheumatic Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59963-2_6
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








