What is the Hormone Oxytocin?

Written and verified by the doctor José Gerardo Rosciano Paganelli
What is the hormone oxytocin?
Oxytocin is known for inducing labor and intervening in breastfeeding. Overall, it’s made up of 9 amino acids, including cysteine, tyrosine, isoleucine, glycine, proline, and asparagine. It’s located in the posterior pituitary gland and is highly involved in various physiological processes.
Its chemical composition is similar to its counterpart hormone, vasopressin, which is located in the anterior pituitary gland and has several functions.
As with any organic substance, oxytocin has various receptors which are mainly found in the:
- Uterus,
- Kidney,
- Bones,
- Heart,
- Brain,
- Ovarian tissue,
- Mammary gland.
Particularly, oxytocin has functional characteristics that make it the hormone of pregnancy because of its behaviors in several processes at a physiological level.
What Does Oxytocin Regulate?
Reproduction
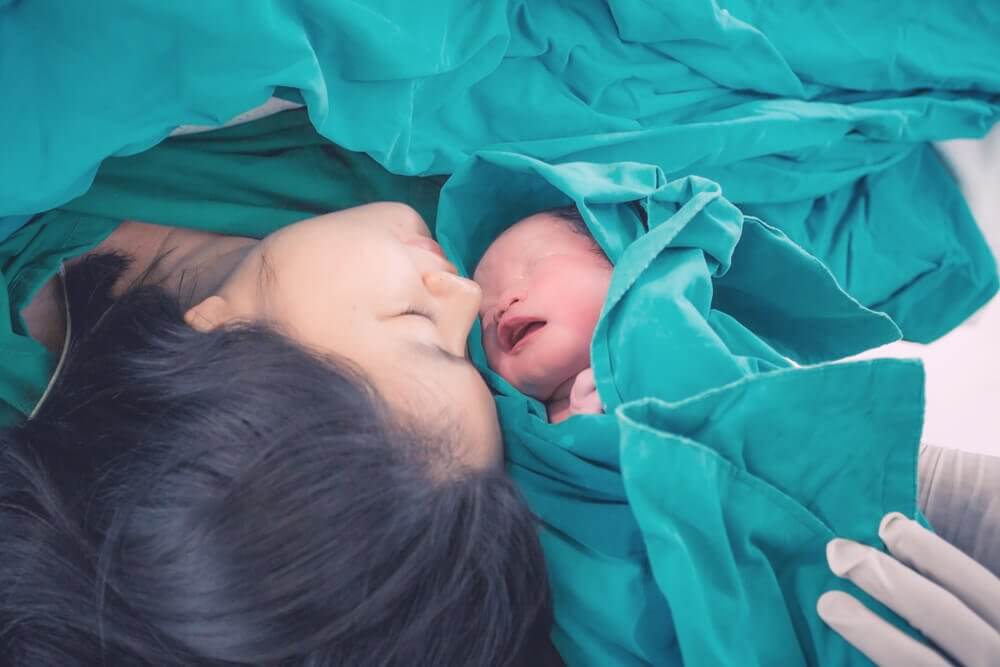

First of all, this hormone has an excellent function in the female reproductive system. For one, it actually induces and increases the speed of labor.
Normally, the body releases high amounts of oxytocin as the labor progresses. Plus, its levels are even higher when there is nipple stimulation in the woman in labor. High oxytocin levels generate contractions of the myometrium, facilitating the physiological extraction of the fetus.
On the other hand, this hormone acts directly on the erectile tissue in both the corpus cavernosum and the corpus spongiosum in the male reproductive system. Thus, this hormone is also associated with ejaculation through the ejaculatory duct and urethra.
Relevant: Pregnancy After Age 35
Mammary Gland
In addition, the hormone oxytocin induces contractions in the myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland. Thus, it intervenes in milk production through the Montgomery glands. Overall, this facilitates the breastfeeding process during stimulation in the areola by the newborn.
Renal System

In addition, urinary retention caused by the hormone oxytocin is closely related to molecular events in the basolateral membrane of the kidney.
Typically, this symptomatic hyponatremia occurs more frequently in pregnant women whose labor was induced with oxytocin.
Labor
Naturally, oxytocin receptors in the uterus for childbirth have a direct dependency on the body’s levels of this hormone. In the early stages of labor, the best starting dose is between 1 to 6 mU/min. Then, it increases by 15 to 60 minutes.
From that moment, the receptors will have a greater hormonal affinity for oxytocin. Thus, it improves the contractions to facilitate labor.
Maternal Relationship
Naturally, the mother-child relationship begins right after birth. Believe it or not, both the natural and artificial synthesis of oxytocin generates this.
Overall, oxytocin strengthens the mother-child relationship. A curious fact is that this same substance causes women to forget the pain of childbirth. That way, they won’t fear having more children in the future.
Side Effects of the Hormone Oxytocin

Like all synthetic hormones, oxytocin is not harmless and can cause adverse effects during its administration. Overall, these include:
- Arterial hypertension,
- Marked mood swings,
- Tachycardia in mother and fetus,
- Abnormal postpartum contractions.
Overall, doctors have noticed the adverse reactions involved with high oxytocin levels in the body in stimulated patients. Despite this, they facilitate contractions during labor.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- López-Ramírez, C. E., Arámbula-Almanza, J., & Camarena-Pulido, E. E. (2014). Oxitocina, la hormona que todos utilizan y que pocos conocen. Ginecol Obstet Mex, 82, 472–482. Retrieved from www.femecog.org.mx
- Hiponatremia hipoosmolar secundaria a síndrome de secreción inadecuada de hormona antidiurética. (n.d.). Retrieved from www.medigraphic.org.mx
clinicadam.com. (2018). Consejos para la lactancia. Retrieved from https://www.clinicadam.com/salud/5/002453.html - 2.5.1. Oxitocina y vasopresina – Biopsicologia. (n.d.). Retrieved December 10, 2018, from http://www.biopsicologia.net/nivel-3-participación-plástica-y-funcional/2.5.1.-oxitocina-y-vasopresina
- Funciones de la oxitocina – Embarazo. (n.d.). Retrieved December 10, 2018, from https://www.webconsultas.com/embarazo/el-parto/funciones-de-la-oxitocina-12989
- Oxitocina – Todo sobre la Oxitocina. (n.d.). Retrieved December 10, 2018, from https://www.infooxitocina.com/
- Introducción a la hipófisis – Trastornos hormonales y metabólicos – Manual MSD versión para público general. (n.d.). Retrieved December 10, 2018, from https://www.msdmanuals.com/es/hogar/trastornos-hormonales-y-metabólicos/trastornos-de-la-hipófisis/introducción-a-la-hipófisis
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








