7+ Stomach Ulcer Symptoms To Be Aware Of
Written and verified by the doctor Nelton Abdon Ramos Rojas
Gastric ulcers can be caused by many things: an acidic diet, unhealthy food habits, and outside factors such as stress. Stomach ulcers symptoms have become a common worry in today’s world in which it’s easy to let healthy habits slip by.
If you’re not sure if you may have an ulcer or are looking for a way to prevent developing one, then you should read more.
Recognize the signs
It can be very easy to overlook the signs our bodies are giving us. Daily pressures, obligations, and family can distract us from the obvious things happening to our bodies.
If you’re letting stress overcome you or not paying attention to what you eat or how fast you are eating, then you may be putting your health in danger.
Your body is a delicate mechanism that requires care and a balanced emotional and physical well being. Did you know that your digestive system is the one system in your body most affected by stress and anxiety?
It actually acts as a second brain and can be damaged just as easily by factors which cause ulcers. It’s a dangerous illness that can have far-reaching effects.
Why not make yourself aware of the stomach ulcer symptoms before it has a chance to get that far?

Read also: Arnica and Coconut Oil Ointment to Treat Lower Back Pain
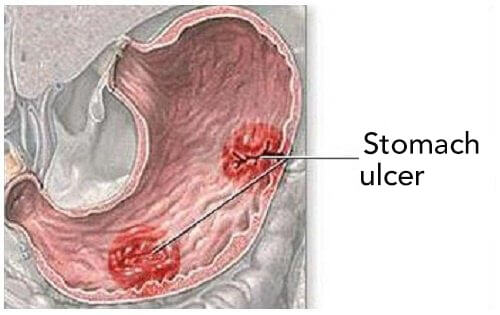
1. Stomach ulcer symptoms and pain
Pains centered in your stomach, especially between your sternum and belly button, should catch your attention. Do you know when these pains most often present themselves? When your belly is empty, most commonly, between meals.
A burning pain. Maybe an antacid will help, but typically antacids treat conditions that present themselves at night or when you’ve skipped a meal.
2. Abnormal pains
You may present symptoms like this on occasion, but when they become chronic conditions it becomes dangerous. Be aware of what your body is saying to you. Keep in mind if you have the following stomach ulcer symptoms:
- Gas or burping.
- Loss of appetite or weight-loss.
- Feeling full after drinking liquids.
- Fatigue or tiredness on a daily basis.
- Morning waves of nausea or feelings of nausea.
3. Advanced ulcers
If you are suffering from an advanced ulcer, there are unique ulcer stomach symptoms. These are considered pressing symptoms and you should visit a doctor.
- Dark stools, bloody stools.
- Daily feelings of vomiting, bloody vomit.
Food suggestions to alleviate ulcers

Read also: Anti-inflammatory Cayenne Pepper Ointments for Joint Pain
You should consult a nutritionist about foods that may worsen the symptoms of an ulcer or the chances of developing an ulcer. Certain foods, like salt, can cause hypertension or inflammations that may cause an ulcer.
In addition to any pharmaceutical treatment, you should consider complimenting your treatment with a stomach-healthy diet.
Food recommendations:
- Avoid salt and sugar.
- Avoid sweets and desserts such as chocolate or caramels.
- Substitute white flour for wheat.
- Avoid sugary drinks or treats.
- Limit your consumption of coffee and avoid alcohol.
- Dairy is not recommended.
- Avoid organ meat such as kidney and hearts.
- Avoid spicy foods.
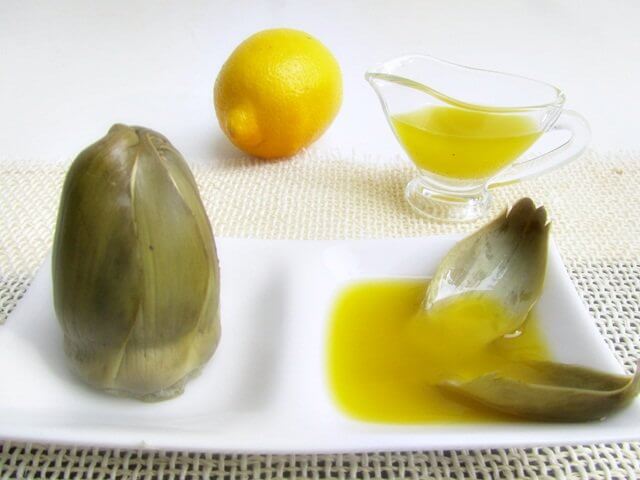
Foods to indulge in
Alkaline greens, such as spinach, artichokes, endives, mushrooms, cauliflower, lettuce, and squash, are wonderful for your belly. Try putting oregano on your food for a flavorful and healthy treat.
Teas of mint, thyme, lemon balm, licorice, and gentian are also recommended. One lukewarm cup twice a day after food, will help put your stomach at ease.
Add a dash of lemon juice, even though it’s a citric acid, as it will do your body good. So, be mindful of any pain that resembles stomach ulcer symptoms and get some help as soon as possible.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bolet Astoviza, M., & Socarrás Suárez, M. M. (2010). Alimentación adecuada para mejorar la salud y evitar enfermedades crónicas. Revista Cubana de Medicina General Integral, 26(2), 321–329. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262650612_Alimentacion_adecuada_para_mejorar_la_salud_y_evitar_enfermedades_cronicas
- Urréa, H. R. (2015). El Segundo Cerebro del ser humano. Revista Científica Tecnológica UPSE, 1(2), 10. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.26423/rctu.v1i2.22
- MedlinePlus, en línea (02/05/2020). “Úlcera gástrica”. https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/pepticulcer.html
- MayoClinic, en línea (02/05/2020). “Úlceras pépticas”. https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/peptic-ulcer/symptoms-causes/syc-20354223
- Academia Americana de Médicos de Familia, en línea (02/05/2020). “Úlceras pépticas” https://familydoctor.org/condition/peptic-ulcer-disease/?adfree=true
- Martín de Argila de Prados, C., & Boixeda de Miquel, D.. (2004). Úlcera péptica. Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas, 96(1), 81-82. Recuperado en 02 de mayo de 2020, de http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1130-01082004000100011&lng=es&tlng=es.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








