Scalp Psoriasis - Symptoms and Treatment
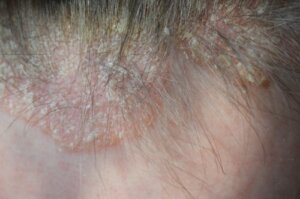
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic recurrent inflammatory type of dermatosis. One of its characteristics is the presence of delimited erythematous plaques with white flaking. The scaly skin is usually in the flexor areas of the limbs and on the scalp.
It’s a disease of great clinical variability and for this reason, it depends on various factors.
Causes of scalp psoriasis – genetic and immune factors
Some studies demonstrate the prevalence of psoriasis in the relatives of those affected by it. However, the development of cellular immunology indicates the involvement of leukocytes in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Environmental factors
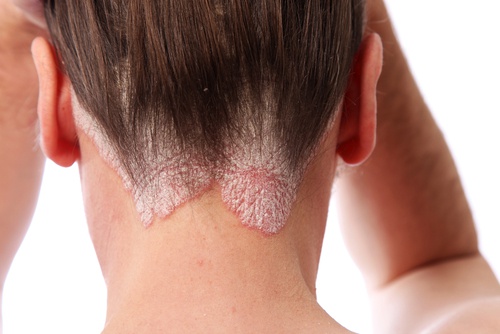
There are several factors related to the onset of an outbreak, particularly in genetically predisposed people. These factors include:
- Emotional stress
- Low ambient humidity
- Certain drugs/pharmaceuticals
- Smoking and weight
Also, any type of skin irritation can cause the appearance of psoriatic lesions. Likewise, stimulation such as scratching or pressure on clothing can cause or aggravate existing injuries.
Drugs/pharmaceuticals
Among the ones that can trigger or aggravate psoriasis are lithium salts, beta-blockers, antimalarials, and the abrupt suspension of corticosteroid treatments.
You may also be interested in: Five Herbal Topical Psoriasis Treatments
Obesity and smoking
Overweight is another important factor to consider. In fact, the relationship between psoriasis and weight is bidirectional as excess weight predisposes to psoriasis and psoriasis promotes obesity. In addition, chronic smoking disrupts many inflammatory processes, including the immune response.
Infectious factors
There’s a relationship between group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection and a first psoriasis outbreak. Especially when the outbreak appears in the oropharynx.
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis
This condition has a wide range of symptoms. There’s much variability among people who suffer from it, even in the same person.
Its appearance can manifest from papules to scaly patches. However, they generally don’t lead to hair loss. They most frequently appear in the occipital region and the forehead.
Itchiness is not a characteristic symptom. However, picking on the patches can lead to bleeding. The diagnosis of scalp psoriasis is based on the presence of erythematous plaques with scales.
Dermatologists use morphological criteria to assess the severity of psoriasis. Specifically, the psoriasis area and severity index. The latter allows them to measure the extent of the lesions, the degree of erythema, and scales.
Also read: Five Ways to Keep Psoriasis at Bay
Treatment for scalp psoriasis

Scalp psoriasis is a chronic disease though, so the goal of treatment is mainly to control its intensity. However, scaling in this area is frequent and also hard to treat.
Topical treatment
Firstly, let’s say that topical treatment is the basic pillar of treatment for this condition. In addition, the classic treatments include:
- Emollients used in combination with pharmacological treatment. In addition, they help maintain hydration and the good condition of the corneal layer of the skin. 20% urea, petrolatum, and glycerin are part of this group.
- Also, keratolytics are used for eliminating rough skin patches and they also promote the absorption of other topical products. For instance, salicylic acid is often present in the composition of shampoos and hair oils. Other keratolytics used in them are 10-30% urea, salicylic, lactic and glycolic acids, sulfur, and Keluamide.
- In addition, coal pitch reduces the thickness of the epidermis. It’s often prescribed for children and for those people who have stable plates. However, it can lead to further irritation even though it isn’t necessarily toxic.
- Finally, topical corticosteroids are the first choice of treatment in mild cases. This is because they have anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive action.
Systemic treatment of psoriasis on the scalp
Dermatologists reserve these for cases where topical treatment fails to make a difference and the prescribed drugs include:
- Methotrexate, a drug for moderate and severe forms of psoriasis
Cyclosporine, an immunosuppressant that inhibits the production of T-dependent antibodies - Acitretin, a derivative of vitamin A that has an inhibitory effect on psoriasis, even on keratolytic disorders
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
-
Sola-Ortigosa, J., Sánchez-Regaña, M., & Umbert-Millet, P. (2009). Psoriasis del cuero cabelludo. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0001-7310(09)71901-5
-
Serrano Grau, P., & Mascaró Galy, J. M. (2006). Metotrexato: Actualización en el tratamiento de la psoriasis. Piel. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0213-9251(06)72510-2
-
Puig, L., Ribera, M., Hernanz, J. M., Belinchón, I., Santos-Juanes, J., Linares, M., … Caballé, G. (2010). Tratamiento de la psoriasis del cuero cabelludo. Revisión de la evidencia y Consenso Delphi del Grupo de Psoriasis de la Academia Española de Dermatología y Venereología. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2010.09.001
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








