Drinks that Cause High Blood Pressure
Researchers recently identified some drinks that can cause high blood pressure. This is why you must limit their consumption. At the very least, you must be aware that the lack of control of this disease can bring about health complications and even subsequent death.
According to a document by SEH-LELHA, 33% of adults have high blood pressure. In fact, cases are on the rise and it’s an issue that raises concerns for both patients and health professionals.
It’s for this reason that efforts to improve the habits that contribute to keeping blood pressure under control are already underway. Dietary adjustments have become decisive in this regard. So, can you guess what are drinks cause high blood pressure? Continue reading to see if you got it right.
The drinks that cause high blood pressure
Due to their composition, some beverages can considerably raise blood pressure. Moreover, they’re a risk factor for hypertension when taken on a regular basis. Thus, limiting the intake of those who pose a risk for the disease is a determining factor when it comes to health.
As detailed in a review published in Pharmacological Research, hypertension is the strongest risk factor for other cardiovascular diseases — arrhythmias, coronary heart disease, and stroke, among others.
1. Sugary drinks can cause high blood pressure
The excessive consumption of sugary beverages is evident in the modern tendency to obesity and overweight. Their consumption has been discouraged for years, in fact, as they’re also a risk factor for metabolic syndrome.
A systematic review published in the American Journal of Cardiology concluded there’s a relationship between the consumption of this type of beverage and an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, people must limit their consumption and opt for more wholesome beverages such as water.

2. Energy drinks
People with heart conditions or high blood pressure shouldn’t have energy drinks. Multiple studies, such as the one published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, revealed these caused high blood pressure in healthy people.
This is because most “energy” drinks contain taurine and caffeine. Researchers believe these substances may be responsible for the increases in blood pressure and heart rate.
All brands that promise to increase energy levels contain caffeine and taurine to a greater or lesser extent. These substances have an impact on the cardiovascular system and this is why people feel energized. For instance, an energy drink is equivalent to two cups of overly strong coffee.
You mustn’t mistake energy drinks with sports drinks. The objective of the latter is to rehydrate the body after heavy physical exertion.
Find out why Controlling High Blood Pressure Isn’t Just About Salt
3. Coffee and tea
All caffeine-containing products can be harmful to patients with hypertension, according to Sheldon Sheps, MD. He stated the following in a Mayo Clinic publication:
“Caffeine can cause a brief but dramatic increase in blood pressure, even in those who aren’t hypertense.”
4. Alcohol can cause high blood pressure
Today, most people are aware that excessive alcohol consumption can lead to serious health consequences. Nevertheless, it’s also one of the beverages that can cause high blood pressure.
This was demonstrated by a comprehensive study published in the World Journal of Cardiology, which also suggests limiting the intake of this type of beverage in order to control high blood pressure and prevent further complications.

The perils of high blood pressure
This condition is often referred to as “the silent disease” because it’s usually asymptomatic.
Hypertension can lead to a degradation of the quality of life due to constant discomfort and even a heart attack. It’s quite serious but luckily there are treatments that can help control it. Keep in mind that said treatments won’t do much without the proper lifestyle changes.
According to information published in the Mayo Clinic, pharmacological treatment may include:
- Diuretics
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
However, the choice between one drug or another depends on the individual case. Thus, your physician will determine the best treatment for you. This is why it’s important to consult a doctor if you think you might have a blood pressure problem.
Did you know that Yoga Can Help Control High Blood Pressure?
What are the most frequent complications?
High blood pressure must be under control in a timely manner, there’ll be serious health consequences otherwise. The National Center for Biotechnology Information mentioned some of these complications in one of their publications.
Arterial damage
Under optimal conditions, arteries are flexible and strong — unless blood pressure increases. They can become damaged and narrow when this happens and affect the lining of the cells inside the arteries.
Any fats you consume in your diet will enter the bloodstream. Furthermore, the damaged cells accumulate as they pass through. This change affects blood flow to various parts of the body (brain, legs, heart, and others, such as the kidneys).
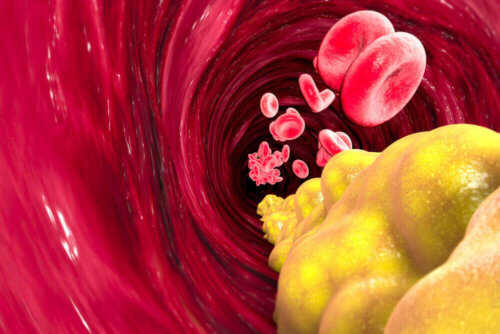
Aneurysm
The constant flow of blood through a damaged artery can cause an increase in the size of the artery wall, leading to an aneurysm. Then, the aneurysm may burst and cause internal bleeding that can seriously threaten the life of the person afflicted by it.
Heart
High blood pressure can affect the heart as this organ is in charge of pumping blood throughout the body. Hypertension can cause chest pains, arrhythmias, or a heart attack as a result of poor blood circulation.
Brain damage can also result from a transient ischemic attack — the brief interruption of cerebral irrigation. These are just some of the serious problems that can result from failing to manage high blood pressure.
Final notes about the drinks that increase blood pressure
Drinks that cause high blood pressure are common in most people’s diets. It’s for this reason that treatment for hypertension requires changes in your daily habits.
Finally, keep in mind that these changes aim to protect the circulatory system of people with hypertension. In any case, the best way to keep your blood pressure in balance is to visit your doctor regularly and follow their instructions.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Kitt J, Fox R, Tucker KL, McManus RJ. New Approaches in Hypertension Management: a Review of Current and Developing Technologies and Their Potential Impact on Hypertension Care. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019;21(6):44. Published 2019 Apr 25. doi:10.1007/s11906-019-0949-4
- Organizacion Mundial de Salud. (2015). OMS | Preguntas y respuestas sobre la hipertensión. Preguntas y Respuestas Sobre La Hipertensión.
- OMS, O. M. de la S. (2013). Información general sobre la hipertension en el mundo. Oms. https://doi.org/WHO/DCO/WHD/2013.2.
- Piskorz, D. (2011). Hipertensión arterial. Salud(i)Ciencia. https://doi.org/10.2319/111211-702.1.
- Malik, A. H., Akram, Y., Shetty, S., Malik, S. S., & Yanchou Njike, V. (2014, May 1). Impact of sugar-sweetened beverages on blood pressure. American Journal of Cardiology. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.01.437
- Fletcher, E. A., Lacey, C. S., Aaron, M., Kolasa, M., Occiano, A., & Shah, S. A. (2017). Randomized controlled trial of high-volume energy drink versus caffeine consumption on ECG and hemodynamic parameters. Journal of the American Heart Association, 6(5). https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.004448
- Husain K, Ansari RA, Ferder L. Alcohol-induced hypertension: Mechanism and prevention. World J Cardiol. 2014;6(5):245–252. doi:10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.245
-
Iqbal AM, Jamal SF. Essential Hypertension. [Updated 2019 Apr 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539859/
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








