Diet for High Bilirubin: Tips and Recommended Foods

Written and verified by the nutritionist Anna Vilarrasa
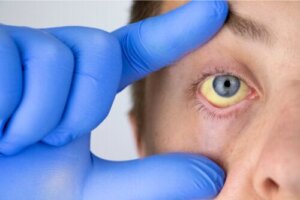
Yellowing of the eyes, skin, or gums isn’t common, but it can occur. This situation is known as jaundice and is a clear sign that there is a problem with liver functioning. A diet for high bilirubin is helpful in these situations as long as it’s always accompanied by the appropriate treatment and directed by a specialist.
To optimize liver function, it’s advisable to adopt healthy eating patterns based on fresh products, soft cooking, and easy digestion. In addition, it’s important to eat food that’s abundant in vitamins, antioxidants, fiber, and water. The following article details everything that’s suitable and what’s best to avoid.
What is hyperbilirubinemia?
Bilirubin is a yellow or orange substance that appears as a result of the degradation of red blood cells. However, it also appears as a consequence of enzymatic metabolism and myoglobin. Its characteristic color come from a pigment.
It circulates through the blood to the liver, which is responsible for excreting it from the body. Through the biliary tract, it’s then expelled into the intestine and thus evacuated through the stool. Normal values should be between 0.1 and 1.2 milligrams per deciliter of blood. When this range is exceeded, hyperbilirubinemia occurs, and with it, jaundice.
Jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes and is one of the signs of bilirubin accumulation in the blood.
This condition is not common in adults, but it can occur in adults with liver diseases such as Gilbert’s syndrome, cirrhosis, or hepatitis. It’s even noticeable in some babies at birth, as the liver may take a few days to be able to process this molecule.
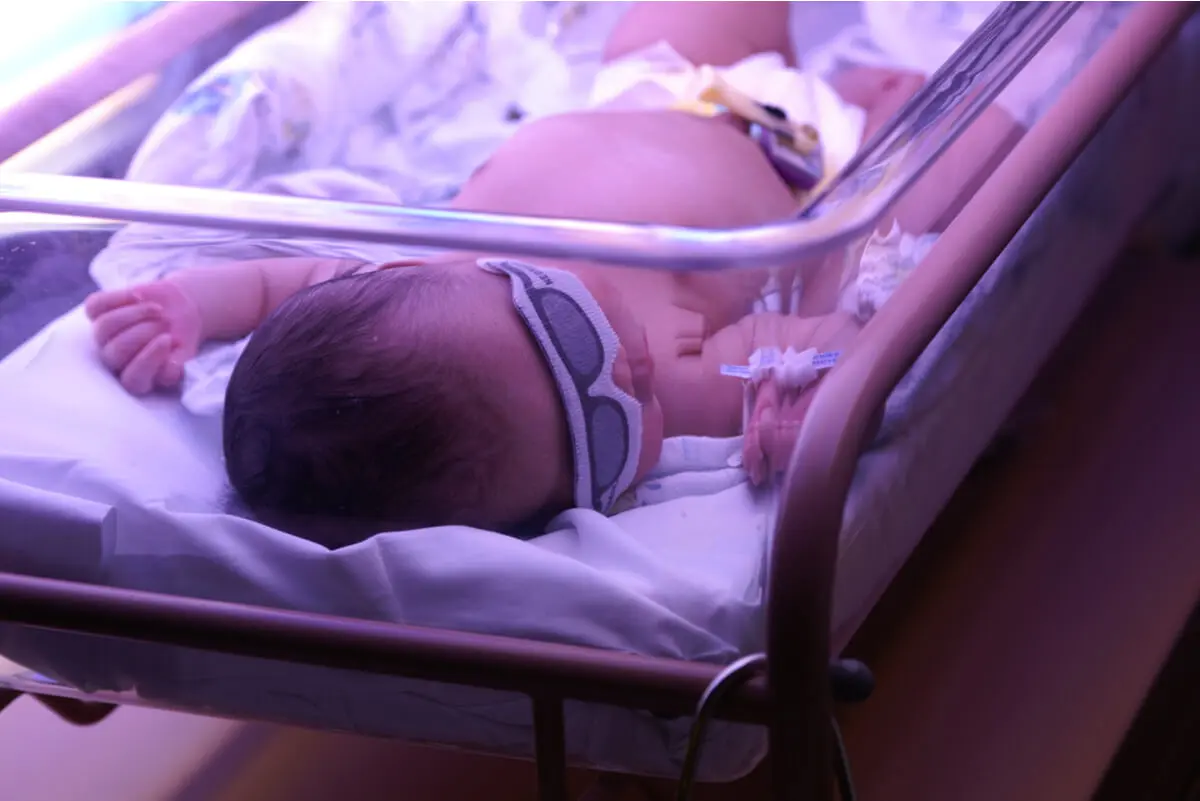
Another common cause of jaundice is diseases that obstruct the bile ducts. A stone or tumor can hinder the passage of bile into the intestine, generating an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood.
In turn, the increased elimination of erythrocytes by the spleen can also explain high bilirubin.
We think you may also enjoy reading this article: 5 Foods that Will Take Care of Your Liver Health at Night
The importance of a healthy diet in regulating bilirubin
The liver has a prominent role in digestion. Everything that’s ingested is filtered by this organ, which is responsible for converting nutrients into energy. It produces bile, which is necessary for the digestion of fats and, in addition, organic waste, alcohol, toxins, and medicines are filtered through it.
Therefore, any food or drink that we consume involves liver work. However, the different nutrients and chemicals present can make this task easier or more complicated. Therefore, we can speak of products that act as liver allies and others that are not so much.
An excess of fats, salt, and sugar, as well as very abundant meals, are all very difficult to digest, thus making the liver work harder. Therefore, none of this is recommended, and it’s necessary to replace unhealthy foods with foods that can help in this function if you have liber problems. This improves jaundice and prevents its reappearance.
Foods to reduce bilirubin levels
A diet for high bilirubin has to be balanced and adapted to the specific needs and situation of each person. It’s important that all dishes contain protein, healthy carbohydrates, and low amounts of fat.
However, there are some foods with a more positive effect on the liver that can reduce symptoms and improve the situation. Let’s take a look at them.
1. Red fruits and vegetables
Antioxidants are an important component in maintaining the oxidative balance in the liver. When this balance is disturbed, liver health is impaired, and so is its optimal functioning. This is why it’s necessary to eat foods that provide these compounds.
The most abundant are found in fruits and vegetables. It’s especially worth mentioning the red ones, as they contain lycopene, and this is one of the antioxidants that seem to have the most important activity in this sense.
In fact, a publication made in Food and Function found that lycopene is beneficial in people with liver damage, cancer, infertility, and metabolic syndrome. This useful antioxidant can be obtained from the following foods:
- Tomatoes
- Watermelon
- Guava
- Persimmons
- Black grapes
2. Fiber in a diet for high bilirubin
As pointed out by the American Liver Foundation, it’s interesting to increase the presence of fiber, as it allows the liver to work at an optimal level. The most recommended sources are vegetables, whole grains, and fruits in general.
On the other hand, a study published in the magazine Nutrition found that the consumption of dietary fiber has multiple effects on the liver. It can decrease both hepatic and systemic inflammation, as well as prevent liver fibrosis.
Like this article? You may also like to read: Nine Properties of Wormwood to Help Keep Your Liver Healthy
3. Lean meat, white fish, and legumes
These are the most suitable sources of protein, as they’re also the lowest in fat. Amino acids are necessary for a diet for high bilirubin, as they help in liver regeneration.
Chicken, rabbit, and white fish varieties, as well as leaner cuts of meat, are all indicated in this situation. In addition, legumes in small portions also provide a lot of fiber in their composition.
4. Whole carbohydrates
Carbohydrates represent a good source of energy, and the foods that provide them are healthy for the liver.
However, it’s best to choose whole grains (rice, millet, rye, wheat, etc.) and their derivatives (bread, pasta). In addition to energy, they also contain vitamins, minerals, and fiber that help improve liver function and reduce bilirubin.
5. Water as a beverage of choice
It’s also very important to drink enough liquid to maintain good hydration and enhance your liver function. The key is to consume between 1.5 and 2 liters of water per day, which translates into about eight glasses.
In this way, bile production will increase, which will favor the elimination of bilirubin.
Another drink that is beneficial is coffee. Scientific evidence has shown that it can prevent the development of a liver problem and improve it when it has already appeared.
Considered until recently as a bad habit, nowadays, the data on coffee consumption seems to go in the opposite direction. However, it’s necessary to be prudent with its use and quantities, especially for those people who are sensitive to its effects or who don’t drink it regularly.
Foods to avoid in a liver-friendly diet
In addition to enhancing all the positive foods in the diet for high bilirubin, there are a series of dietary tips about everything that is more harmful.
According to different experts agree, these are the ones to be avoided as far as possible:
- Saturated fats and processed meat such as cream, cured cheeses, whole milk, sausages, and non-lean meats. Fast food, cooking such as fried foods, trans fats, and palm oil should also be avoided.
- Avoid alcohol as it causes additional damage to the liver, which is in charge of filtering it.
- Fish and seafood: raw or undercooked versions should be avoided.
- Soft drinks, cakes, cookies, and other foods with a lot of added sugar can increase fat deposits in the liver.

What else to take into account in a diet for high bilirubin
People who have this health problem for whatever reason should follow a balanced and healthy diet adapted to their condition.
It’s important to eat 4 or 5 small volume meals a day, with all the nutrients present and with light and easily digestible cooking.
Ideally, your daily diet should consist of 3 main dishes and 1 or 2 snacks. In addition, you should ensure that no more than 5 hours elapse between each meal. Breakfast should also be eaten less than one hour after waking up to prevent an increase in bilirubin.
Apart from watching the diet and the foods that compose it, there are other habits or behaviors that can increase bilirubin levels in the blood. As pointed out by the British Liver Trust Foundation, jaundice becomes more evident in the following situations:
- Fasting periods and low-calorie diets
- Times of stress
- During infectious diseases
- With vigorous sports practice
On the other hand, activities to promote liver health, such as avoiding saturated fats and alcoholic beverages, are also recommended.
In addition, regular exercise has been shown to improve liver function and decrease fat in the organ, according to the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
A proper diet helps improve high bilirubin
A diet that provides fiber, protein, vitamins, and whole carbohydrates is necessary to lower blood bilirubin levels and care for liver function. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and lean meats are the most suitable foods in this situation.
However, you should keep in mind that if jaundice is accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, loss of appetite, a lack of energy, or fluid retention, it may be necessary to follow another diet for high bilirubin.
It may also be necessary to adopt more specific guidelines that need to be personalized, so it’s essential to consult a specialist as soon as possible.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Casas-Grajales S, Muriel P. Antioxidants in liver health. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pharmacology and Thereutics. Agosto 2015.6(3):59-72.
- Dranoff JA. Coffee Consumption and Prevention of Cirrhosis: In Support of the Caffeine Hypothesis. Gene Expression. Marzo 2018;18(1):1-3.
- Mosquera, Jairo Téllez, and Miguel Cote Menéndez. “Alcohol etílico: un tóxico de alto riesgo para la salud humana socialmente aceptado.” Revista de la Facultad de Medicina 54.1 (2006): 32-47.
- Gollan JL, Bateman C, Billing BH. Effect of dietary composition on the unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia of Gilbert’s syndrome. Gut. Mayo 1976. 17(5):335-340.
- Jensen T, Abdelmalek MF, Sullivan S, et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal Hepatol. Febrero 2018.68(5):1063-1075.
- Vitaglione P, et al. Dietary antioxidant compounds and liver health. Critical reviews in food and nutrition science. 2004. 44(7-8):575-86.
- Vreman RA, et al. Health and economic benefits of reducing sugar intake in the USA, including effects via non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a microsimulation model. BMJ Open. Agosto 2017. 7(8):e013543.
- de La Fuente, Rocio Aller, Natalia Fernández Angulo, and Daniel de Luis Roman. “Nutrición en el hígado graso no alcohólico.” Nutrición Clínica 13.2-2019 (2019): 89-98.
- Parras_Ortega, Nadia. “Dietas altas en grasa. Estudio del metabolismo lipídico en músculo e hígado.” (2018).
- Feart, Catherine. “Nutrition and frailty: Current knowledge.” Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 95 (2019): 109703.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








