How to Cure Canker and Mouth Sores

Canker and mouth sores are small wounds that manifest in the mouth. Although they tend to be small, their location makes them uncomfortable and painful. Hot, cold, crunchy, and acidic foods can irritate them, causing further discomfort.
They take a while to cure due to the moisture in the mouth and the consumption of food. So, we wanted to find a quick solution that treats and relieves painful sores and mouth sores. In today’s article, we’ll you the solutions we found to help cure canker and mouth sores fast.
The causes of canker and mouth sores
Although they’re very common, the truth is that no one knows precisely why they appear. What we do know is that canker and mouth sores cause painful speaking and eating. There are two types: simple or complex.
The first type appear a few times a year and last for about a week. The second type are less common and people afflicted by them usually had some sort of mouth sore before. The appearance of sores could be the result of many things. Some factors that might trigger them are:
- According to this study of the Faculty of Dentistry of the Complutense University of Madrid, stress might be linked to mouth sores.
- Acid or citrus intake.
- Injuries from food or eating utensils.
- Nutritional problems or gastrointestinal disease (although there’s no evidence to support this).
- Orthodontic devices.
We must pay attention to the difference between canker sores and herpes labialis, which can be identical in their appearance. Herpes labialis is caused by a simple virus and is contagious, while canker sores aren’t. In addition, the former may appear on other parts of the face, such as the lips, nose, and under the chin.
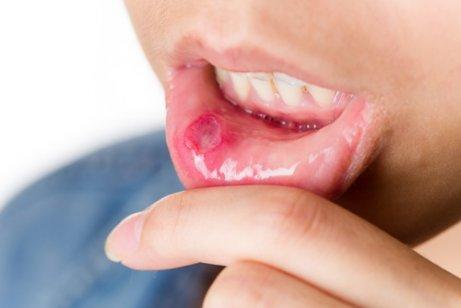
If you have a canker sore, you may experience burning and a painful tingling sensation, as well as white or gray round sores with red borders. Also, you may have a fever and swollen lymph nodes.
The good thing about canker sores is that they almost always disappear on their own. The pain can be very bothersome, but the important thing isn’t to touch it with your teeth nor tongue, even though you may be tempted to. They’ll be a bad memory in a period of seven to ten days.
Natural remedies for canker and mouth sores
According to popular beliefs, the following natural remedies may help accelerate the healing of mouth sores and canker sores. Since there are still unknowns regarding their effectiveness, you should never take them as a substitute for your doctor’s recommendations.
Salt
Salt is attributed antiseptic properties. Thus, it’s said that it’s a great ally to heal wounds naturally. To use it as a remedy, all you have to do is mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth with it. Spit the mixture out and repeat the process at least three times a day. Your pain and discomfort will gradually decrease.
You should also read: 8 Remedies That May Help Heal Mouth Ulcers
Baking soda
It’s often said that baking soda works like salt as an effective antiseptic. However, experts in chemistry (such as Deborah García Bello wrote in her book ¡Que se van las vitamins! As in different digital media) indicate that this is an extremely abrasive substance and that it shouldn’t be used as a home remedy, not even in a punctual way.
If you still want to try it out, mix a teaspoon of baking soda in half a glass of water. Then, rinse your mouth with the mixture without swallowing the liquid. You can also make a baking soda paste with some water and apply it on your canker or mouth sore. Leave it on for a few minutes so it does its thing. Then, rinse it with cold water.
Hydrogen peroxide
This is another surefire remedy for canker and mouth sores, according to a study from the University of Barcelona. Take a cotton swab or ball and soak it in hydrogen peroxide. Apply it directly on the sore three times a day. It’ll soothe your discomfort and help reduce the risk of infection.
*Don’t use this remedy for extended periods of time.
This may interest you: 8 Natural Hydrogen Peroxide Remedies
Mouthwash

Mouthwash is a remedy that can soothe your discomfort and control the growth of bacteria. This is immediate relief that’ll control the growth of bacteria. Don’t use too much of it, though, especially if it’s strong, because it’ll probably sting.
Ice
An ice cube can reduce inflammation and relieve pain. According to this study from the University of the Americas, the cold acts as a sedative. Put an ice cube on the affected area as often as you consider necessary.
Is yogurt recommended?
We used to believe that, due to its acid content together with its bacteria, yogurt could help change the pH of the mouth and control the growth of new bacteria. However, many studies say that the appearance of canker sores could be directly related to the consumption of dairy products, as well as flour, tomato skin, and nuts.
Tips to avoid the formation of canker and mouth sores
Mineral or vitamin deficiency can cause canker sores. Therefore, it’s best to include them in your diet. Other conditions that may cause sores are iron or folate deficiency anemia (sometimes caused by intestinal malabsorption), celiac disease, and Crohn’s disease, among others. Don’t hesitate to add foods that contain iron, such as leafy greens, whole grains, and milk, among others, to your diet.
Likewise, be careful when you brush your teeth, because it can cause similar injuries or irritation. The same goes for when you eat crunchy foods such as cookies, bread, toast, etc. Finally, avoid acidic or spicy foods and chewing gum and don’t forget to floss after every meal to always keep your mouth clean and healthy.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
Edgar NR, Saleh D, Miller RA. Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis: A Review. J Clin Aesthetic Dermatol. 2017;10(3):26-36.
Ediriweera ERHSS, Premarathna NYS. Medicinal and cosmetic uses of bee′s honey – A review. Ayu. 2012;33(2):178. doi:10.4103/0974-8520.105233
Huynh NC-N, Everts V, Leethanakul C, Pavasant P, Ampornaramveth RS. Rinsing with saline promotes human gingival fibroblast wound healing in vitro. PLoS One. 2016;11(7). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159843
Madeswaran S, Jayachandran S. Sodium bicarbonate: A review and its uses in dentistry. Indian Journal of Dental Research. 2018;29(5):672-677. doi:10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_30_17
Rafieian N, Abdolsamadi H, Moghadamnia A, et al. Efficacy of alum for treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Caspian J Intern Med. 2016;7(3):201-205. PMID:27757206.
Scully C, Gorsky M, Lozada-Nur F. Aphthous ulcerations. Dermatologic Therapy. 2002: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01528.x.
Scully C, Shotts R.. Mouth ulcers and other causes of orofacial soreness and pain. Western Journal of Medicine. 2001: https://doi.org/10.1136/ewjm.174.6.421.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








