Characteristics of Cerumen Impaction
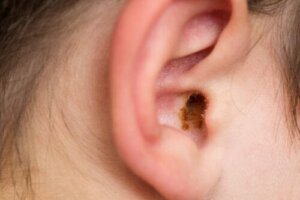
Cerumen impaction is one of the many human body defense mechanisms against foreign agents. Indeed, wax plays a fundamental role in protecting and moisturizing the ears. However, this substance often accumulates and leads to blockage. Continue reading to find out more about this condition and how to treat it.
Wax or cerumen is a yellowish-orange substance resulting from the secretions of the sebaceous and sweat glands. It aids the lubrication and cleaning of the human ear, as well as its defense. It’s part of the elimination process to replace superficial skin cells and by the movement of the jaw and head.
In some people, the secretion accumulates and impacts deep in the ear, leading to cerumen impaction. The most frequent symptom is decreased hearing on the affected side. However, early diagnosis and prompt treatment can mitigate the condition.
Symptoms of cerumen impaction
This is quite annoying and can deeply affect a person’s quality of life. Estimates indicate that this condition, together with otitis media and external, are the main causes of conductive hearing loss in young patients.
Affected people experience anything from difficulty hearing distant sounds to a total blockage of the hearing capacity of the obstructed ear. Similarly, patients with cerumen impaction often experience the following symptoms:
- Pain in the ear
- The sensation of pressure or swelling in the area
- Ringing or tinnitus
- Itchy ear
- Nausea and dizziness
- Fluid coming out of the ear canal
- The perception of an unpleasant odor coming from the ear
Read these Five Recommendations to Remove Earwax
When to consult a physician?
Seek specialized medical help whenever you experience unpleasant or strange ear symptoms that affect your daily life. Physicians are usually qualified to evaluate an ear’s state of health by means of inquiry and comprehensive examination of the ear canal.
It’s important not to delay medical help and to consult a specialist as soon as possible. This is because it could impair the prognosis of this condition. In addition, don’t attempt to remove earwax on your own or with traditional home methods. Mainly because these situations increase the risk of complications.
Causes of cerumen impaction
The presence of wax in the ear is normal and part of the physiology of the human body. It goes away on its own as a result of jaw movements we make when chewing, speaking, and also when we move our head and with the change of the superficial epithelium of the skin.
In this respect, cerumen impaction is due to factors that increase wax production or hinder its outflow. Furthermore, the main associated mechanism is impaction when using cotton swabs or hairpins as part of daily hygiene.
This is because cotton swabs displace the wax distributed in the ear canal to the posterior part and may even cause lesions in this structure. In addition, earwax blockage is also due to the presence of hearing devices, hearing aids, and earplugs.
Moreover, studies reveal that, as a person ages, the serous and sweat glands atrophy and produce a drier earwax that tends to accumulate. Similarly, some patients with developmental disabilities have hypoplastic or smaller ear canals that hinder the natural outflow of earwax.
Diagnosis and treatment
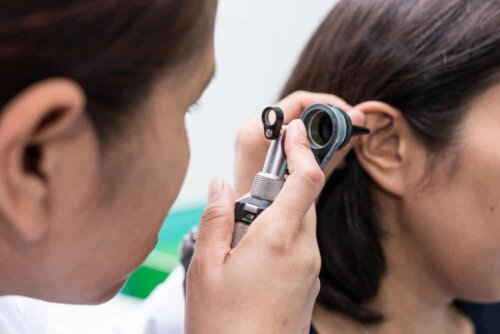
A general practitioner or otolaryngology specialist can easily diagnose cerumen impaction using an otoscope. This hand-held device uses a beam of light and a magnifying lens to visualize the inside of the ear canal.
The examination of the ear through this instrument is known as otoscopy. The physician introduces a small cone into the ear opening, which facilitates the diagnosis of lesions. Once they recognize the obstruction, the specialist may use the following medical procedures to remove the cerumen:
- The application of cerumenolytics consists of applying drops of certain solutions inside the ear canal to hydrate and soften the accumulated cerumen. They let it do its thing for a period of 5 to 10 minutes with the head inclined. Afterward, they extract the diluted wax.
- Irrigation is the application of distilled water, hydrogen peroxide, or saline into the ear at moderate pressure with a syringe. It softens the cerumen to extract it by dragging it from within. Doctors often use it in conjunction with cerumenolytics to facilitate the procedure.
- Manual extraction requires a curette or a small suction device to locate the impacted cerumen and pull it out.
Prevention of cerumen impaction and recommendations
Don’t use cotton buds or swabs inside the ear canal. Use them only for external cleaning of the pinna. Likewise, reduce the periodic and long-term use of earphones.
Professionals recommend prophylactic application of natural oils or 70% alcohol if you’re prone to experience this condition, under strict medical supervision. In addition, patients with recurrent cerumen impaction should visit the doctor every 6 months in order to assess the health status of both ears.
We must also point out that specialized cleaning usually prevents the appearance of new episodes, so the specialist may indicate prophylactic treatment. In addition, there are also ways to remove earwax safely and without causing any damage to the ear.
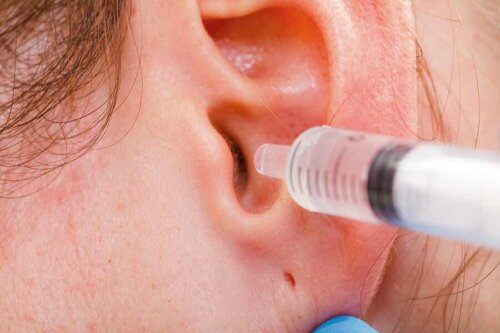
Check out how to Remove Earwax Blockage without Damaging Your Ears
Avoiding the use of traditional wax removal methods
There’s currently a long list of non-medical alternative procedures for removing ear wax impaction. Most are based on the use of heat via candles or other hollow instruments to which the wax adheres.
However, these methods are risky and associated with burn injuries and even ear canal perforations. Thus, consult a doctor in a timely manner if you suspect you have an earwax plug. A properly trained one can identify and address the condition quickly and provide treatment.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Benito Orejas J, Garrido Redondo M, Velasco V, Mata J et al. Extracción de la cera de los oídos. Rev Pediatr Aten Primaria. 2015; 17(67): e223-e231.
- Cardemil F, Mena P, Herrera M, Fuentes E et al. Prevalencia y causas de hipoacusia en una muestra de escolares de la zona sur de Santiago. Rev. Otorrinolaringol. Cir. Cabeza Cuello. 2016; 76(1): 15-20.
- Sevy JO, Singh A. Cerumen Impaction Removal. 2020. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan–.
- Michaudet C, Malaty J. Cerumen Impaction: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(8):525-529.
- Schwartz SR, Magit AE, Rosenfeld RM, Ballachanda BB et al. Clinical Practice Guideline (Update): Earwax (Cerumen Impaction). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;156(1_suppl):S1-S29.
- McCarter DF, Courtney AU, Pollart SM. Cerumen impaction. Am Fam Physician. 2007 May 15;75(10):1523-8.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








