What is Osteopathy and When is it Recommended?

There are several disciplines that seek to address the human body from a holistic point of view. Osteopathy is a therapeutic branch whose purpose is to restore the balance of the body by means of manual techniques. In this article, we’ll tell you more about this practice.
Osteopathic medicine, or osteopathy, is dedicated to preserving the perfect harmony of organic functions within the osteomuscular, cardiovascular, respiratory, lymphatic, and nervous spectrum. As such, it’s a complement to conventional medicine.
Osteopathy should not replace the professional medical approach.
What is osteopathy?
Osteopathy is a therapeutic branch that seeks to prevent and treat health ailments through a set of manual techniques and non-invasive procedures. It requires extensive knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the human body and focuses on restoring the homeostasis of all organs and systems.
Likewise, this discipline has a holistic view of health; that is, it analyzes and approaches the human body as a unit and not as a series of independent organs. For osteopaths, alterations in one system affect and compromise the functioning of the rest.
An example would be mental health problems that also affect intestinal well-being. Such is the case of irritable bowel syndrome.
What does it consist of?
Osteopathic treatments are aimed at relieving ailments through external stimuli that seek to generate internal responses that restore integral functioning. This is unlike traditional medicine, whose focus is to treat only the focus or symptom that triggers the discomfort.
A study conducted between 2013 and 2020 showed that osteopathy could be promising in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. According to the authors, it shows effective evidence in the relief of chronic low back pain and low back pain in pregnancy.
Osteopathy was developed in the United States, in 1874, by Andrew Taylor Still, and is currently recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO). Likewise, this professional practice is legal in the United States, England, and France. Meanwhile, in Spain, it’s included within the competencies of physiotherapy.
We think you may also enjoy reading this article: Weak Bones and Joints: Learn How to Strengthen Them
Is there a relationship between osteopathy and physiotherapy?
Osteopathy and physiotherapy have a very close relationship, since both disciplines use manual techniques and non-invasive maneuvers to correct health conditions.
Furthermore, they are aimed at relieving pain in the patient, recovering individual well-being and improving quality of life. Therefore, it’s common for both branches to work together to obtain better results.
The benefits of osteopathic medicine
The main benefit of osteopathic therapy is its philosophy of minimal intervention and invasion of the human body. In general, it’s governed by holism and globalism in the approach to ailments.
The osteopath studies the origin and evolution of the disease without direct intrusion into a single focus or ailment. In turn, the discipline promotes and stimulates the self-healing of the human body, without the need to use invasive techniques, such as drugs and surgery.
On the other hand, there are few unwanted side effects of osteopathy. There are bodily reactions, but these are considered useful to restore body functioning. Likewise, fatigue and dizziness are usually explained by the state of recovery to which the body is exposed after the sessions.
Also, one of the major advantages of this type of therapy is the reduction in the consumption of certain medications. However, people shouldn’t abandon conventional medical treatment at any time without strict professional approval.
Types of osteopathy
Osteopathy is classified into three main branches. Each one is aimed at addressing different groups of organs to alleviate the discomfort of people.
1. Structural osteopathy
This branch focuses its attention on the locomotor system and the musculoskeletal system. It performs a detailed study and a comprehensive approach to bones, muscles, joints, tendons, fasciae, and ligaments.
However, structural osteopathy has shown inconclusive results in the management of osteoarthritis, for example. This is affirmed by scientific studies.
2. Visceral osteopathy
The main objective of this branch is the holistic analysis of all the hollow and solid viscera of the human body, with special emphasis on the gastrointestinal and genitourinary apparatus. Consequently, it makes it possible to identify and address conditions such as chronic gastritis.
3. Cranial osteopathy
Cranial osteopathy is aimed at addressing the encephalic structures and their intimate relationship with the central nervous system. It pays special attention to disorders such as vertigo, migraine, and postural problems. It’s also of great interest in otorhinolaryngological and endocrine exploration.
Like this article? You may also like to read: Calcium Requirements in Children: How Much do They Need?
Some of the most common osteopathic techniques
Osteopaths use a wide variety of manual techniques and non-invasive procedures in the relief of ailments. Among the most commonly used are the following:
- Muscle energy technique: It applies a gradual resistance to the active contraction of the person’s musculature. Consequently, it makes it possible to treat muscle weakness, reduce inflammation, and improve joint activity.
- Jones technique: This involves locating sensitive areas and pain trigger points, as well as mobilization angles that reduce pain. It’s useful in muscle contractures, neuralgia, and musculoskeletal overload.
- Myofascial release: This aims to release the fascia that covers the muscles and reduce pain caused by its abnormal adhesion.
- Trust technique: This is based on the realignment of the joints through rapid, painless, and controlled movements. It usually causes a feeling of immediate relief. This is the best-known technique.
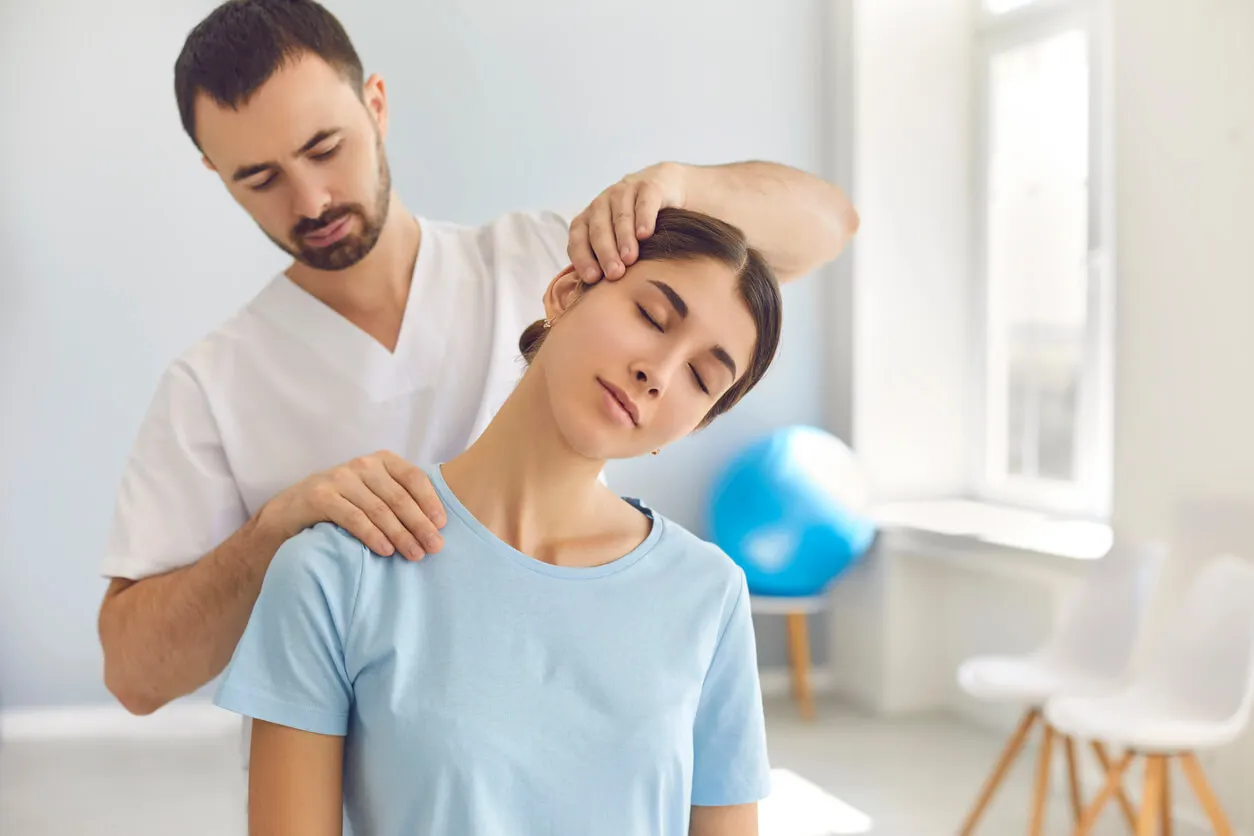

When is osteopathy recommended?
Osteopathy is useful in a wide variety of bodily and functional disorders. First of all, the person should see a physician to obtain an accurate diagnosis of the disease. In this way, the specialist can guide the treatment and offer different therapeutic alternatives. Some of the most frequent indications of osteopathy are the following:
- Musculoskeletal problems: contractures, tendinitis, sprains, radiculopathies, trauma and degenerative joint disorders.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: gas, constipation, gastritis, abdominal colic, irritable bowel syndrome and indigestion.
- Respiratory diseases: bronchitis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Genitourinary disorders: dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, and bladder incontinence.
- Pregnancyproblems: lumbar pain, sciatica, pubic pain.
- Cranial disorders: trigeminal neuralgia, vertigo, migraine, insomnia and chronic fatigue.
- Pediatric conditions: infant colic.
Contraindications of osteopathy
Osteopathic therapy is contraindicated in those people with evidence of structural bone weakness due to tumor processes, and rheumatic, inflammatory, or vascular alterations. Such is the case in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, bone metastasis, fractures, unstable joints, osteopenia and recent surgeries.
Other conditions in which osteopathy is contraindicated include the following:
- Carotid or vertebrobasilar disease
- Hypercoagulable states
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Respiratory infections
- Psychiatric disorders
- Open wounds
- Tumors
Continuous medical supervision will ensure the success of the treatment
Osteopathy is a therapeutic discipline that employs external stimuli through manual techniques to alleviate various conditions in the body. Therefore, it’s a complementary tool to professional management that shouldn’t replace the treatment provided by a specialist.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Jagua Gualdrónz A. Medicina alternativa en el tratamiento de la osteoartrosis y artritis reumatoide. Revisión sistemática de la literatura y meta-análisis. Rev.Colomb.Reumatol. 2012; 19( 4 ): 234-244.
-
Bagagiolo D, Rosa D, Borrelli F. Efficacy and safety of osteopathic manipulative treatment: an overview of systematic reviewsBMJ Open. 2022; 12: e053468.
- Dal Farra F, Risio RG, Vismara L, Bergna A. Effectiveness of osteopathic interventions in chronic non-specific low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement Ther Med. 2021 Jan;56:102616.
- Cicchitti L, Martelli M, Cerritelli F. Chronic inflammatory disease and osteopathy: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0121327.
- Ruffini N, D’Alessandro G, Cardinali L, Frondaroli F, Cerritelli F. Osteopathic manipulative treatment in gynecology and obstetrics: A systematic review. Complement Ther Med. 2016 Jun;26:72-8.
- Eguaras N, Rodríguez-López ES, Lopez-Dicastillo O, Franco-Sierra MÁ, Ricard F, Oliva-Pascual-Vaca Á. Effects of Osteopathic Visceral Treatment in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 19;8(10):1738.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








