What Is Abdominal Strain?
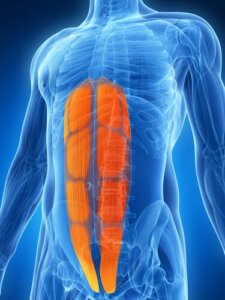
Abdominal muscle strain is sometimes called an abdominal muscle sprain. It’s an injury where the internal structure of the abdominal muscles is damaged.
Strains involve ripping or tearing of muscle tissue. Normally, these rips or tears are very small. However, they can be quite bothersome.
What does the abdominal musculature consist of? What purposes does it serve?

The musculature of the abdomen consists of 4 main muscle groups:
- External obliques
- Internal obliques
- Rectus abdominis
- Transversus abdominis
People have always thought that training the abdominal muscles was a “miracle exercise” to uncover abs and improve one’s appearance. However, these muscle groups have other much more important functions.
They’re necessary for the lumbar rachis to function correctly. They additionally play a stabilization role based on their ability to decrease pressure on the dorsal lumbar intervertebral discs. Due to this, they provide stability both while still or in motion, and prevent pelvic anteversion.
What can cause abdominal strain?
This injury can occur with any abrupt movement. We often move using incorrect posture that feels fine at first, but in the end injures us.
Sometimes people try to lift heavy items and overexert themselves because they think they can handle it, without thinking of the consequences. In this sense, an abdominal strain can occur when performing an activity for which the musculature of this part of the body wasn’t prepared.
You might enjoy reading: The Role of Lactic Acid in Exercise
Additionally, we need to keep in mind that anything in excess is bad, including physical exercise. Pushing your body too far can have serious consequences. In this case, it can produce abdominal strain. However, it can lead to much more serious injuries if you don’t take proper precautions.
It’s also very important to make sure you’re practicing sports or exercises correctly, since using the wrong techniques can also lead to this injury.
Lastly, abdominal strain can occur when you twist your body abruptly if something startles you, or due to an emergency. The muscles suddenly tense up and get damaged.
Risk factors
We’ve covered possible causes that can trigger this injury. Now we’ll explain some other factors that contribute to the occurrence of this painful lesion. Some of the main ones we’ll mention are:
- Not warming up before exercising: Warm-up exercises before physical activity are essential for avoiding any type of injury. Warming up prepares the musculature, boosts circulation, and activates the muscles before challenging them.
- Weak musculature of the back: If the muscle mass isn’t strong and healthy, injuries from any movement can occur more easily. For this reason, regularly practicing moderate physical exercise is fundamental for enjoying good health.
- Exercising in cold weather: Cold weather worsens the situation in a similar way that not warming up correctly does. Abrupt movements can cause abdominal strain. In cold weather, it’s even more essential to warm up gradually when you exercise.
What are the symptoms of this injury?
Although the following symptoms we’ll mention can occur if you experience an abdominal strain, it doesn’t always mean that’s the cause. For this reason, you shouldn’t assume that you’ve injured the muscles, since something else could be the cause of these symptoms.
It’s important to turn to your doctor to avoid complications and clear up any questions. Some common symptoms of this injury are:
- Muscle pain immediately after the injury
- Stiffness and physical discomfort
- Difficulty flexing abs, or pain when stretching the abdominal muscles
- Pain when you touch the affected area
- Muscle spasms
- Inflammation or bruising
Also read: Five Habits to Recover from a Muscle Injury
Treatment
The abdominals aren’t muscles that we can allow to rest like quadriceps or biceps. It’s a muscle group that, as we’ve outlined, is critical for posture and movement.
You can apply a bag of ice over the affected area for approximately 20 minutes. Don’t put the ice directly on the skin, or you could injure your skin.
However, don’t hesitate to turn to your doctor so they can provide you with appropriate treatment. If necessary, they can prescribe you pharmaceutical pain relief.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Conte SA, Thompson MM, Marks MA, Dines JS. Abdominal muscle strains in professional baseball: 1991-2010. Am J Sports Med. 2012 Mar;40(3):650-6.
- Forsythe B, Knapik DM, Crawford MD, Diaz CC, Hardin D, Gallucci J, Silvers-Granelli HJ, Mandelbaum BR, Lemak L, Putukian M, Giza E. Incidence of Injury for Professional Soccer Players in the United States: A 6-Year Prospective Study of Major League Soccer. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022 Mar 24;10(3):23259671211055136.
- Johnson R. Abdominal wall injuries: rectus abdominis strains, oblique strains, rectus sheath hematoma. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2006 Apr;5(2):99-103.
- Maquirriain J, Ghisi JP, Kokalj AM. Rectus abdominis muscle strains in tennis players. Br J Sports Med. 2007 Nov;41(11):842-8.
- Ruff AN, Cornelson SM, Panter AS, Kettner NW. Rectus abdominis muscle tear diagnosed with sonography and its conservative management. J Ultrasound. 2020 Sep;23(3):401-406.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








