What Causes Superficial Thrombophlebitis?

Written and verified by the pharmacist Fabiola Marín Aguilar
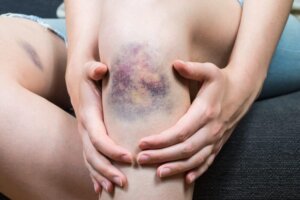
Prolonged inactivity, as a consequence of injury or surgery, can lead to the formation of clots, which impede normal blood flow. This situation can cause deep or superficial thrombophlebitis and directly affects our health and quality of life.
What is thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is an inflammatory process that results from the formation of a blood clot or thrombus in a vein that obstructs blood flow. In fact, it most commonly appears on the legs or lower extremities. Depending on the affected vein, thrombophlebitis can be one of two types:
- Deep
- Superficial
Generally, deep thrombophlebitis occurs in the deep venous system, which supplies muscles and tissues with blood, and can lead to very serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism.
Superficial thrombophlebitis primarily affects the great saphenous vein, which is the large superficial vein in the thigh and leg. To date, superficial thrombophlebitis has been perceived as self-limiting and relatively benign, but we should note that it can lead to the development of deep vein thrombosis and other complications.
Although the rate of incidence of superficial thrombosis is not very clear, it’s thought to be higher than that of deep vein thrombophlebitis, which affects approximately 1 in 1,000 people.
Types of superficial thrombophlebitis
- Sterile superficial thrombosis. This is the type that happens most frequently.
- Superficial traumatic thrombophlebitis. This happens after an injury to the limb and normally causes the appearance of large bruises in the surrounding tissue.
- Infectious thrombophlebitis. Most are the consequence of prolonged intravenous cannulation.
- Migratory thrombophlebitis. This is a recurring superficial thrombophlebitis with no identifiable cause. It can be associated with more serious diseases, such as carcinoma of the pancreas.
You might also be interested in: 5 Alternative Treatments for Varicose Veins
Symptoms associated with superficial vein thrombosis
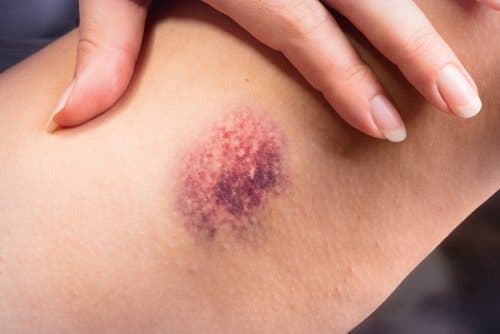
Diagnosis is based on the appearance of the following symptoms:
- Local pain
- Erythema
- Pruritus
- Sensitivity
- Reddening of the skin
- Tightening of adjacent tissue
What causes superficial thrombophlebitis?
Superficial thrombophlebitis shares many risk factors with other thrombotic disorders. Of all the risk factors associated with the development of superficial thrombophlebitis, the most important and clinically identifiable is varicose veins.
Other common causes associated with the appearance of thrombophlebitis:
- Prolonged immobility or inactivity
- Hypercoagulable state
- Previous episodes of superficial thrombophlebitis
- Long trips
- Surgery
- Pregnancy
- Estrogen-dependent hormone therapy
- Excess weight or obesity
What’s the treatment?
Current treatment is focused on relieving pain, inflammation, and above all, preventing progression to deep vein thrombophlebitis. The risk of progression to venous thromboembolism is approximately 5%.
Additionally, patients with thrombi above the knee, that is, near the sapheno-femoral junction, or clots greater than 5 cm, are considered patients at risk of thromboembolic complications.
Treatment is based on the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, for local pain relief. However, in more severe cases or in situations where the patient has risk factors, doctors use low-molecular-weight anticoagulants, such as some heparins. Doctors also often prescribe these after surgery to prevent clot formation.
You might be interested in: Auscultation of Veins and Arteries
How can you prevent superficial thrombophlebitis?
Remember that your risk of suffering thrombophlebitis increases with prolonged inactivity. This can happen because of a long trip, a surgical procedure, or as a consequence of a disease, such as obesity. In order to prevent the formation of a blood clot you can:
- Go for a walk
- Move your legs regularly
- Wear loose clothing
- Drink plenty of fluids
Currently, there is greater medical knowledge about superficial vein thrombosis, which has changed the methods of diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Until a decade ago, doctors considered it a banal and easy-to-diagnose disease, but it also had no clear treatment.
However, doctors now classify superficial venous thrombosis as a potentially serious condition, since it can lead to deep thrombosis and which has fatal consequences, such as pulmonary embolism.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- https://www.cochrane.org/CD004982/PVD_treatment-superficial-thrombophlebitis-leg
- https://www.fisterra.com/guias-clinicas/trombosis-venosa-superficial/
- Nasr H, Scriven JM. Superficial thrombophebitis (superficial venous thrombosis). BMJ. 2015, 350: h2039.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








