Tapeworm Infection: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment


Written and verified by the biologist Samuel Antonio Sánchez Amador
Tapeworm intestinal infection is common among people who eat undercooked beef or pork. According to information published by the World Health Organization (WHO), taeniasis (the medical name for this parasitic disease) causes digestive discomfort and neurological complications in the most severe cases.
How does infection happen? What are the types of tapeworms that infect humans? These and other questions may arise when talking about this parasite.
Below, we’ll take a closer look at the most relevant aspects of this parasite.
Contracting the parasite
Taenia is a genus of parasitic flatworms in the cestodes class. They’re extracellular endoparasites since they live inside their host, but they don’t work at the cellular level, as is the case with viruses.
They have a complex life cycle and, depending on the stage causing the condition, two diseases can occur in the affected individual.
- Adult tapeworms produce taeniasis when they lodge in the intestine of the final host.
- The larval and juvenile forms produce cysticercosis, an even more serious condition that occurs when these are located in various organs and tissues of the affected person.
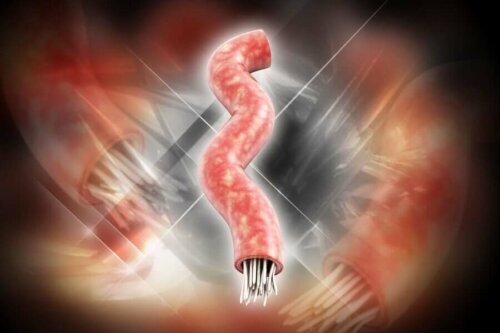
In their adult form, tapeworms are shaped like clearly segmented and flattened worms. In their head or scolex, they have a series of hooks, which allow them to attach their oral apparatus to the patient’s intestinal walls and feed on the food that passes through it.
Learn more: 5 Tips to Eliminate Intestinal Parasites
A complex cycle
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the human tapeworm is caused by three species:
- Taenia saginata or bovine tapeworm.
- Taenia solium or bovine tapeworm.
- A species of Asian origin, Taenia asiatica.
It’s important to emphasize that humans are the only definitive host for this parasite, unlike many other diseases transmitted from animals to people. To simplify their complex life cycle, we can summarize the steps in three main ones.
- In the first place, an infected human expels eggs or segments of the adult tapeworm in their feces, releasing them to the ground, where they can remain for up to months.
- Then, pigs and cows can accidentally consume these eggs and, over time, the larval forms settle in the tissues of the animals, leading to cysticercosis.
- Finally, humans ingest these meats infected with juvenile worms, and one of them develops as an adult in the intestinal tract, closing the cycle.
Human feces -> meat from infected pigs or cows -> intestine
Symptoms of a tapeworm infection
Most cases of tapeworm infection are asymptomatic. However, some have gastrointestinal disorders and other complications. The clinical manifestations of taeniasis include the following:
- Abdominal pain and loss of appetite.
- Progressive weight loss with no apparent explanation.
- General upset stomach.
These symptoms don’t appear until the parasite is large. Unless a doctor does a stool culture (where they can see the eggs of the adult tapeworm), an infected patient may have tapeworm for years without realizing it.
However, the case of cysticercosis is very different. In fact, this is a condition caused only by Taenia solium. In this case, the human being isn’t infected by eating meat with the larvae, but by ingesting the eggs directly. Thus, the parasite mistakes the human being for the intermediate host (pig or cow) and produces cysticercosis, or an invasion of larvae into the tissues, in the human body. However, we should note that this is not the natural cycle of tapeworms.
Additionally, the clinical symptoms differ greatly, depending on the affected tissues. However, when the larvae settle in the brain, neurological symptoms are decisive in detecting the disease. These include the following:
- Constant and strong headaches
- Epileptic seizures
- Disorientation
- Memory loss

You might be interested in: Natural Remedies that May Help Eliminate Parasites
Prevention and treatment
You can treat both cysticercosis and taeniasis with antiparasitic medications. Especially in the case taeniasis, the prognosis is very positive. However, cysticercosis sometimes requires surgery and, if left unattended, can be fatal.
The best prevention is, as in almost all cases, good hygiene and food safety. This is why these intestinal parasites are so rare in high-income countries: the food follows rigorous checks and they avoid the sale of meat with cysticercosis.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- CDC, C. para el control y la prevención de enfermedades. (2013). Teniasis, definición. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/taeniasis/es/enfermedad.html
- Taenia, wikipedia. Recogido a 10 de junio en https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taenia#Fase_adulta
- World Health Organization. (2017). OMS | Teniasis y cisticercosis.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








