What to Do When Someone is Choking

Written and verified by psychologist Valeria Sabater
Whether you have choked on something before or not, it’s a good idea to learn the Heimlich maneuver. This way, you’ll know what to do when someone is choking.
Choking is more common than you might think. A piece of food or another foreign object can get stuck in an airway and suffocate someone slowly. It’s terrible when this happens to you, or if you’re there when someone is choking. Here are some simple tips that may help you save a life.
What to do when someone is choking
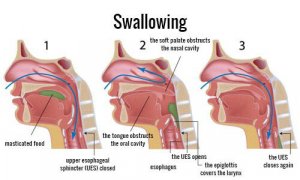
1. Identify the type of choking
-Partial obstruction: If the person is making sounds or coughing, this is a good sign. It means that their airway isn’t completely obstructed. Coughing is a defense mechanism that expels pieces of food or other objects from the airway. Thus, it’s best to encourage the person to continue coughing.
If you can see the object that is obstructing their throat, remove it by using your index finger and thumb.
Even if the situation starts with partial choking, you should be aware that this could change to complete obstruction of the airway. If the child is not even one year old, remember that if they’re crying and coughing, that’s always a good sign.
-Complete obstruction: the person isn’t making any sound but is conscious. They can’t cough because the object is completely blocking their airway. This is when the Heimlich maneuver should be used.
2. Use the Heimlich maneuver on adults and children over the age of one
Remember to only use the Heimlich maneuver if the person can’t cough, talk, shout, but is conscious. We must help them immediately in this situation, otherwise the person will lose consciousness. It’s important to act quickly, but also calmly and confidently. It’s a simple operation:
- Stand behind the person, slightly to one side. If you’re right-handed, stand a little to your left, and if you’re left-handed, a little to your right.
- Now hold their chest with one hand and bend the person or child slightly forward, so that the object that is choking them will move into the mouth, forward, and not further down the throat.
- Then, give the person 5 blows between the shoulder blades, with the heel of your hand, the part between your palm and your wrist. The blows should be hard.
- After each blow, check if the obstruction has moved.
- If the airway is still blocked and the person still can’t breathe, give five abdominal thrusts.
- Make a fist with one hand and place it in the middle of their stomach. Put the other hand over the first. Pull both hands towards you. Repeat this movement until the object comes out (Don’t do this on pregnant women, children under the age of one, and obese people).
- If the airways are still obstructed after three cycles of abdominal thrusts and three cycles of back blows, tell someone to call an ambulance. Never leave the person on their own and keep on doing the Heimlich maneuver.
Discover: Laurel Remedies to Improve your Respiratory Health
Babies under the age of one
- If the baby isn’t crying or coughing, quickly lie them on their stomach along the length of your forearm or over your legs, with their head facing down. Support their head with one hand.
- Give five firm blows to the baby’s back with the heel of your hand. After each blow, look inside their mouth and remove any obstruction you can see.
- However, never put your fingers in a baby’s mouth if you can’t see and reach the obstruction, as you may push it further down their throat and worsen the situation.
- If their airway is still blocked, apply five chest thrusts with your fingers. After each thrust, check if the object has come out of their mouth.
Read on: 7 Signs That Indicate You Should Take Your Baby to the Doctor
As you can see, this technique is very simple, just keep calm and be sure of yourself. If you’re wondering what to do when someone is choking, the Heimlich maneuver is effective. This is why you should learn how to do it and apply it when someone is choking. You might save someone’s life one day!
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Lapostolle, F., Desmaizieres, M., Adnet, F., & Minadeo, J. (2000). Telephone-assisted Heimlich maneuver [3]. Annals of Emergency Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1067/mem.2000.108176
- Guildner, C. W., Williams, D., & Subitch, T. (1976). Airway obstructed by foreign material: The Heimlich maneuver. Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-1124(76)80099-8
- Pai-Dhungat, J. V., & Parikh, F. (2008). Heimlich Maneuver. The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








