Pulmonary Edema: Symptoms and Causes

Written and verified by the doctor Leonardo Biolatto
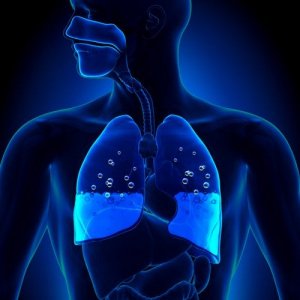
Pulmonary edema is a condition that consists of fluid accumulation in the lungs. This accumulation causes difficulty in breathing. Therefore, it puts the patient’s life at risk.
In most cases, pulmonary edema occurs due to heart problems. However, trauma, pneumonia (lung infection), or even drugs can also cause it. When the edema appears suddenly, it’s a medical emergency. Thus, it can be fatal. At other times, however, it occurs gradually. Nonetheless, it’s a very urgent condition that must be dealt with.
In this article, we’ll explain what pulmonary edema is, as well as its causes and symptoms.
What’s a pulmonary edema?
The alveoli are air pockets the lungs form. In this sense, they’re responsible for absorbing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide during respiration. When they fill with liquid instead of air, this gas exchange can’t be done correctly.
This accumulation of fluid is called pulmonary edema. It’s often caused by heart-related problems. In these circumstances, it’s called cardiogenic pulmonary edema. It mainly occurs when the heart’s left ventricle is weakened.
Moreover, it may not be related to the heart (noncardiogenic pulmonary edema). For example, it may happen when a person goes to high altitudes.
This article may interest you: Everything You Need to Know About Treating Pneumonia
The causes of pulmonary edema
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
As we mentioned above, cardiogenic pulmonary edema occurs due to heart disease. The most common problems pulmonary edema causes are:
- Coronary artery abnormalities. These arteries are responsible for the circulation of the heart. They usually become clogged due to an accumulation of fat (atheromatous plaque). This weakens the heart. Thus, the blood tends to accumulate in the lungs, and this makes the liquid pass to the alveoli.
- Heart muscle injuries. This is called cardiomyopathy. As in the previous case, when the heart doesn’t beat strongly enough, the fluid returns to the lungs.
- Heart valve problems.
- Hypertension.
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
These don’t involve heart problems. In this case, the main causes are:
- High altitudes. When a person goes to high altitudes, a pressure increase due to vasoconstriction of pulmonary capillaries may occur. As a consequence, the liquid passes into the alveoli.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome. This condition occurs when the lungs fill with fluid and white blood cells. Trauma or infection can cause it.
- Medication.
- Pulmonary embolism. This occurs when a clot clogs a pulmonary blood vessel. This doesn’t allow blood to circulate properly.
- Viral infections.
- Smoke inhalation or choking.
You might like this article: Pericardial Effusion: Diagnosis and Treatment
Symptoms
Overall, the symptoms depend on the cause and how fast it occurs. In this regard, when it occurs acutely, the main symptoms are:
- Shortness of breath that worsens when the person lies down.
- Choking sensation.
- Breathing noises (also known as wheezing).
- Cough (with or without blood).
- Tachycardia; the heart beats at an accelerated pace.
- The patient’s skin may be cool and moist and their lips may be blue.
On the other hand, when the edema occurs gradually, the symptoms are slightly different:
- Difficulty breathing also occurs, both with effort as well as when the patient lies down.
- The legs may swell.
- Increased feeling of fatigue.
- Cough that occurs when the person lies down and disappears when they sit down.
- Weight gain.
How to prevent it
To try to prevent it, you should prevent any heart problems. In this sense, it’s necessary to control your blood pressure. This is because hypertension is a major risk factor for heart disease.
Also, exercising moderately every day and following a proper diet are essential measures. These measures help control blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels. This is important because cholesterol is related to coronary artery disease.
On the other hand, patients should avoid smoking and drinking alcohol. Also, experts recommend maintaining a healthy weight. Finally, of course, you should try to control your stress.
Conclusion
If you feel shortness of breath, fatigue, or any of these symptoms, please see a doctor urgently. Remember that pulmonary edema is a severe situation. As such, it puts your life at risk.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Edema Pulmonar: Síntomas, Tratamientos, Causas e Información. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2019, from https://cuidateplus.marca.com/enfermedades/respiratorias/edema-pulmonar.html
- EDEMA PULMONAR » Causas, Síntomas y Tratamientos. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2019, from https://www.edemapulmonar.com/
- Insuficiencia cardíaca – Trastornos del corazón y los vasos sanguíneos – Manual MSD versión para público general. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2019, from https://www.msdmanuals.com/es/hogar/trastornos-del-corazón-y-los-vasos-sanguíneos/insuficiencia-cardíaca/insuficiencia-cardíaca
- Definición de edema pulmonar – Diccionario de cáncer – National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2019, from https://www.cancer.gov/espanol/publicaciones/diccionario/def/edema-pulmonar
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








