6 Possible Causes of a Lump on the Head


Reviewed and approved by the doctor Leonardo Biolatto
A lump on the head can appear in many forms, and be due to different factors. They’re small masses of variable consistency and size that usually appear progressively. Even if they increase in size in this area, it isn’t always indicative of a malignant tumor. Here are 6 possible causes of a lump on the head.
The human head is covered by several layers in which various types of glands, blood vessels, and nerve pathways are located. It’s also protected by the cranial bones that surround the entire brain structure.
The presence of a lump on the head isn’t usually accompanied by other symptoms, so, in some people, it goes unnoticed for a long time. However, it’s possible to feel discomfort when touching the scalp. Early assessment by a professional is vital if the lesion persists.
Common causes of a lump on the head
People are often alarmed when they feel a lump on the skin of the skull. However, these lesions aren’t usually dangerous and a large number of them disappear quickly with treatment.
1. Head trauma
Direct blows to the head often result in the appearance of lumps of varying sizes. As a rule, the increase in volume on the scalp is inflammatory in nature. In this regard, the affected person may suffer pain in the area of the blow, together with headaches and redness in the area.
Similarly, severe blows to the head are associated with larger lumps and bleeding. Studies affirm that, in mild cranial trauma, it’s common to see a subgaleal hematoma without skull fracture. This is nothing more than a collection of blood between the scalp and the bones in the head.
Lumps from mild to moderate blows usually disappear on their own after a couple of days. However, it’s advisable to use cold compresses and analgesic medication to alleviate the symptoms.
In case of severe trauma with loss of consciousness, medical attention should be sought as soon as possible.
Read more: What Are the Causes of Left Side Headaches?
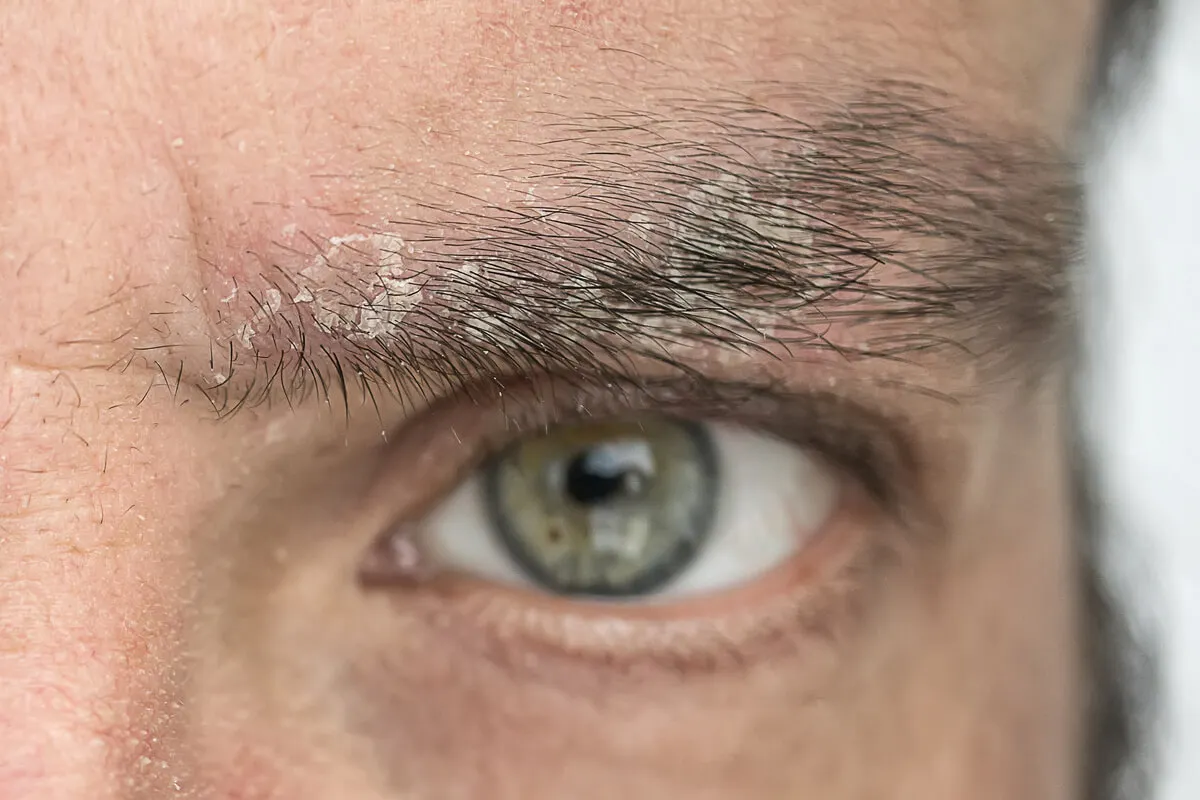
2. Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a condition characterized by the excessive production of sebum by the skin glands. This is one of the most common causes of a lump on the head and is often accompanied by whitish crusting and dandruff. In addition, some people may experience itching and redness.
Research indicates that the most affected area is the scalp, due to the large number of sebaceous glands. However, it can also affect the eyebrows, nose, chest, and eyelids. The area around the lump is usually soft and painful to the touch.
The diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is made by a physician specializing in dermatology. Treatment usually includes the use of keratolytic and antifungal shampoos, as well as topical corticosteroids.
3. Lipomas and sebaceous cysts
A lipoma is a small benign fatty tumor that forms between the skin and underlying muscle tissue. It’s commonly found on the back of the head, extremities, and thorax. This type of lesion may be painless or accompanied by discomfort, indicating the need for surgical removal.
Sebaceous cysts, on the other hand, occur as a lump on the head containing fatty fluid, resulting from the obstruction of a follicular duct for various reasons. These can be uncomfortable when brushing the hair and if there’s pain then this usually means there’s been an infection of the cyst.
Know more: Reasons for a Hard Lump Under the Skin
4. Folliculitis
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicles found in the skin. This condition is usually rare on the scalp and is usually associated with infection of the follicle by bacteria or fungi. It may produce a purulent discharge.
Similarly, the affected person may have itching and tenderness in the area. In most cases, these bumps disappear quickly when treatment starts. Treatment of folliculitis includes antifungals and antibiotics.
5. Allergic reaction
Allergic reactions on the skin usually take the form of urticaria. This is characterized by the appearance of red spots, bumps, wheals and intense itching. In this regard, allergy to hair products is one of the frequent causes of a bump on the head.
Treatment is aimed at reducing the overreaction of the immune system and alleviating the symptoms. It includes the use of anti-allergic drugs, such as loratadine, or corticosteroids.
6. Skin cancer
Skin cancer is one of the causes of a lump on the head. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of tumor lesions on the skin surface. This type of neoplasm appears as a pearly, non-painful lump, accompanied by dark spots with raised edges.
In this regard, it’s advisable to seek medical attention if you have a lump on the scalp with spots around it. The diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma is usually made by biopsy. Treatment is usually surgical.
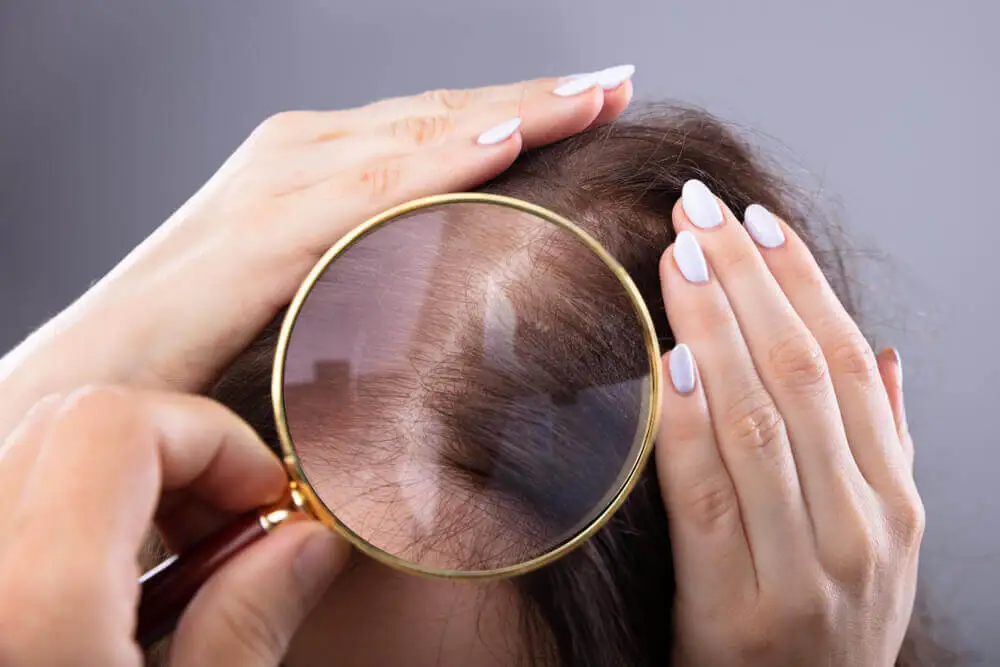

When to seek medical attention for a lump on the head?
The causes of a lump on the head can be very varied and in most cases are benign. However, it’s advisable to see a medical specialist if there are changes in the lesion. Such is the case of an increase in size, changes in color, appearance of new lesions, purulent discharge, or bleeding.
Health professionals are the only ones qualified to identify the cause of the lump and indicate the best course of action to follow. Prompt treatment is the key to ensuring a good long-term prognosis.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Rodríguez J, Mederos A, Cisneros M, Estrada M. Trauma craneal leve. Rev Cub Med Mil. 2000 Abr ; 29( 1 ): 46-51.
- González F. Manejo dermatológico. Rev Obstet Ginecol Venez. 2016 Jun ; 76(1 ): 97-103.
- Bertona E, De Paulis A, Gutiérrez M, Santa M, et al. Un caso inusual de quiste sebáceo infectado por Dermabacter hominis. Rev. argent. microbiol. 2016 Dic ; 48( 4 ): 303-307.
- Maldonado C. Foliculitis infecciosas. (Parte I). Rev Cent Dermatol Pascua. 2014 ; 23(3): 90-98.
- Darias C, Garrido J. Carcinoma basocelular. Un reto actual para el dermatólogo. Rev.Med.Electrón. 2018 Feb ; 40( 1 ): 172-182.
- Tincopa-Wong Ó. Urticaria y angioedema: una visión general. Acta méd. peruana. 2014 Abr ; 31( 2 ): 111-124.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








