The Main Symptoms of Hypocalcemia


Written and verified by psychologist Valeria Sabater
A medical professional diagnoses you with hypocalcemia when your blood calcium levels are low. Now, to understand why this occurs and how it affects your health, you need to understand some important aspects.
Below, we’ll review in greater detail the importance of calcium in the body, what hypocalcemia consists of, and its causes, main symptoms, prevention, and treatment, among other important information to make sure you’re well-informed.
How does calcium affect health?
Calcium is a mineral that helps the body to perform multiple basic and essential functions for your health and well-being. Contrary to popular belief, you don’t only need it for strong bones and teeth.

In general, calcium is essential because it:
- Favors vitamin B12 absorption.
- Allows blood to clot.
- Is important for the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contractions.
- Contributes to the activation of many basic body enzymes.
- Also, it aids the internal tasks of cell membranes, favoring the exchange of oxygen and nutrients.
- In addition, calcium helps certain hormones fulfill their functions in the kidneys and intestines.
When there isn’t enough calcium in your blood, your health suffers and various changes begin to manifest in your body, some more forceful than others.
This article may interest you: How to Choose a Calcium Supplement
What are the causes of hypocalcemia?
According to Dr. James L. Lewis, hypocalcemia can result from a disorder of the parathyroid glands, as well as diet, kidney disorders, or certain drugs.
Here are other causes of hypocalcemia:
- Pancreatitis.
- Hypomagnesemia.
- DiGeorge syndrome.
- Kidney failure.
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism.
- The consumption of certain drugs (such as anticonvulsants, bisphosphonates, and some antibiotics, among others).
However, the most common causes are:
- Vitamin D deficiency (due to lack of sun exposure or poor diet).
- Inadequate calcium intake.
- Disorders that reduce calcium absorption.
The main symptoms of hypocalcemia
Although it doesn’t manifest with strong symptoms at first, as time passes (and there’s no treatment or improvements in diet or other lifestyle aspects), various discomforts appear, such as muscle cramps in the back and legs.
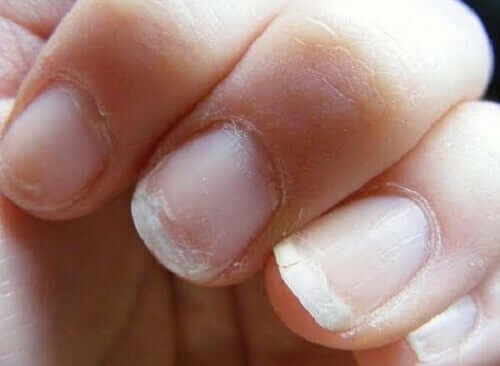
People with hypocalcemia may have dry, flaky skin, as well as weak and brittle nails, in contrast to thicker hair.
In advanced cases, hypocalcemia can cause a tingling sensation. In addition, it can affect the brain and cause confusion, trouble concentrating and remembering, delirium, depression, and hallucinations. Nevertheless, we should note that these symptoms disappear once the blood calcium levels are restored.
A medical professional can diagnose hypocalcemia with a simple blood test.
How’s hypocalcemia treated?
Treatment of hypocalcemia varies depending on the underlying cause and the patient. However, it’s common for doctors to prescribe calcium supplements and, in some cases, vitamin D supplements.
Calcium supplements are taken orally with the goal of normalizing blood calcium levels. Along with this, doctors often make diet recommendations.
- Not only dairy products are rich in calcium. Also, you can find it in legumes, such as lentils or chickpeas.
- Eggs, nuts, and broccoli are also very suitable foods to include in your diet.
- Hypocalcemic patients should avoid excessive consumption of beverages that contain caffeine, as they can interfere nutrient absorption.
- The key is to follow a balanced diet, which includes all the food groups in enough quantities.

Can it be prevented?
Yes, it’s possible to prevent hypocalcemia. How? Following a healthy lifestyle and getting periodic medical checkups.
The best thing to do to prevent hypocalcemia is to follow a balanced diet. This way, your body can get everything it needs to work properly.
While diet plays a key role, you should also exercise outdoors, as it has health benefits. Therefore, it’s advisable to take walks and take advantage of the sun’s rays to synthesize vitamin D.
Finally, regarding the prevention of hypocalcemia, it’s important to clarify something. You should never take calcium supplements without your doctor’s authorization, as it can be counterproductive.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Paula, F. J. A., & Foss, M. C. (2003). Tratamento da hipercalcemia e hipocalcemia. In Medicina. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.01.031
- Boulanger, H., Saksi, S. A., Chhuy, F., & Flamant, M. (2014). Hipocalcemia. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1636-5410(14)67518-8
- Martín, A. G., Garach, A. M., & Torres, M. M. (2016). Alteraciones del metabolismo fosfocálcico. Hipocalcemia. Medicine (Spain). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.med.2016.07.001
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








