Fatty Liver: Foods that You Should Avoid
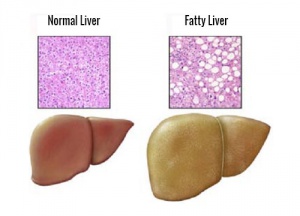
Fatty liver disease has become one of the most important medical problems of our time. One of the main causes behind this issue is our modern lifestyle based on long periods of time without engaging in physical activity. Furthermore, there’s been an increase in the consumption of snacks and junk food that put excess fat into our body but contain very little nutritional value.
The ramifications of these dietary changes are excess weight, issues having to do with obesity and lastly, excess fat that accumulates in the liver and complicates the performance of basic functions.
Foods you should avoid if you suffer from fatty liver disease
Once a doctor diagnoses someone with fatty liver disease, adopting healthy habits immediately is crucial. In other words, a person with fatty liver disease should follow a balanced diet. Also, they should incorporate exercise into their daily routine. This way, they’ll be able to stabilize their weight and facilitate the recovery of their liver functions.
Foods that are high in fat

(Photo: PABLO TESTIGOCRIMINAL/ Flickr.com)
A fatty liver will have problems digesting food that’s high in fat and other similar elements. Which is why they should avoid eating fatty foods or reduce them to the bare minimum. Moreover, foods that are high in fat lead to weight gain. This may also cause health complications for someone suffering from fatty liver disease.
Foods to avoid include:
- Fried foods
- Foods baked in the oven that contain cheese or fat
- Dairy products
It’s absolutely essential that someone who suffers from fatty liver disease eliminates completely from their diet foods that contain a lot of fat.
Read also:
Foods with a high glycemic index
Some foods that are rich in natural sugars or those that have a high glycemic index cause blood glucose levels to rise, which severely affects the liver. Foods that people with fatty liver disease should eat in moderation include potatoes, watermelon, raisins, banana, white bread, corn derived products, ice cream, flavored yogurts and chocolate that’s high in simple carbohydrates.
Processed grains
People who have fatty liver disease should consume whole grains and avoid processed grains at all costs. This way, they add more fiber to their diet which helps to control cholesterol and blood glucose levels, a vital step in reversing the medical condition of fatty liver disease.
Read also:
Alcohol
Alcohol consumption, whether it’s moderate or excessive, will lead to the accumulation of fat in the cells of the liver. When the accumulation of this fat surpasses the normal limits, the cells begin to become inflamed and over time scars are generated in the tissue. After this occurs, normal blood flow is obstructed and if this process is not stopped or reversed, the liver can be irreparably damaged.
Because of this, alcohol consumption should be at a minimum. And if you’ve already been diagnosed with fatty liver disease, it would be recommendable to abstain completely from alcohol consumption.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Ajmera, V. H., Terrault, N. A., & Harrison, S. A. (2017). Is moderate alcohol use in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease good or bad? A critical review. Hepatology, 65(6), 2090-2099. https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/hep.29055
- Chung, M., Ma, J., Patel, K., Berger, S., Lau, J., & Lichtenstein, A. H. (2014). Fructose, high-fructose corn syrup, sucrose, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or indexes of liver health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 100(3), 833-849. https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/pmc4135494
- Georgoulis, M., Kontogianni, M. D., Tileli, N., Margariti, A., Fragopoulou, E., Tiniakos, D., … & Papatheodoridis, G. (2014). The impact of cereal grain consumption on the development and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. European journal of nutrition, 53, 1727-1735. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24604574/
- Hajihashemi, P., & Haghighatdoost, F. (2019). Effects of whole-grain consumption on selected biomarkers of systematic inflammation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 38(3), 275-285. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07315724.2018.1490935
- Kechagias, S., Blomdahl, J., & Ekstedt, M. (2019). Alcohol consumption in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—harmful or beneficial?. Hepatobiliary Surgery and Nutrition, 8(3), 311. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6561895/
- Parry, S. A., & Hodson, L. (2017). Influence of dietary macronutrients on liver fat accumulation and metabolism. Journal of investigative medicine: the official publication of the American Federation for Clinical Research, 65(8), 1102-1115. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28947639/
- Perdomo, C. M., Frühbeck, G., & Escalada, J. (2019). Impact of nutritional changes on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients, 11(3), 677. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/3/677
- Roerecke, M., Vafaei, A., Hasan, O. S., Chrystoja, B. R., Cruz, M., Lee, R., … & Rehm, J. (2019). Alcohol consumption and risk of liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 114(10), 1574. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6776700/
- Shen, X., Jin, C., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Huang, W., … & Gao, X. (2019). Prospective study of perceived dietary salt intake and the risk of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics, 32(6), 802-809. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/JHN.12674
- Tanaka, N., Kimura, T., Fujimori, N., Nagaya, T., Komatsu, M., & Tanaka, E. (2019). Current status, problems, and perspectives of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease research. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 25(2), 163. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6337019/
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (25 de febrero de 2023). Sodium in Your Diet. https://www.fda.gov/food/nutrition-education-resources-materials/sodium-your-diet
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








