Everyday Habits that Cause Knee Pain
Written and verified by the doctor Nelton Abdon Ramos Rojas
But, what do our knees do anyway? They aren’t responsible only for stabilizing the body, but they also allow for the flexibility to bend and stretch our legs.
Without our knees, we wouldn’t be able to walk, run or turn.
The following parts contribute to the aforementioned functions:
- Muscles
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Bones
- Cartilage
If any of these parts suffer damages, pain can result in the knees.
Age doesn’t matter: kids can experience this problems just as the elderly can.
Symptoms
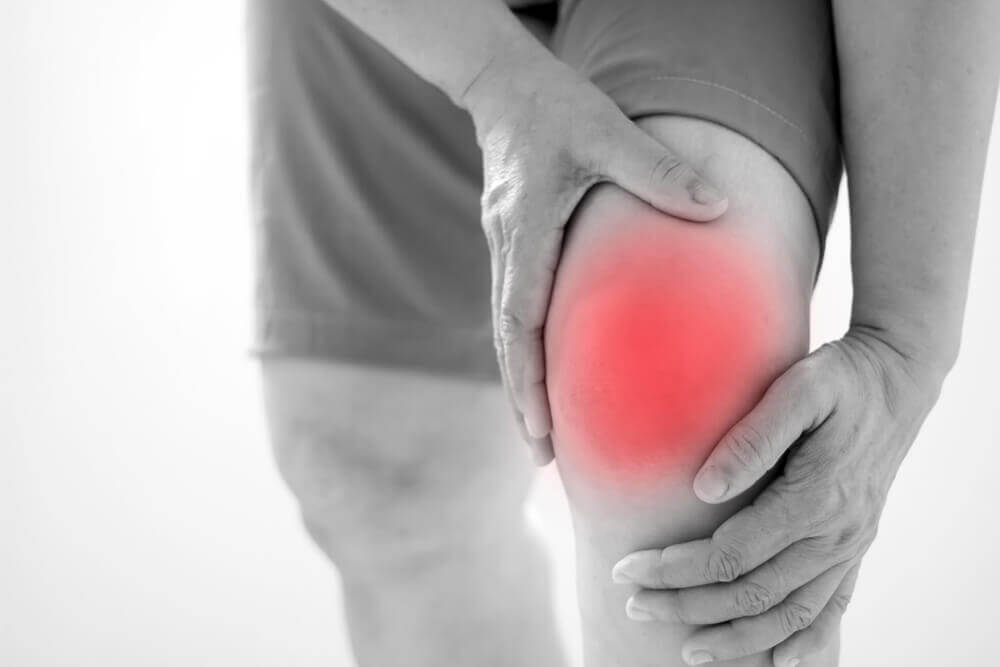
The symptoms that cause knee pain vary according to the cause of the problem. However, general symptoms are the following:
- Inflammation and rigidness
- Reddening
- Warmth to touch
- Loss of balance
- Crunching noises with movement
- Difficulties straightening the leg completly
Also read: 5 Tips and Exercises for Strong Knees
Why should I be worried?
- You can no longer put weight on your knee.
- Swelling is excessive in the area.
- You experience severe pain when extending or bending your knee.
- There’s a visible deformity.
- You suffer from fever and knee pain.
- You have the sensation that your knee moving out of its place.
What causes it?
Any mechanic anomaly in the knees can result from:
- An impact or rough movement that leads to a twist or kink.
- Knee osteoarthritis caused by the use and wearing down of its parts.
- Rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Being overweight: Excess fat increases the pressure on joints. As a result, cartilage distorts under said pressure.
- Sedentary lifestyle: When we stay in just one position for hours, our muscles weaken. Muscles are in charge of protecting our upper and lower limbs.
- Age: As time passes, the knee’s cartilage and its mechanisms loose the liquid, elasticity and flexibility that allow them to move freely.
- Extreme sports: There are some sports that are so aggressive on the knees that they damage its joints.
- High heels: The pressure that you need to use this kind of footwear shifts the spine into an unnatural position. As a result, the knees receive double the normal load.
You didn’t know? Relieve Knee Pain with This Medicinal Treatment
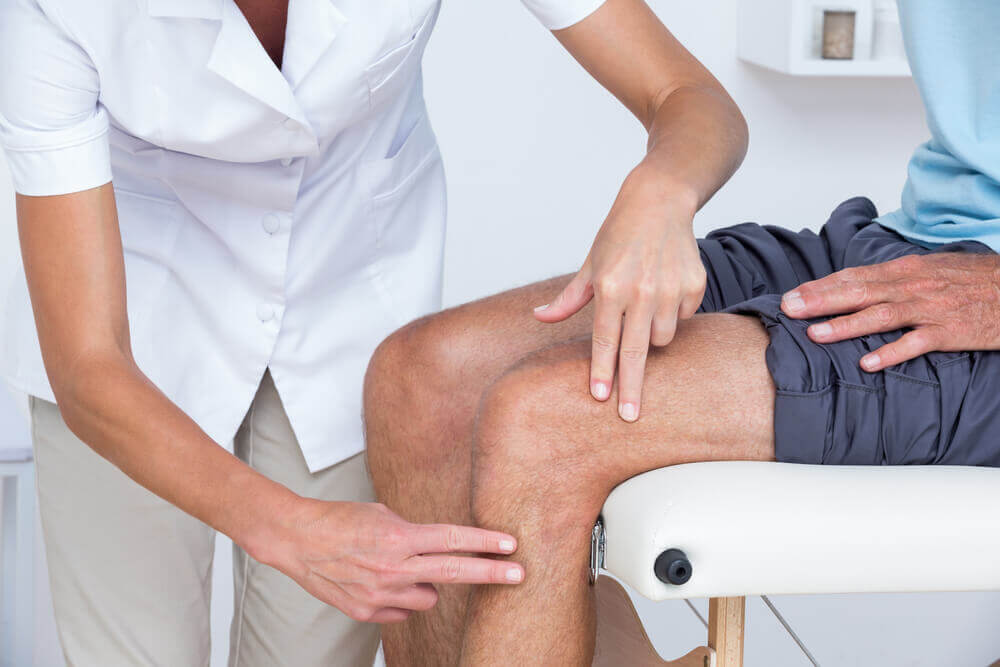
Upon noticing the first symptom of knee pain, the patient should make an appointment with a medical specialist. The specialist will then proceed to do the following:
- First, he or she will ask a set of questions to gather the patient’s medical history.
- Afterwards, the specialist will do a physical exam.
- In ambiguous cases, the doctor may order X-rays, a bone density test and CT scans. In addition, MRI scans, arthroscopes or biopsies may be necessary depending on the case.
Types of injuries
- Bursitis: Bursitis is an inflammation caused by constant pressure on the knee (for example, from kneeling for a long period of time).
- Dislocation of the kneecap: This happens when the triangular shaped bone, that covers the knee, falls out of place.
- Iliotibial band syndrome: This syndrome is an injury to the thick band that runs from the hip to the outside part of the knee.
- Pain in the front and center part of the knee.
- Rupture of ligaments: Ruptures can cause bleeding in the knee, swelling or imbalance in the knee.
- Sprains: These are minor injuries in the ligaments caused by twists.
How can you prevent knee pain?

It’s obvious that in risky situations, such as accidents, the consequences can’t be avoided. However, there are other occasions where we can do something to about the matter, for example:
- Walk and do stretching exercises before playing any sport.
- Muscles need to be strengthened. In order to do so, you need to lift weights, get on the bike and do aerobic exercises.
- You need to try to find consistency in your exercise routine. Abrupt changes raise the risk of suffering an injury. The key is to go little by little, in both aspects of strength and duration.
- One of the simplest reasons, but most frequent, for knee pain is improper footwear. It has to be comfortable and in good condition.
- If you want to maintain the right weight in order to prevent excess pressure on your knees, physical activity is an obligation. You need to exercise at least 3 times a week.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Bumbaširevic, M., Lešic, A., & Bumbaširevic, V. (2010). Anterior knee pain. Orthopaedics and Trauma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mporth.2009.06.005
- Heidari, B. (2011). Knee osteoarthritis prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis and features: Part I. Caspian Journal of Internal Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.86.056008
- English, S., & Perret, D. (2010). Posterior knee pain. Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-010-9057-4
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








