Discover the Benefits of Seaweed for Hypothyroidism
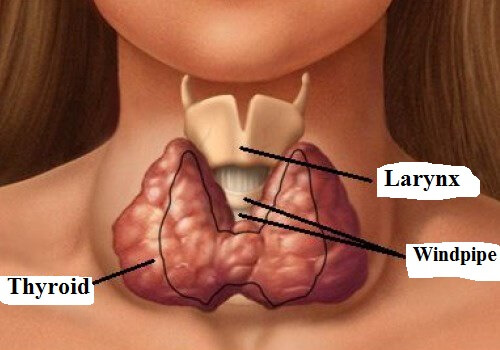
Hypothyroidism is an illness that usually affects women over the age of 50, but can also appear after giving birth. It brings with it symptoms that can affect one’s quality of life and even the physical appearance of those who suffer from it. One of the benefits of seaweed is that it helps to reduce the risk of hypothyroidism.
In this article we will explain some of the many benefits of seaweed, and particularly how it can help you thanks to its iodine content and other minerals. We will also provide some suggestions so you can discover how easy and fun it is to cook with seaweed.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is an illness that is experienced by 3% of the population. Those who suffer from this disease have decreased levels of thyroid hormones in their blood plasma.
See Also: 6 Habits that Alter Thyroid Function
The most common symptoms are the following:
- Tiredness and exhaustion.
- Muscle weakness.
- Feeling cold.
- Increase or decrease of weight without an apparent cause.
- Depression.
- Double chin in thin people.
- Hair loss.
- Pale or yellowish face.
- Fluid retention.
- Extremely dry skin.
- Lack of hair on the outer ends of the eyebrows.
What is the cause?
Also Read: Foods that Can Make You Tired
The most common causes of this disease are the following:
- Different types of thyroiditis.
- Birth defects.
- Radiation therapy on the neck.
- Anti-thyroid medication.
- Treatment with lithium.
- Chronic iodine deficiency.
Seaweed Types
Seaweed is still relatively unknown in the culinary world, despite being a medicinal food that also allows for numerous uses in our dishes.
Most people who don’t eat seaweed admit that it’s because they don’t know how to cook with it. However, adding seaweed to our dishes is much simpler than it seems and it can also add an original touch to our everyday recipes.
Thanks to Japanese cooking, seaweed has been introduced into our kitchens. Also vegetarian and macrobiotic diets are paving the way for their increased usage. They can significantly increase the amounts of minerals, including iodine in the body. This is usually very low in people with hypothyroidism.
Before using these recommendations, it’s very important to note that seaweed should always be ecological or with the guarantee that it does not contain toxic substances.

How can this food to enjoy the benefits of seaweed?
Every seaweed type has different usage instructions according to its particular characteristics. You only need to soak the more delicate kind for a few minutes, while the thicker, stronger kinds should be cooked for up to 30 or 40 minutes.
Below, we will provide a few suggestions:
- Nori: This seaweed is used in very thin sheets for making sushi. Simply moisten it and use it to wrap rice or any stuffing you choose.
- Kombu: A piece of kombu in our vegetable stews will make it easier to soften and will improve digestion.
- Wakame: If we add a little wakame while cooking creamed vegetables, it will add creaminess when you blend it, letting you replace the potato or cheese.
- Sea spaghetti: Ideal with pasta or rice.
- Dulse: These need almost no cooking, so it is very suitable for quick soups, sauces and vinaigrettes or salads.
On the other hand, there are two very beneficial seaweeds that we recommend you use as a supplemental form:
- Spirulina.
- Fucus.
Always obtain medical advice before embarking on any new diet plan.

Seaweed salt
Another option to consume seaweed daily is to prepare a salt made from seaweed, which will help increase the flavor of your foods, aside from providing you with the other benefits of seaweed.
- To make it, you must grind sea salt and whichever seaweed you choose, mix them well and keep them in a glass bottle with a tight lid. You can also add a few aromatic plants.
- The salt will act as a preservative.
You can use it the same way you would normal salt when cooking, in soup, stew, etc.
We suggest making this salt with kelp seaweed, since one of the benefits of seaweed of this type is that it’s rich in iodine and widely used in prepared salts, which are sold as dietary salts.

Foods which are best avoided
Along with the consumption of seaweed, we should limit or avoid eating foods that, although may be good for many people, are the best choice for those suffering from hypothyroidism because they block the absorption of iodine:
- Cruciferous vegetables: cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, broccoli and cabbage.
- Spinach
- Soy
- Peaches
- Beans
- Limes
Also, every type of processed or refined food is prejudicial to your health.
Images courtesy of Jacqueline and Michel Kappel.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Pineda, J., Galofré, J. C., Toni, M., & Anda, E. (2016). Hipotiroidismo. Medicine (Spain). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.med.2016.06.002
- Lozano, J. A. (2006). Hipotiroidismo. Offarm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.datak.2007.05.004
- Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre. (Consulta 2018). ALGA. Online [https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alga].
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








