11 Complications of Diabetes
Before we go into details about the complications of diabetes, it’s important to revisit what this condition actually is, the different types, its symptoms, how it’s caused, and how to avoid it.
Finally, we’ll share 11 of the most serious complications caused by diabetes.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition that occurs when the pancreas does not produce the amount of insulin that the body needs. Thus, eith it makes too little or none at all.
Diabetes develops when the level of glucose in the blood, known as your blood sugar level, is too high. Glucose in the blood is the main source of energy and is obtained from your food.
Insulin helps the glucose get to the cells of the body to be used as energy, allowing your tissues and muscles to work. When the body doesn’t produce insulin, or doesn’t produce enough, the glucose stays in the blood and doesn’t find its way to the cells.
If a diabetes patient is not treated correctly, the tissues can suffer serious damage, as well as other complications. As time passes, excess glucose in the blood causes highly serious health problems.
Despite not having a cure, diabetes can be managed in a healthy and controlled way.
Types of diabetes
- Diabetes Insipidus
- Infantile diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes
- Type-1
- Type-2
Symptoms

Amongst the main symptoms of diabetes are:
- Increased thirst and need to urinate.
- Weakness, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Irritability and mood swings.
- Feeling unwell in the stomach and vomiting.
- Blurred vision.
- Scratches and cuts that heal slowly.
- Itching or numbness in the hands and feet.
- Recurrent skin, gum, or bladder infections.
- High levels of glucose in the blood and urine.
Causes of diabetes
The causes and complications of diabetes depend on what type it is. However, some of the general factors that can cause this condition are:
- The immune system attacking and destroying beta cells in the pancreas, the cells responsible for producing insulin.
- Very little production of insulin.
- Environmental factors that can trigger the disease, like a virus.
- Being overweight and physically inactive.
- Insulin resistance.
- A family history of diabetes.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Genetic factors.
- Lifestyle.
Other causes
- Genetic mutations
- Injury to the pancreas
- Certain medications
- Other illnesses
Preventing diabetes

Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, by Type 2 can, since it’s related to obesity. Practicing healthy habits like frequent exercise and a sticking to a balanced diet will help prevent it from developing.
Advice for preventing hypoglycemia in diabetics:
- Adjust your doses of medication to suit your new needs.
- Stick to a balanced diet.
- Consume carbohydrates moderately before doing exercise.
- Always carry a source of sugar and water to take at anytime that you spot the signs of hypoglycemia.
Complications of diabetes
1. Cardiovascular problems

2. Diabetic Nephropathy
This is a disease that is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the kidneys, which means that they can’t filter the blood properly. Some people with diabetes require dialysis and, when the disease is very advanced, they may require a kidney transplant.
3. Diabetic Neuropathy

Around half of all diabetics show some form of neuropathy. A daily check of the arms and legs is very important. If they show any signs of bruising, reddening of the skin, or some other feature, they need to visit a doctor.
Among the most serious consequences of neuropathy is the amputation of feet, toes, or legs, as well as a loss of feeling in the limbs.
4. Diabetic retinopathy
This is an ocular complication that happens when the blood vessels in the retina deteriorate so much that patients can suffer a leak of fluid or blood. It’s one of the main causes of blindness.
At first, the patient may notice some changes in vision, but then the retinopathy can quickly get worse. This complication of diabetes cannot be completely avoided. However, you can reduce the risk by controlling blood sugar levels diligently.
5. Gestational diabetes

This affects approximately 18% of pregnant women and appears at around week 24 of the pregnancy. It’s characterized by a high level of glucose in the blood during pregnancy. It happens due to the hormones of the placenta blocking the action of insulin, causing an insulin resistance.
When the pregnant woman cannot receive treatment, the glucose can pass to the baby and be stored as fat. The consequence could be an obese baby or fetal macrosomia.
6. Hypertension
One of the most serious complications of diabetes is arterial hypertension. It’s one of the main causes of death in diabetics. People who have high blood pressure have a much higher risk of developing type-2 diabetes.
7. Skin complications

Skin complications can be one of the first symptoms of diabetes. If they’re noticed early, they can generally be treated successfully. Bacterial infections, fungal infections and skin irritations are some of the problems that are seen.
There are also skin problems that affect only diabetics, such as diabetic dermopathy, diabetic lipoidica necrobiosis, diabetic blisters and eruptive xantomatosis.
8. Complications with feet
These complications occur when there is damage to the nervous system. As a consequence of poor blood flow, diabetics lose sensitivity in their feet. Once a person loses feeling in the feet, they are more prone to have circulatory problems. Unfortunately, it’s even worse if the person has neuropathy.
When a diabetic patient loses sensation in their feet, sores or wounds can appear without their knowledge and form ulcers. They don’t feel pain when they do damage. A simple stone in their shoe could cause an infection and they may not realize it.
9. Amputations
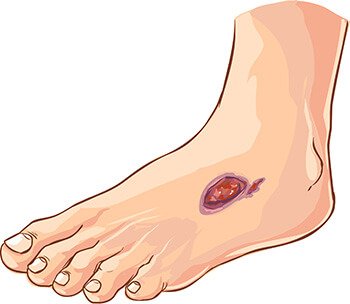
Another complication of diabetes is diabetic foot. This is an infection, ulceration, or destruction of deep tissues in the foot, which can require an amputation.
People in this situation tend to have a high level of glucose in the blood and arterial hypertension. Thus, they need to keep both of these need to be kept under control to reduce the risk of amputation.
10. Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS)
This is a serious condition, which is very common in older people with diabetes (mainly Type 2 diabetes). This causes the excess blood sugar to be passed to the urine. With this condition, when the patient doesn’t drink a lot of water, there is a greater risk of dehydration and fainting, or even falling into a coma.
To detect HHNS, you need to be vigilant to the symptoms of extreme thirst, a blood sugar level above 600 mg/dL, dry mouth, dry skin without sweat, loss of vision, high temperature, and weakness on one side of the body.
11. Male impotence

Male impotence is another complication of diabetes which is quite common in the majority of diabetic patients. The increase blood sugar level can affect circulation and nerve endings. This can do damage to the nerves responsible to achieving and maintaining an erection.
Medications used to control and regulate diabetes can also cause erectile dysfunction. However, impotence can improve gradually with healthy habits and the correct medication.
Recommendations for controlling blood sugar levels
- Assess your blood sugar levels regularly.
- Stick to your prescribed treatment 100%.
- Use the insulin prescribed by your doctor.
- Stick to an appropriate diet.
- Do regular exercise.
- Avoid products containing lots of refined sugars.
- Sleep well and maintain a regular sleep cycle.
- Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and cigarettes.
Tests
To measure the concentration of glucose in the blood, they’ll need to take a blood sample, which should be taken after fasting for 8 hours.
There is another form of blood test called an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. This test is done when a woman is suspected of having gestational diabetes.
Diagnosis
There are also other tests that they might take to establish the cause of associated symptoms like excessive thirst, urination, or hunger.
They will also check for other risk factors, such as a family history of diabetes, obesity, frequent infections, or any other complication associated with diabetes.
Treatments
The treatment of diabetes mellitus is mainly based on three things: diet, physical exercise, and medication. It aims to keep blood sugar between the normal levels to reduce the risk of complications.
In many patients with Type 2 diabetes medication is not necessary, as long as they can control their weight and do regular exercise. However, some form of medication with insulin or hypoglycemic drugs may often be required.
Most of the time, diabetes does not show itself until the patient has had it for many years. It tends to develop silently and gradually over a long period of time. This means that someone could already have diabetes and have no idea about it.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








