Oxygen Therapy: What Is it and What's its Purpose?

Oxygen therapy is a prescribed treatment that consists of administering oxygen in high concentrations. In this sense, its purpose is to treat hypoxia or blood and tissue oxygen deficiency. Also, experts mainly indicate it to treat chronic respiratory failure. However, in recent years, people have also successfully used it in the world of cosmetics.
What is it?
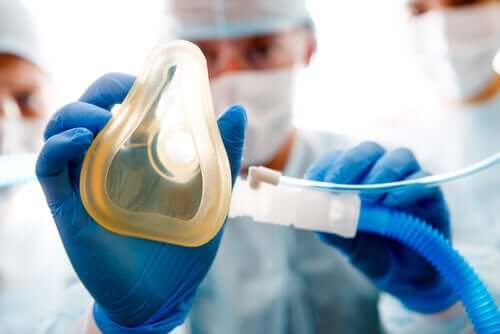
Nowadays, this type of therapy is even used for aesthetic treatments, especially for dry, oily, tired, or wrinkly skin. Also, it yields good results regarding the reduction of dark circles and skin blemishes. On the other hand, in the world of cosmetics, oxygen provides the hydration the skin needs. Also, it stimulates collagen production and helps the skin look more youthful. However, to understand how this works, it’s important to first know a little bit more about oxygen therapy.
Types
The use of oxygen therapy is key in the treatment of respiratory failure, which is when medical professionals prescribe oxygen administration. The most frequently used types of this type of therapy are:
Normobaric oxygen therapy
Normobaric oxygen therapy administers oxygen at different concentrations. Normally, it does this at a concentration between 21 and 100%. One of the most common application options are nasal prongs or masks.
Discover: 8 Tips to Treat and Control Asthma
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
This type of oxygen therapy consists of delivering 100% oxygen. In hyperbaric oxygen therapy, the patient is inside a pressure chamber. For application, a helmet or a mask is used.
The goal of this therapy is to increase oxygen supply to the tissues through hemoglobin. When a lot of oxygen enters the body, there’s more pressure in the alveolus as a result, which causes hemoglobin saturation. Therefore, alveolar oxygen pressure increases and respiratory and heart work decreases. Consequently, the body can maintain constant oxygen pressure.
Possible complications
As with any treatment, oxygen therapy may have complications. These typically arise from inadequate oxygen concentration. However, they may also be caused by excessive treatment time.
The symptoms that may occur include:
- Tracheitis and bronchitis.
- Impaired mucociliary clearance.
- Acute lung injury.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Furthermore, as a result of breathing the cold and dry mixture of gases, the patient may suffer from mucosal dryness and tears. Also, a patient may suffer from impaired mucociliary transport, sputum retention, and increased sputum density.
You should also read: How to Help Treat Bronchitis Naturally
Routes of administration

When patients are spontaneously breathing, the therapy may be applied by nasal prongs and face masks. Some of the masks include the following:
- Venturi mask. A venturi mask manages the exact oxygen concentration. During administration, the patient can’t eat or speak. Also, the patient may experience the sensation of heat and may suffer skin irritation.
- Simple face mask. A soft plastic device that covers the mouth and nose. It has lateral openings that allow the exit of exhaled air. You have to correctly position it with an elastic band to prevent leakage.
Another route of administration is the low-flow system. This system is suitable for people who need minimal oxygen. Also, the high-flow system and the hyperbaric chamber can also be used. However, patients who can’t breathe on their own will need to be treated with a mechanical ventilator.
Conclusion
Although this type of therapy is a prescribed treatment, it’s important to remember that it isn’t only used to solve health problems. Nowadays, it’s even used in some beauty treatments.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
-
Ortega Ruiz, F., Díaz Lobato, S., Galdiz Iturri, J. B., García Rio, F., Güell Rous, R., Morante Velez, F., … Tàrrega Camarasa, J. (2014). Oxigenoterapia continua domiciliaria. Archivos de Bronconeumología. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2013.11.025
-
Desola, J. (2009). Indicaciones actuales de la oxigenoterapia hiperbárica. FMC – Formación Médica Continuada En Atención Primaria. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1134-2072(09)72308-4
-
Donaire, E. C. V. J. G. (2014). Sistemas de oxigenoterapia. Manual Separ De Procedimientos.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








