How to Treat Fatty Liver Naturally
Liver steatosis, more commonly referred to as “fatty liver” disease, is a reversible condition that can disappear with the modification of a few daily habits. Although this is rather uncommon, it doesn’t become serious if treated on time. Learn how to treat fatty liver naturally in the following article.
Characteristics of fatty liver
Fatty liver disease presents itself in those whose total liver weight is comprised of 5 to 10% fat. The majority of people who suffer from this condition are either over the age of 50 or have diabetes. However, it’s true that oftentimes patients with liver fat have no complications worth mentioning. There are two classifications of this disease:
- Alcoholic liver fat: is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It is the earliest stage of liver diseases such as cirrhosis. When the liver is weak, it begins to accumulate the fats that it is unable to break down. If a patient stops drinking alcohol, the condition disappears on its own (after six to eight weeks of abstaining). There’s no doubt that if the person continues to drink, that more severe complications can come down the road.
- Non-alcoholic liver fat: is not a result of alcohol consumption, even though it is also one of the early causes of cirrhosis. This disease forms a “scarred” lining instead of a healthy one, which in the long-term prevents the organ from functioning as it normally should. Obesity, Type-II Diabetes, high cholesterol, metabolic syndrome (also known as syndrome X), high levels of triglycerides, or losing weight too quickly can all trigger this condition.
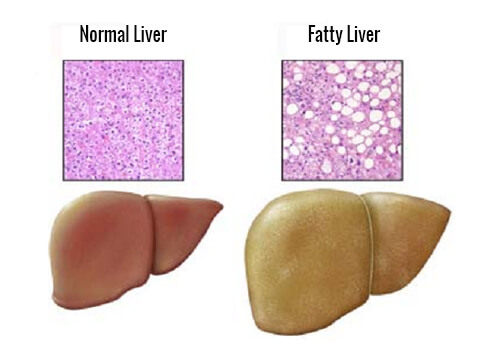
Something that makes fatty liver disease distinct is that there aren’t any particularly evident or characteristic symptoms. This makes it very easy to confuse with other pathologies. As the disease progresses, the warning signs that emerge include:
- Evening anxiety
- Fibromyalgia
- Abdominal fat
- High levels of uric acid, cholesterol, and triglycerides
- Hair loss
- Acne
- Warts on the neck and armpits
- Sleep apnea (snoring)
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight-loss problems
- Nausea
- Difficulties concentrating
We recommend you read:
Remedies that help treat fatty liver naturally
In addition to taking advantage of some home remedies, it is important for people who suffer from fatty liver disease to make some genuine lifestyle changes. Especially with regards to nutrition and some personal habits (such as excessive drinking). Liver repair can take some time if the patient doesn’t commit and leave behind things that may jeopardize this organ’s health. The most effective home remedies are:
- Artichoke: Don’t think twice about adding this vegetable to your diet in order to improve liver health. It does not have many calories, is an excellent diuretic, helps regulate cholesterol and blood sugar, and reduces fat absorption, among other health benefits. It is advisable to eat fresh artichokes at least twice a week. Preparing them in healthy ways such as steamed or baked without dressings, sauces, or creams is a good idea.
- Loquat: This fruit is known for fighting many different issues, one of which is fatty live disease. This is due to a purifying effect it has on the body which improves liver functions. The fruit can be eaten as a dessert. Thus, it can help treat fatty liver naturally.

- Radish and beet: You can easily incorporate this into your diet to reduce swelling and cleanse the liver. They are very nutritious with a low-calorie food. You can eat radishes raw or cut up in salads. You can boil beets to include them in salads or on the side. These are great to help treat fatty liver naturally.
- Milk thistle: It is a plant used to help treat fatty liver disease naturally. You can use the dried leaves in an herbal tea that protects this organ and improves its functions. Drinking this three times daily, with one tablespoon of milk thistle in each cup, will help.
- Dandelion: This is one of the most potent cleansers that exist. It helps to clean the liver and to improve its function. You should drink three cups a day of herbal tea made up of 1/4 liter of boiling water to each tablespoon of dandelions.

Other natural treatments for fatty liver
- Boldo: This plant is extremely popular because it cleans out toxins and eliminates fats from the liver, allowing this organ to heal. You can drink boldo tea after meals, and it will also help with digestion.
- Lemon: This works well for those who do not have any issues with acid. Add some lemon juice to your tea, salad, drink, or other foods. It is a potent cleanser for the liver, and help eliminate fats that accumulate in this organ, thus helping to treat fatty liver naturally.
- Ginger: Some studies show that ginger is very helpful in reducing liver fat due to the fact that it contains antioxidants that help reduce triglyceride levels. Thus, use two teaspoons of crushed ginger in boiling water to make a cup of tea. It can also be shredded and included in salads.
- Chicory: Wash and chop up one kilogram of fresh chicory. Blend it and add it to a saucepan with one kilogram of sugar. Then, bring to a boil until it becomes a syrup-like texture. Keep in a glass bottle with an air-tight cap, and drink one teaspoon a day.
- Grapefruit: This is very good for those who suffer from fatty liver disease because it contains naringenin, which activates the chemicals responsible for breaking down fatty acids. It also reduces body fat and alleviates metabolic syndrome, both of which are oftentimes connected to fatty liver disease. This fruit may help treat fatty liver naturally and efficiently.

All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Beevi, SS, Mangamoori, LN y Gowda, BB (2012). Perfil polifenólico y propiedades antioxidantes de Rafhanus sativusL. Investigación de productos naturales, 26 (6), 557–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2010.521884
- Claudia, D. C., Mosca, A., Alterio, A., Comparcola, D., Ferretti, F., & Nobili, V. (2018). Fatty liver disease. In Contemporary Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68192-4_26
- Fan, J. G., & Cao, H. X. (2013). Role of diet and nutritional management in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (Australia). https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12244
-
Flora, K., Hahn, M., Rosen, H. y Benner, K. (1998). Cardo mariano (Silybum marianum) para la terapia de enfermedades hepáticas. Revista estadounidense de gastroenterología, 93 (2), 139-143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00139.x
- Kim, J., Ahn, M., Kim, S.-E., Lee, HS, Kim, HK, Kim, GO y Shin, T. (2017). Efecto hepatoprotector del rábano negro fermentado (Raphanus sativus L.var niger) en la lesión hepática inducida por CCl4 en ratas. Revista de Medicina Veterinaria Preventiva, 41 (4), 143-149. https://doi.org/10.13041/jpvm.2017.41.4.143
- Melzer, O. A., Rothkopf, M. M., & Ganjhu, L. (2014). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. In Metabolic Medicine and Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1201/b17616
- Mirmiran, P., Amirhamidi, Z., Ejtahed, HS, Bahadoran, Z. y Azizi, F. (2017). Relación entre la dieta y la enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico: un artículo de revisión. Revista iraní de salud pública , 46 (8), 1007–1017.
- Mun, J., Park, J., Yoon, H.-G., Tú, Y., Choi, K.-C., Lee, Y.-H., Kim, K., Lee, J., Kim , O.-K. y Jun, W. (2019). Efectos del extracto de agua de Eriobotrya japonica sobre el deterioro del hígado graso alcohólico y no alcohólico. Journal of Medicinal Food, 22 (12), 1262-1270. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2019.4493
- Ochoa, Christiam y Granda, Cecilia y Chapoñan, Martín y Borja, Rubén y Borjas, Paulo y Ortiz, Jhon y Ugaz, Graciela y Puerta, Eberth y Pucutay, Mario (2008). Efecto Protector de Peumus Boldus en ratas con toxicidad hepática inducida por Paracetamol. CIMEL Ciencia e Investigación Médica Estudiantil Latinoamericana, 13 (1), 20-25. [Fecha de Consulta 15 de Diciembre de 2020]. ISSN: 1680-8398. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=717/71720914005
- Vos, M. B., & Lavine, J. E. (2013). Dietary fructose in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26299
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.









